Maven Profile 与 Spring Profile 管理多环境打包
一般开发团队会有多个部署环境,如 dev 环境用于开发自测,QA 环境让测试团队测试, Production 环境作为线上环境。通常不同环境的配置不同,我们希望打包时的人力消耗最少。
Spring Boot Profile
Spring Boot Profile 有许多的功能,这里只说管理配置的内容。Spring 加载配置的 顺序 如下:
application-{profile}.properties
application-{profile}.properties
application.properties
application.properties
例如,如果我们在 application.properties 中指定
spring.profiles.active = dev
则 spring 会使用 application-dev.properties 文件中的配置来覆盖 application.properties 文件中的相应配置。
如果用的不是 Spring 要怎么管理多个 Profile 呢?可以从构建工具 Maven 下手。
Maven 也提供了 Profile 支持,它允许我们在 pom.xml 中定义多个 Profile ,每个 profile 可以指定自己的一些配置、依赖、触发条件等。例如:
<profiles>
<profile>
<id>dev</id>
<activation>
<activeByDefault>true</activeByDefault>
</activation>
<properties>
<profile.active>dev</profile.active>
</properties>
</profile>
<profile>
<id>prod</id>
<properties>
<profile.active>prod</profile.active>
</properties>
</profile>
</profiles>
上面指定了两个 profile: dev 和 prod ,其中 dev 是默认启用的,当profile 被启用时,它定义的的属性、依赖等内容就会起效。这里我们定义了 profile.active 属性,之后会用到。
在编译时指定 mvn clean install -Pprod 就能切换成 prod profile。
多环境打包的具体步骤
Maven 与 Spring Profile 的功能是有重合的,只使用一种其实就能实现多环境多配置。但它们各有千秋:
- Spring profile 除了指定配置,还有一些其它作用(如为不同的 profile 生成不同的 bean),但每次打包前都需要手工指定启用哪个 profile
- Maven Profile 可以通过命令行指定使用的 profile,但缺少了 spring profile 的一些特定功能。
因此我们希望融合二者,取长补短。步骤如下:
在 pom.xml 中定义 Profile
这里跟上面介绍的一样,定义两个/多个 profile 并为各个 profile 指定自己的属性:
<profiles>
<profile>
<id>dev</id>
<activation>
<activeByDefault>true</activeByDefault>
</activation>
<properties>
<profile.active>dev</profile.active>
</properties>
</profile>
<profile>
<id>prod</id>
<properties>
<profile.active>prod</profile.active>
</properties>
</profile>
</profiles>
在 pom.xml 中定义资源过滤
目的是为了让 maven 在构建时用 profile 中指定的属性来替换 application.properties 中的内容。
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/resources</directory>
<!--①-->
<excludes>
<exclude>application*.properties</exclude>
</excludes>
</resource>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/resources</directory>
<!--②-->
<filtering>true</filtering>
<includes>
<include>application.properties</include>
<include>application-${profile.active}.properties</include>
</includes>
</resource>
</resources>
①中,我们通过 excludes 来将所有的 application*.properties 排除在外,这样 maven 在打包时就不会复制这些文件。毕竟我们不希望把 application-dev.properties 也包含在 prod 的 jar 包里。
②中,通过开启 filtering ,maven 会将文件中的 @XX@ 替换 profile 中定义的 XX 变量/属性。另外,我们还通过 includes 来告诉 maven 根据profile 来复制对应的 properties 文件。
用 Maven 变量指定 Spring Profile
在 application.properties 文件中加入下面这行:
spring.profiles.active = @profile.active@
这里 profile.active 是在 maven profile 中的 properties 定义的,而 @XX@ 的语法则是上节提到的 maven filtering 替换变量的语法。
mvn clean package -P<profile_name>
与 Intellij IDEA 集成
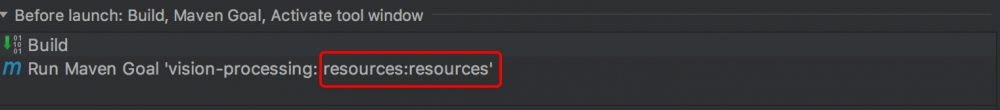
IDEA 在 Build 时并不会处理 Maven Profile 的 filtering 设置,在 Run 的时候会直接复制 application.properties 文件到 target/class 目录下,而由于文件中包含 @profile.active@ (没有被 maven 替换)且 @ 是非法字符,因此没有办法运行。
解决方法是让 IDEA Run 之前执行 mvn resources:resouces ,如下图:
Maven profile 与 Spring profile 有自的优点,结合起来的步骤如下:
- 在
pom.xml中定义多个 profile 及自己的属性 - 在
pom.xml中定义 resource filtering,一方面控制 jar 中包含的资源文件,一方面允许@XX@的变量替换 - 在
application.properties中指定spring.profiles.active,值为 maven profile 中定义的属性。 - 构建时使用
mvm clean package -P<profile>来指定 profile。
- Maven管理SpringBoot Profile
- Spring 外化配置文件











![[HBLOG]公众号](http://www.liuhaihua.cn/img/qrcode_gzh.jpg)

