SpringBoot启动过程
SpringBoot项目通过SpringApplication.run(App.class, args)来启动:
@Configuration
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(App.class, args);
}
}
接下来,通过源码来看看SpringApplication.run()方法的执行过程。如果对源码不感兴趣,直接下拉到文章末尾,看启动框图。
1、调用SpringApplication类的静态方法
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Object source, String... args) {
return run(new Object[] { source }, args);
}
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Object[] sources, String[] args) {
return new SpringApplication(sources).run(args);
}
2、SpringApplication对象初始化
public SpringApplication(Object... sources) {
initialize(sources);
}
@SuppressWarnings({ "unchecked", "rawtypes" })
private void initialize(Object[] sources) {
if (sources != null && sources.length > 0) {
this.sources.addAll(Arrays.asList(sources));
}
// 判断是否为WEB环境
this.webEnvironment = deduceWebEnvironment();
// 找到META-INF/spring.factories中ApplicationContextInitializer所有实现类,并将其实例化
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(
ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
// 找到META-INF/spring.factories中ApplicationListener所有实现类,并将其实例化
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
// 获取当前main方法类对象,即测试类中的App实例
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
对象初始化过程中,使用到了getSpringFactoriesInstances方法:
private <T> Collection<? extends T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type) {
return getSpringFactoriesInstances(type, new Class<?>[] {});
}
private <T> Collection<? extends T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type,
Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Object... args) {
ClassLoader classLoader = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
// Use names and ensure unique to protect against duplicates
// 读取META-INF/spring.factories指定接口的实现类
Set<String> names = new LinkedHashSet<String>(
SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader));
List<T> instances = createSpringFactoriesInstances(type, parameterTypes,
classLoader, args, names);
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(instances);
return instances;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private <T> List<T> createSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type,
Class<?>[] parameterTypes, ClassLoader classLoader, Object[] args,
Set<String> names) {
List<T> instances = new ArrayList<T>(names.size());
for (String name : names) {
try {
Class<?> instanceClass = ClassUtils.forName(name, classLoader);
Assert.isAssignable(type, instanceClass);
Constructor<?> constructor = instanceClass.getConstructor(parameterTypes);
T instance = (T) constructor.newInstance(args);
instances.add(instance);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Cannot instantiate " + type + " : " + name, ex);
}
}
return instances;
}
// 读取META-INF/spring.factories文件
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryClass, ClassLoader classLoader) {
String factoryClassName = factoryClass.getName();
try {
Enumeration<URL> urls = (classLoader != null ? classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION) :
ClassLoader.getSystemResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION));
List<String> result = new ArrayList<String>();
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = urls.nextElement();
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(new UrlResource(url));
String factoryClassNames = properties.getProperty(factoryClassName);
result.addAll(Arrays.asList(StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(factoryClassNames)));
}
return result;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load [" + factoryClass.getName() +
"] factories from location [" + FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION + "]", ex);
}
}
META-INF/spring.factories文件内容,spring boot版本1.3.6.RELEASE
# PropertySource Loaders org.springframework.boot.env.PropertySourceLoader=/ org.springframework.boot.env.PropertiesPropertySourceLoader,/ org.springframework.boot.env.YamlPropertySourceLoader # Run Listeners org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener=/ org.springframework.boot.context.event.EventPublishingRunListener # Application Context Initializers org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer=/ org.springframework.boot.context.ConfigurationWarningsApplicationContextInitializer,/ org.springframework.boot.context.ContextIdApplicationContextInitializer,/ org.springframework.boot.context.config.DelegatingApplicationContextInitializer,/ org.springframework.boot.context.web.ServerPortInfoApplicationContextInitializer # Application Listeners org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener=/ org.springframework.boot.builder.ParentContextCloserApplicationListener,/ org.springframework.boot.context.FileEncodingApplicationListener,/ org.springframework.boot.context.config.AnsiOutputApplicationListener,/ org.springframework.boot.context.config.ConfigFileApplicationListener,/ org.springframework.boot.context.config.DelegatingApplicationListener,/ org.springframework.boot.liquibase.LiquibaseServiceLocatorApplicationListener,/ org.springframework.boot.logging.ClasspathLoggingApplicationListener,/ org.springframework.boot.logging.LoggingApplicationListener # Environment Post Processors org.springframework.boot.env.EnvironmentPostProcessor=/ org.springframework.boot.cloud.CloudFoundryVcapEnvironmentPostProcessor,/ org.springframework.boot.env.SpringApplicationJsonEnvironmentPostProcessor
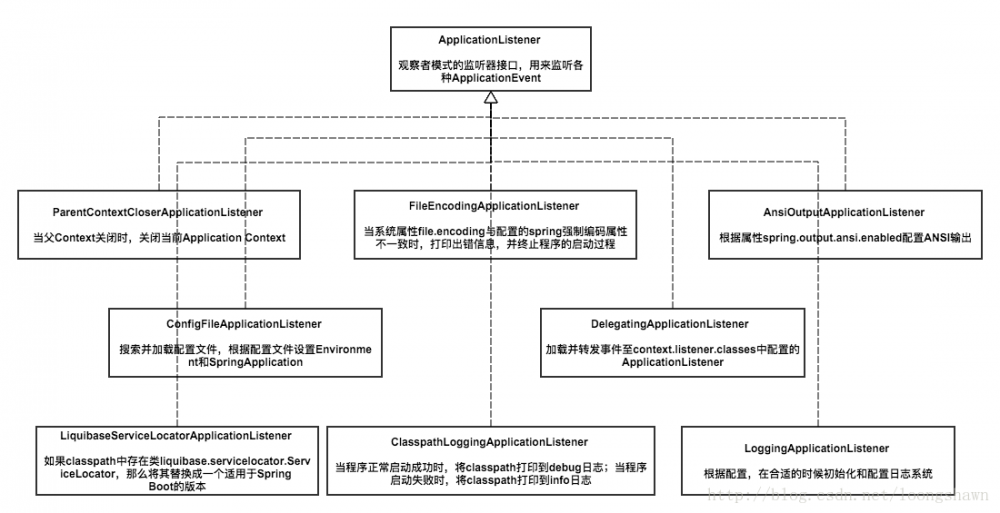
ApplicationListener接口是Spring框架的事件监听器,其作用可理解为SpringApplicationRunListener发布通知事件时,由ApplicationListener负责接收。SpringApplicationRunListener接口的实现类就是EventPublishingRunListener,其在SpringBoot启动过程中,负责注册ApplicationListener监听器,在不同时间节点发布不同事件类型,如果有ApplicationListener实现类监听了该事件,则接收处理。
public interface SpringApplicationRunListener {
/**
* 通知监听器,SpringBoot开始启动
*/
void started();
/**
* 通知监听器,环境配置完成
*/
void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableEnvironment environment);
/**
* 通知监听器,ApplicationContext已创建并初始化完成
*/
void contextPrepared(ConfigurableApplicationContext context);
/**
* 通知监听器,ApplicationContext已完成IOC配置
*/
void contextLoaded(ConfigurableApplicationContext context);
/**
* 通知监听器,SpringBoot开始完毕
*/
void finished(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Throwable exception);
}
附图为ApplicationListener监听接口实现类,每个类对应了一种事件。
3、SpringApplication核心run方法
/**
* Run the Spring application, creating and refreshing a new
* {@link ApplicationContext}.
* @param args the application arguments (usually passed from a Java main method)
* @return a running {@link ApplicationContext}
*/
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
// 任务执行时间监听,记录起止时间差
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
configureHeadlessProperty();
// 启动SpringApplicationRunListener监听器
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.started();
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(
args);
// 创建并刷新ApplicationContext
context = createAndRefreshContext(listeners, applicationArguments);
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
// 通知监听器,应用启动完毕
listeners.finished(context, null);
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass)
.logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
return context;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, listeners, ex);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
}
这里,需要看看createAndRefreshContext()方法是如何创建并刷新ApplicationContext。
private ConfigurableApplicationContext createAndRefreshContext(
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext context;
// Create and configure the environment
// 创建并配置运行环境,WebEnvironment与StandardEnvironment选其一
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
listeners.environmentPrepared(environment);
if (isWebEnvironment(environment) && !this.webEnvironment) {
environment = convertToStandardEnvironment(environment);
}
// 是否打印Banner,就是启动程序时出现的图形
if (this.bannerMode != Banner.Mode.OFF) {
printBanner(environment);
}
// Create, load, refresh and run the ApplicationContext
// 创建、装置、刷新、运行ApplicationContext
context = createApplicationContext();
context.setEnvironment(environment);
postProcessApplicationContext(context);
applyInitializers(context);
// 通知监听器,ApplicationContext创建完毕
listeners.contextPrepared(context);
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
logStartupInfo(context.getParent() == null);
logStartupProfileInfo(context);
}
// Add boot specific singleton beans
context.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments",
applicationArguments);
// Load the sources
// 将beans载入到ApplicationContext容器中
Set<Object> sources = getSources();
Assert.notEmpty(sources, "Sources must not be empty");
load(context, sources.toArray(new Object[sources.size()]));
// 通知监听器,beans载入ApplicationContext完毕
listeners.contextLoaded(context);
// Refresh the context
refresh(context);
if (this.registerShutdownHook) {
try {
context.registerShutdownHook();
}
catch (AccessControlException ex) {
// Not allowed in some environments.
