必须得学一学Spring 的ORM机制
小编昨天一整天都在入手一份工程代码,可是搞了一整天,发现最后卡在一个数据库操作上,自己再琢磨了会,发现工程是采用Spring orm整合hibernate的方式对数据库进行操作,但是我不会啊!我以前是学过SSH的整合,可是那些宝贵的知识都还给老师了呀!小编也是非常地无奈。好吧!既然不会,那就学学嘛!我们这就动手!
一、总体说下Spring ORM框架的结构
说到ORM,就是所谓的对象关系映射,可以简单地理解成将java中的对象与数据库中的表对应起来的一种模型。那么Spring ORM到底是什么东西呢?我们来看看Spring ORM的源码结构就知道了!下面我贴一张图:
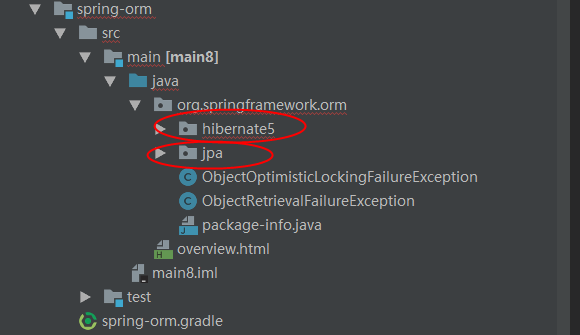
从图中可以看到在Spring ORM模块中默认对两种技术提供了支持,分别是hibernate5和jpa,hibernate是一个ORM框架,jpa它是java持久化API,下面我将会重点结合hibernate来讲解Spring ORM。关于这两种技术的详细信息,请自行谷哥咯!
在对下面第二节的阅读前,我想以我的理解讲讲我们一般是如何对数据库进行操作的,方便我们从根本上来了解操作原理,不至于被Spring ORM中的各种类给弄蒙蔽了!
一般程序操作数据库有以下步骤:
- 1、配置一个数据库源
(DataSource),这个很好理解,既然你要对数据库进行操作,那么你的数据是从哪里来的呢?肯定是数据库嘛! - 2、建立与数据库的链接
(Connection),非常好理解,你要和小编通电话,总得有个链接你我的工具吧!没错,那就是电话线! - 3、获取会话
(Session),会话就是你和小编的一次通话,通话完,上面的链接可以关闭,也可以不关闭,看心情!哈哈! - 4、然后就是对数据库进行操作啦!
二、详细讲下Spring ORM重要类及其使用
下面我们对Spring ORM源码中的hibernate进行展开,如下图:
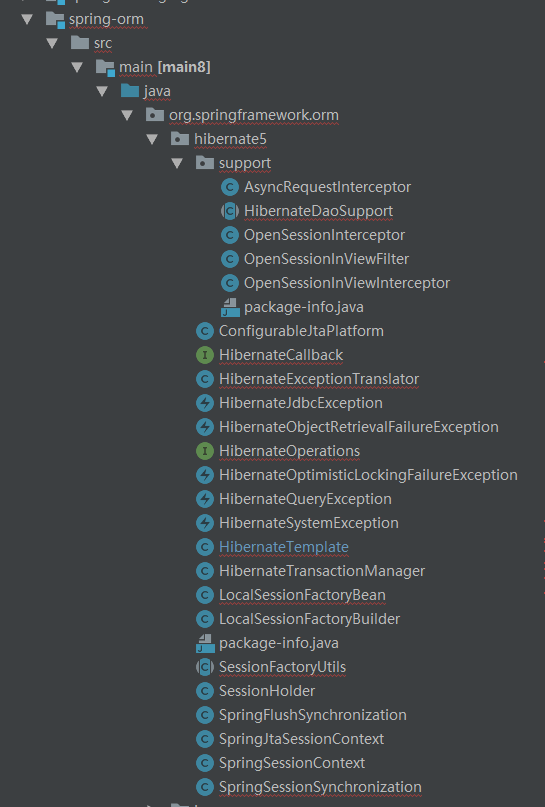
源码中我们重点关注几个重要的类及接口,分别是:
-
HibernateOperations接口,该接口封装了很多基于hibernate api的操作,该接口被HibernateTemplate实现,虽然该接口不经常使用,但是在Spring中可以用于测试。 -
HibernateTemplate类,该类实现了HibernateOperations接口,因此该类同样拥有了很对基于hibernate的数据库操作。但细心的小伙伴会发现,它的命名中出现了Template模板,可以推测它是一个模板类,没错,该类是模板方法设计模式的一个体现,关于模板方法设计模式,可以参考我之前的博文 谈一谈我对‘模板方法’设计模式的理解(Template) ,该类中提供了一个模板方法,具体如下:
@Override
@Nullable
public <T> T execute(HibernateCallback<T> action) throws DataAccessException {
return doExecute(action, false);
}
该模板方法超级简单,传入一个Hibernate回调实例,然后执行 doExecute() 方法。你可能会问,那这个 HibernateCallback 是什么? doExecute() 又是什么? 打开 HibernateCallback 源码:
@FunctionalInterface
public interface HibernateCallback<T> {
@Nullable
T doInHibernate(Session session) throws HibernateException;
}
哇,太简单了,这时我会想,那既然是个接口,肯定有实现类吧!然后我找呀找呀还是没找到。最后发现,该接口原来被 @FunctionalInterface 修饰,是一个函数式接口,所以我们可以用Lamada表达式来使用它!至于接口中声明的参数 Session 和 doInHibernate() 方法,其实道理很简单,就是通过获取一个会话实例 (还记得你和小编的一次通电话吗!上面第一节第三步) 来做些操作数据库的事 (上面第四步) ,这些操作 (比如数据持久化) 你就可以在 doInHibernate() 方法中写嘛!具体如下:
