dubbo源码解析(四十二)序列化——开篇
序列化——开篇
目标:介绍dubbo中序列化的内容,对dubbo中支持的序列化方式做对比,介绍dubbo-serialization-api下的源码
前言
序列化就是将对象转成字节流,用于网络传输,以及将字节流转为对象,用于在收到字节流数据后还原成对象。序列化的好处我就不多说了,无非就是安全性更好、可跨平台等。网上有很多总结的很好,我在这里主要讲讲dubbo中序列化的设计和实现了哪些序列化方式。
dubbo在2.6.x版本中,支持五种序列化方式,分别是
- fastjson:依赖阿里的fastjson库,功能强大(支持普通JDK类包括任意Java Bean Class、Collection、Map、Date或enum)
- fst:完全兼容JDK序列化协议的系列化框架,序列化速度大概是JDK的4-10倍,大小是JDK大小的1/3左右。
- hessian2:hessian是一种跨语言的高效二进制序列化方式。但这里实际不是原生的hessian2序列化,而是阿里修改过的hessian lite,它是dubbo RPC默认启用的序列化方式
- jdk:JDK自带的Java序列化实现。
- kryo:是一个快速序列化/反序列化工具,其使用了字节码生成机制(底层依赖了 ASM 库),因此具有比较好的运行速度,速度快,序列化后体积小,跨语言支持较复杂
在dubbo最新的2.7.0版本中支持了protostuff,之前的版本dubbo还实现了自己的dubbo序列化,但是由于还不够成熟,所有暂时移除了dubbo序列化的实现。
从性能上对比,fst和kryo>hessian2>fastjson>jdk。
他们具体的实现我不讲解,因为很多都直接使用了对应的依赖裤,我只讲解dubbo序列化的接口设计。
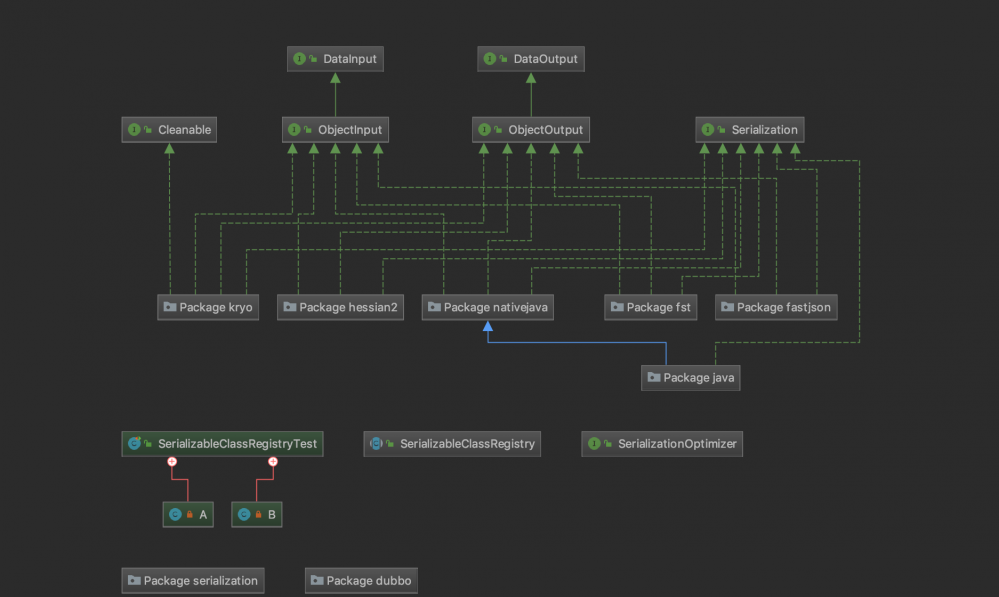
源码分析
(一)DataInput
public interface DataInput {
/**
* Read boolean.
* 读取布尔类型
* @return boolean.
* @throws IOException
*/
boolean readBool() throws IOException;
/**
* Read byte.
* 读取字节
* @return byte value.
* @throws IOException
*/
byte readByte() throws IOException;
/**
* Read short integer.
* 读取short类型
* @return short.
* @throws IOException
*/
short readShort() throws IOException;
/**
* Read integer.
* 读取integer类型
* @return integer.
* @throws IOException
*/
int readInt() throws IOException;
/**
* Read long.
* 读取long类型
* @return long.
* @throws IOException
*/
long readLong() throws IOException;
/**
* Read float.
* 读取float类型
* @return float.
* @throws IOException
*/
float readFloat() throws IOException;
/**
* Read double.
* 读取double类型
* @return double.
* @throws IOException
*/
double readDouble() throws IOException;
/**
* Read UTF-8 string.
* 读取UTF-8 string
* @return string.
* @throws IOException
*/
String readUTF() throws IOException;
/**
* Read byte array.
* 读取byte数组
* @return byte array.
* @throws IOException
*/
byte[] readBytes() throws IOException;
}
该接口是数据输入接口,可以看到定义了从 InputStream 中各类数据类型的读取方法。
(二)DataOutput
public interface DataOutput {
/**
* Write boolean.