}
}
return context;
}
其中利用createApplicationContext()来实例化ApplicationContext对象,即DEFAULT_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS 、DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS两个对象其中一个。
protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() {
Class<?> contextClass = this.applicationContextClass;
if (contextClass == null) {
try {
contextClass = Class.forName(this.webEnvironment
? DEFAULT_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS : DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS);
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Unable create a default ApplicationContext, "
+ "please specify an ApplicationContextClass",
ex);
}
}
return (ConfigurableApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiate(contextClass);
}
postProcessApplicationContext(context)、applyInitializers(context)均为初始化ApplicationContext工作。
SpringBoot启动过程分析就先到这里,过程中关注几个对象:
- ApplicationContext:Spring高级容器,与BeanFactory类似。
- SpringApplicationRunListener:SprintBoot启动监听器,负责向ApplicationListener注册各类事件。
- Environment:运行环境。
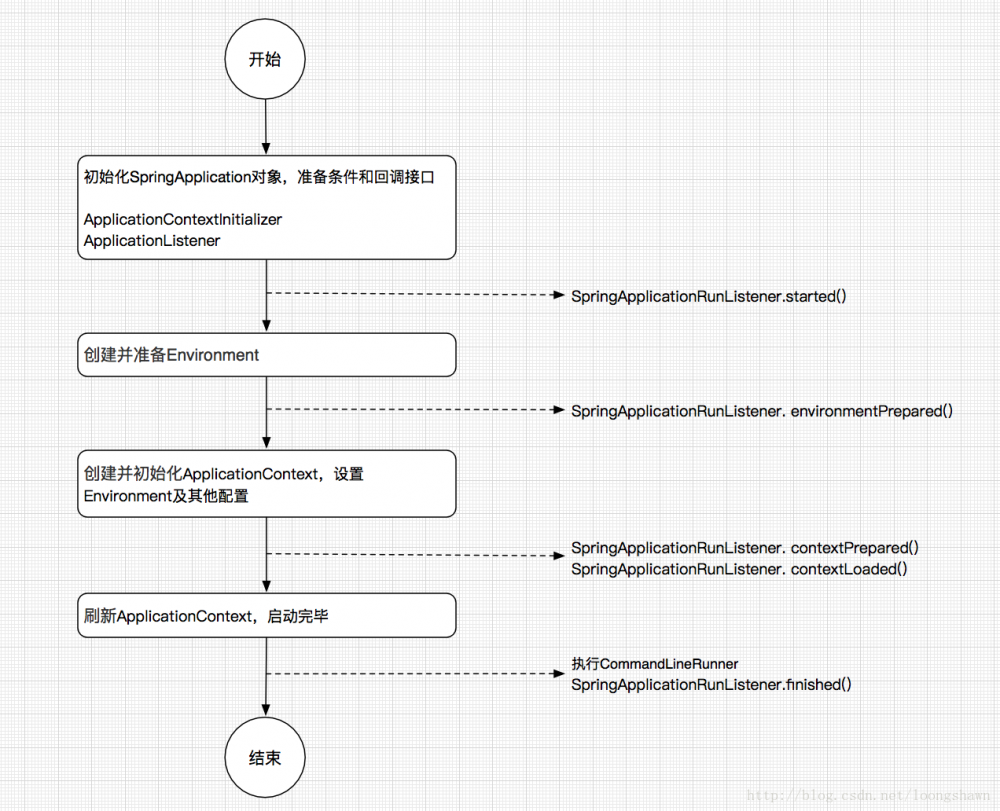
4、启动过程框图
5、接口文档
http://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/current/javadoc-api/
- 本文标签: 启动过程 cat URLs http bean 测试 tar App src Service ssl CTO build Property springboot web js 时间 对象初始化 监听器 Spring Boot java struct SDN BeanUtils Logging id spring API list Listeners Collection 源码 UI json 文章 IO classpath 配置 实例 ACE ioc
- 版权声明: 本文为互联网转载文章,出处已在文章中说明(部分除外)。如果侵权,请联系本站长删除,谢谢。
- 本文海报: 生成海报一 生成海报二











![[HBLOG]公众号](http://www.liuhaihua.cn/img/qrcode_gzh.jpg)