new HibernateTemplate().execute((e) -> e.createQuery("select * from user"));
当然在实际使用中我们不能直接就这么 new HibernateTemplate() ,你还必须传入一个 sessionFactory 的实例,再者一般实例化都是交给Spring容器去做的,不需要显示去new,这里只是栗子,重点在于演示 HibernateCallback 怎么去使用。或者既然它是一个函数式接口,也不一定要依赖 HibernateTemplate 类,只要你传入一个 Session 实例即可!
接下来我们看一看 doExecute() 方法:
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
@Nullable
protected <T> T doExecute(HibernateCallback<T> action, boolean enforceNativeSession) throws DataAccessException {
Assert.notNull(action, "Callback object must not be null");//先断言保证action不为空
Session session = null;//会话对象
boolean isNew = false;//是不是新的会话
try {
session = obtainSessionFactory().getCurrentSession();//初始化会话对象
}
catch (HibernateException ex) {
logger.debug("Could not retrieve pre-bound Hibernate session", ex);
}
if (session == null) {
session = obtainSessionFactory().openSession();
session.setFlushMode(FlushMode.MANUAL);//设置提交方式
isNew = true;
}
try {
enableFilters(session);
//根据是否强制将原生Hibernate会话session暴露给回调代码,默认为false,如果是true,就做一个代理
Session sessionToExpose =
(enforceNativeSession || isExposeNativeSession() ? session : createSessionProxy(session));
return action.doInHibernate(sessionToExpose);
}
catch (HibernateException ex) {
throw SessionFactoryUtils.convertHibernateAccessException(ex);
}
catch (PersistenceException ex) {
if (ex.getCause() instanceof HibernateException) {
throw SessionFactoryUtils.convertHibernateAccessException((HibernateException) ex.getCause());
}
throw ex;
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
// Callback code threw application exception...
throw ex;
}
finally {
if (isNew) {
SessionFactoryUtils.closeSession(session);
}
else {
disableFilters(session);
}
}
}
-
LocalSessionFactoryBean类,该类表示一个FactoryBean对象,用于生成所有的Session,一般我们在Spring配置文件中配置该bean
三、来个栗子压压惊!