* 输出boolean类型
* @param v value.
* @throws IOException
*/
void writeBool(boolean v) throws IOException;
/**
* Write byte.
* 输出byte类型
* @param v value.
* @throws IOException
*/
void writeByte(byte v) throws IOException;
/**
* Write short.
* 输出short类型
* @param v value.
* @throws IOException
*/
void writeShort(short v) throws IOException;
/**
* Write integer.
* 输出integer类型
* @param v value.
* @throws IOException
*/
void writeInt(int v) throws IOException;
/**
* Write long.
* 输出long类型
* @param v value.
* @throws IOException
*/
void writeLong(long v) throws IOException;
/**
* Write float.
* 输出float类型
* @param v value.
* @throws IOException
*/
void writeFloat(float v) throws IOException;
/**
* Write double.
* 输出double类型
* @param v value.
* @throws IOException
*/
void writeDouble(double v) throws IOException;
/**
* Write string.
* 输出string类型
* @param v value.
* @throws IOException
*/
void writeUTF(String v) throws IOException;
/**
* Write byte array.
* 输出byte数组
* @param v value.
* @throws IOException
*/
void writeBytes(byte[] v) throws IOException;
/**
* Write byte array.
* 输出byte数组中部分数据
* @param v value.
* @param off offset.
* @param len length.
* @throws IOException
*/
void writeBytes(byte[] v, int off, int len) throws IOException;
/**
* Flush buffer.
* 刷新缓冲区
* @throws IOException
*/
void flushBuffer() throws IOException;
}
该接口是数据输出接口,可以看到定义了向 InputStream 中,写入基本类型的数据。
(三)ObjectOutput
public interface ObjectOutput extends DataOutput {
/**
* write object.
* 输入object类型
* @param obj object.
*/
void writeObject(Object obj) throws IOException;
}
在 DataOutput 的基础上,增加写入object类型的数据。
(四)ObjectInput
public interface ObjectInput extends DataInput {
/**
* read object.
* 读取object类型数据
* @return object.
*/
Object readObject() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException;
/**
* read object.
* 根据class类型读取object类型数据
* @param cls object type.
* @return object.
*/
<T> T readObject(Class<T> cls) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException;
/**
* read object.
* 取object类型数据
* @param cls object type.
* @return object.
*/
<T> T readObject(Class<T> cls, Type type) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException;
}
该接口是继承了DataInput 接口,在 DataInput 的基础上,增加读取object类型的数据。
(五)Cleanable
public interface Cleanable {
/**
* 清理
*/
void cleanup();
}
该接口是清理接口,定义了一个清理方法。目前只有kryo实现的时候,完成序列化或反序列化,需要做清理。通过实现该接口,执行清理的逻辑。
(六)Serialization
@SPI("hessian2")
public interface Serialization {
/**
* get content type id
* 获得内容类型编号
* @return content type id
*/
byte getContentTypeId();
/**
* get content type
* 获得内容类型名
* @return content type
*/
String getContentType();
/**
* create serializer
* 创建 ObjectOutput 对象,序列化输出到 OutputStream
* @param url
* @param output
* @return serializer
* @throws IOException
*/
@Adaptive
ObjectOutput serialize(URL url, OutputStream output) throws IOException;
/**
* create deserializer
* 创建 ObjectInput 对象,从 InputStream 反序列化
* @param url
* @param input
* @return deserializer
* @throws IOException
*/
@Adaptive
ObjectInput deserialize(URL url, InputStream input) throws IOException;
}
该接口是序列化接口,该接口也是可扩展接口,默认是使用hessian2序列化方式。其中定义了序列化和反序列化等方法
(七)SerializableClassRegistry
public abstract class SerializableClassRegistry {
/**
* 可序列化类类的集合
*/
private static final Set<Class> registrations = new LinkedHashSet<Class>();
/**
* only supposed to be called at startup time
* 把可序列化的类加入到集合
*/
public static void registerClass(Class clazz) {
registrations.add(clazz);
}
/**
* 获得可序列化的类的集合
* @return
*/
public static Set<Class> getRegisteredClasses() {
return registrations;
}
}
该类提供一个序列化统一的注册中心,其实就是封装了可序列化类的集合
(八)SerializationOptimizer
public interface SerializationOptimizer {
/**
* 需要序列化的类的集合
* @return
*/
Collection<Class> getSerializableClasses();
}
该接口序列化优化器接口,在 Kryo 、FST 中,支持配置需要优化的类。业务系统中,可以实现自定义的 SerializationOptimizer,进行配置。或者使用文件来配置也是一个选择。
后记
该部分相关的源码解析地址: https://github.com/CrazyHZM/i...
该文章讲解了dubbo支持的几种序列化方式,介绍了序列化的接口设计,具体的实现我不再讲述,因为大部分都是调用了不同的依赖库。接下来我会说一个分割线,我讲开始讲解2.7.x版本的新特性,然后分析新特性的实现,下一篇就先讲解一下dubbo2.7.0的大改动。











![[HBLOG]公众号](http://www.liuhaihua.cn/img/qrcode_gzh.jpg)

