使用HTTP Headers防御WEB攻击(Part3)
在FreeBuf之前发布的《 使用HTTP Headers防御WEB攻击(Part1) 》,《 使用HTTP Headers防御WEB攻击(Part2) 》中讲述了如何使用HTTP Headers对WEB攻击进行防御,比如使用X-Frame-Options以及X-XSS-Protection。在本文中,我们将探索如何利用HTTP Headers保卫我们的Cookies。
简介
在用户会话中Cookies是一个十分重要的东西,一个身份验证的Cookies就相当于是密码。保卫这些身份验证的Cookies是一个十分重要的话题。在本文中,我们将演示如何在PHP应用中执行某些Cookies属性从而在某些攻击中保护我们的Cookies。
使用HTTP Header保护Cookies
这是一个已知的事实,跨站脚本攻击是一个十分危险的漏洞,其能够让攻击者从用户浏览器窃取到Cookies。HttpOnly的引进能够禁用外部JavaScript脚本读取Cookies。即使应用程序本身存在XSS漏洞,只要开启了HTTPOnly标记就无法读取Cookies。
现在我们就打开上一篇文章中使用过的简单应用程序。
首先,观察HTTP响应中的头信息
HTTP/1.1 200 OK Date: Sun, 12 Apr 2015 15:07:14 GMT Server: Apache/2.2.29 (Unix) mod_fastcgi/2.4.6 mod_wsgi/3.4 Python/2.7.8 PHP/5.6.2 mod_ssl/2.2.29 OpenSSL/0.9.8y DAV/2 mod_perl/2.0.8 Perl/v5.20.0 X-Powered-By: PHP/5.6.2 Expires: Thu, 19 Nov 1981 08:52:00 GMT Cache-Control: no-store, no-cache, must-revalidate, post-check=0, pre-check=0 Pragma: no-cache Set-Cookie: PHPSESSID=a2ed2bf468dd811c09bf62521b07a023; path=/ Content-Length: 820 Keep-Alive: timeout=5, max=100 Connection: Keep-Alive Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
正如我们所见,在Set-Cookie头中没有额外的标记。如果该应用存在Xss漏洞那么攻击者就能够轻松获取到Cookies信息。
为了避免这种情况,我们可以使用HTTPOnly标记。这使得我们只能够通过HTTP协议来发送Cookies信息,而不能使用JavaScript。
启用HTTPOnly标记
如下示例代码片段中演示了在PHP应用中启用HTTPOnly标记的一种方法:
<?php ini_set("session.cookie_httponly", "True"); session_start(); session_regenerate_id(); if(!isset($_SESSION['admin_loggedin'])) { header('Location: index.php'); } if(isset($_GET['search'])) { if(!empty($_GET['search'])) { $text = $_GET['search']; } else { $text = "No text Entered"; } } ?> <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Admin Home</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="styles.css"> </head> <body> <div id="home"><center> </br><legend><text id=text><text id="text2">Welcome to Dashboard...</text></br></br> You are logged in as: <?php echo $_SESSION['admin_loggedin']; ?> <a href="logout.php">[logout]</a></text></legend></br> <form action="" method="GET"> <div id="search"> <text id="text">Search Values</text><input type="text" name="search" id="textbox"></br></br> <input type="submit" value="Search" name="Search" id="but"/> <div id="error"><text id="text2">You Entered:</text><?php echo $text; ?></div> </div> </form></center> </div> </body> </html> 从上面的代码片段中我们可以看出下面这一行代码是用来开启HTTPOnly的:
ini_set("session.cookie_httponly", "True"); 接下来我们就来看看在HTTPOnly标记开启之后获得的HTTP头信息
HTTP/1.1 200 OK Date: Sun, 12 Apr 2015 15:03:15 GMT Server: Apache/2.2.29 (Unix) mod_fastcgi/2.4.6 mod_wsgi/3.4 Python/2.7.8 PHP/5.6.2 mod_ssl/2.2.29 OpenSSL/0.9.8y DAV/2 mod_perl/2.0.8 Perl/v5.20.0 X-Powered-By: PHP/5.6.2 Expires: Thu, 19 Nov 1981 08:52:00 GMT Cache-Control: no-store, no-cache, must-revalidate, post-check=0, pre-check=0 Pragma: no-cache Set-Cookie: PHPSESSID=36cb82e1d98853f8e250d89be857a0d3; path=/; HttpOnly Content-Length: 820 Keep-Alive: timeout=5, max=100 Connection: Keep-Alive Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
在上面的信息中我们可以从Set-Cookie头信息中看出已经成功开启HTTPOnly
Set-Cookie: PHPSESSID=36cb82e1d98853f8e250d89be857a0d3; path=/; HttpOnly
HttpOnly标记的效果如下,当攻击者挖掘到一个Xss漏洞之后,尝试着使用JavaScript脚本读取Cookies时,是不会被执行的。