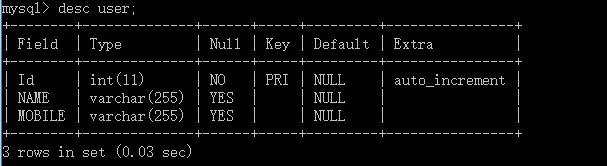
数据库结构 :
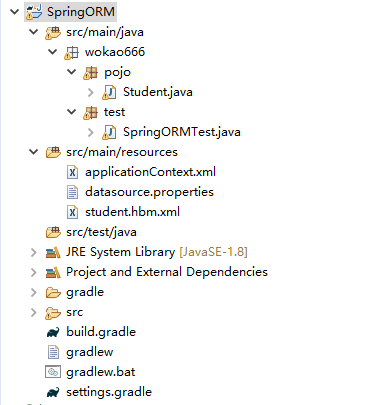
工程结构 :
Student.java
package wokao666.pojo;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Student implements Serializable {//序列化
private int id;
private String name;
private String mobile;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", mobile=" + mobile + "]";
}
public Student(int id, String name, String mobile) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.mobile = mobile;
}
public Student() {
super();
}
public Student(String name, String mobile) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.mobile = mobile;
}
这里省略一大堆get/set方法
}
SpringORMTest.java
package wokao666.test;
import java.util.Arrays;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.orm.hibernate5.HibernateTemplate;
import wokao666.pojo.Student;
public class SpringORMTest {
public static void saveStudent(ApplicationContext context) {
HibernateTemplate template = (HibernateTemplate) context.getBean("hibernateTemplate");
//默认为只读模式,要设置改为允许delete、save、update等操作
template.setCheckWriteOperations(false);//注意此处一定要设置关闭,因为HibernateTemplate默认会对Session进行检查
Student stu = new Student("0", "000000000000000");
template.save(stu);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(template.find("from Student", null).toArray()).toString());
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
saveStudent(context);
}
}
applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:jdbc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc
http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc/spring-jdbc.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!-- 加载属性文件 -->
<context:property-placeholder
ignore-unresolvable="true" location="classpath*:datasource.properties" />
<!-- 配置数据源 -->
<bean id="dataSource"
class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${spring.datasource.driverClassName}" />
<property name="url" value="${spring.datasource.url}" />
<property name="username" value="${spring.datasource.username}" />
<property name="password" value="${spring.datasource.password}" />
</bean>
<!-- 配置session工厂 -->
<bean id="sessionFactory"
class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate5.LocalSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
<property name="hibernateProperties">
<props>
<prop key="hibernate.dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</prop>
<prop key="hibernate.show_sql">true</prop>
</props>
</property>
<property name="mappingResources">
<list>
<value>./student.hbm.xml</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<!-- 最后配置 HibernateTemplate bean-->
<bean id="hibernateTemplate" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate5.HibernateTemplate">
<property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
datasource.properties
spring.datasource.url = jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/demo_db?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&useSSL=true spring.datasource.username=root spring.datasource.password=root spring.datasource.driverClassName = com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
student.hbm.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <hibernate-mapping> <class name="wokao666.pojo.Student" table="user"> <id name="id" type="java.lang.Integer"> <column name="Id" /> <generator class="identity" /> </id> <property name="mobile" type="java.lang.String" column="MOBILE" length="100" /> <property name="name" type="java.lang.String" column="NAME" length="100" /> </class> </hibernate-mapping>
build.gradle
apply plugin: 'java'
repositories {
jcenter()
}
dependencies {
compile 'org.slf4j:slf4j-api:1.7.21'
testCompile 'junit:junit:4.12'
compile 'org.springframework:spring-context:5.0.4.RELEASE'
compile 'org.springframework:spring-orm:5.0.4.RELEASE'
compile group: 'mysql', name: 'mysql-connector-java', version: '6.0.4'
compile group: 'org.hibernate', name: 'hibernate-core', version: '5.2.9.Final'
compile group: 'cglib', name: 'cglib', version: '3.2.4'
compile group: 'org.springframework', name: 'spring-tx', version: '5.0.0.RELEASE'
compile group: 'org.aspectj', name: 'aspectjweaver', version: '1.8.8'
}
- 本文标签: root https UI App dependencies entity Action 模型 update 配置 CTO 参数 src Property id ssh db map CEO list lib Persistence MQ java tab sql 设计模式 value build JPA AOP spring 源码 cat 代码 key schema ACE IO mysql classpath 数据库 API XML Connection Word plugin 测试 find IDE 实例 dataSource http ORM ssl 数据 Select final core bean bug
- 版权声明: 本文为互联网转载文章,出处已在文章中说明(部分除外)。如果侵权,请联系本站长删除,谢谢。
- 本文海报: 生成海报一 生成海报二











![[HBLOG]公众号](http://www.liuhaihua.cn/img/qrcode_gzh.jpg)