从上图中我们可以看出,不能通过执行脚本来读取Cookies,即使存在Xss漏洞!
Secure标记
另一个Cookies属性就是“Secure”,我们经常能够见到一个网站同时存在着HTTP协议和HTTPS协议。当应用通过HTTP传送其Cookies的时候,由于使用的是明文传输方式,所以攻击者可以有多种方法劫持信息。“Secure”属性也是设置在Set-Cookie头中,它可以保证所有的Cookies信息只通过HTTPS协议进行传输。
如下示例代码片段中演示了在PHP应用中启用Secure标记的一种方法:
<?php ini_set("session.cookie_secure", "True"); session_start(); session_regenerate_id(); if(!isset($_SESSION['admin_loggedin'])) { header('Location: index.php'); } if(isset($_GET['search'])) { if(!empty($_GET['search'])) { $text = $_GET['search']; } else { $text = "No text Entered"; } } ?> <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Admin Home</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="styles.css"> </head> <body> <div id="home"><center> </br><legend><text id=text><text id="text2">Welcome to Dashboard...</text></br></br> You are logged in as: <?php echo $_SESSION['admin_loggedin']; ?> <a href="logout.php">[logout]</a></text></legend></br> <form action="" method="GET"> <div id="search"> <text id="text">Search Values</text><input type="text" name="search" id="textbox"></br></br> <input type="submit" value="Search" name="Search" id="but"/> <div id="error"><text id="text2">You Entered:</text><?php echo $text; ?></div> </div> </form></center> </div> </body> </html> 从上面的代码片段中我们可以看出下面这一行代码是用来开启Secure的:
ini_set("session.cookie_secure", "True"); 接下来我们就看看上面代码执行后获取到的HTTP Headers
HTTP/1.1 200 OK Date: Sun, 12 Apr 2015 15:14:30 GMT Server: Apache/2.2.29 (Unix) mod_fastcgi/2.4.6 mod_wsgi/3.4 Python/2.7.8 PHP/5.6.2 mod_ssl/2.2.29 OpenSSL/0.9.8y DAV/2 mod_perl/2.0.8 Perl/v5.20.0 X-Powered-By: PHP/5.6.2 Expires: Thu, 19 Nov 1981 08:52:00 GMT Cache-Control: no-store, no-cache, must-revalidate, post-check=0, pre-check=0 Pragma: no-cache Set-Cookie: PHPSESSID=f95afc96ecb7acc6c288d31f941e682f; path=/; secure Content-Length: 820 Keep-Alive: timeout=5, max=100 Connection: Keep-Alive Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
从上面的头信息中我们看到,Secure属性已经成功启用。我的本地主机没有开启HTTPS支持,当我刷新页面时,由于没有HTTPS协议支持Cookies没有通过Secure通道,且会话不会通过HTTP协议。这是由于会话没有发送到服务器,因为必须要HTTPS协议才可用。
关闭浏览器结束会话
关闭浏览器前没有单击注销按钮对于用户来说这十分常见。当我们在使用一个敏感的应用时,在关闭浏览器时强制注销Cookies很有必要。
下面两行代码可以在PHP中实现该过程
session_set_cookie_params(0); session_start();
假设我们运行的页面集合了上面的属性。登录应用然后关闭浏览器,如果我们重新打开这个页面,会话不会活跃。
为了检测这个属性是否已经成功启用,我们可以在chrome浏览器中使用类似“EditThisCookie”的cookie编辑器。
登录页面并启用EditThisCookie扩展
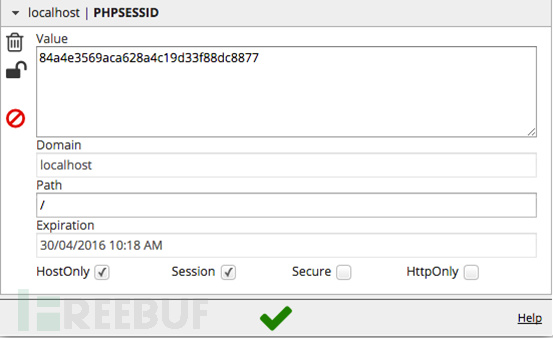
如上图,将Session选项勾选上,这会保证我们的会话在关闭浏览器后不会继续活跃。
同样我们也可以在Chrome的开发者工具中设置

以下为Cookies的其他一些属性
Domain: 该属性控制着哪些Cookies能够访问域
Path: 指定Cookies能够访问域的路径
Expiration: 该属性指定Cookies过期后不再能使用
只需要3行代码即可将这三个属性加入到PHP应用中:
ini_set("session.cookie_secure", "True"); //secure ini_set("session.cookie_httponly", "True"); //httponly session_set_cookie_params(3, '/', '.localhost'); //This cookie is valid for 3 seconds (max age) // “/” ensures that this cookie is valid on all //paths of this domain // since the domain is prefixed with dot, this //cookie is accessible from all the subdomains. session_start(); 重新加载该页面,看看响应头
HTTP/1.1 200 OK Date: Thu, 30 Apr 2015 03:04:11 GMT Server: Apache/2.2.29 (Unix) mod_fastcgi/2.4.6 mod_wsgi/3.4 Python/2.7.8 PHP/5.6.2 mod_ssl/2.2.29 OpenSSL/0.9.8y DAV/2 mod_perl/2.0.8 Perl/v5.20.0 X-Powered-By: PHP/5.6.2 Expires: Thu, 19 Nov 1981 08:52:00 GMT Cache-Control: no-store, no-cache, must-revalidate, post-check=0, pre-check=0 Pragma: no-cache Set-Cookie: PHPSESSID=f4d99777d9810bfedb6869acd556bc66; expires=Thu, 30-Apr-2015 03:04:14 GMT; Max-Age=3; path=/; domain=.localhost; secure; HttpOnly X-XSS-Protection: 1 Content-Security-Policy: script-src 'self' Content-Length: 820 Keep-Alive: timeout=5, max=100 Connection: Keep-Alive Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
在本文中,我们了解了如何使用HTTP头保卫我们的Cookies。虽说这些头可以帮助我们提高WEB应用的安全,但是我们不能完全依赖这些头来保护我们的WEB安全,我们应该考虑使用添加额外的安全层。
* 参考来源 infosec ,译者/鸢尾 转载请注明来自FreeBuf黑客与极客(FreeBuf.COM)











![[HBLOG]公众号](http://www.liuhaihua.cn/img/qrcode_gzh.jpg)

