Netty源码分析(五):EventLoop
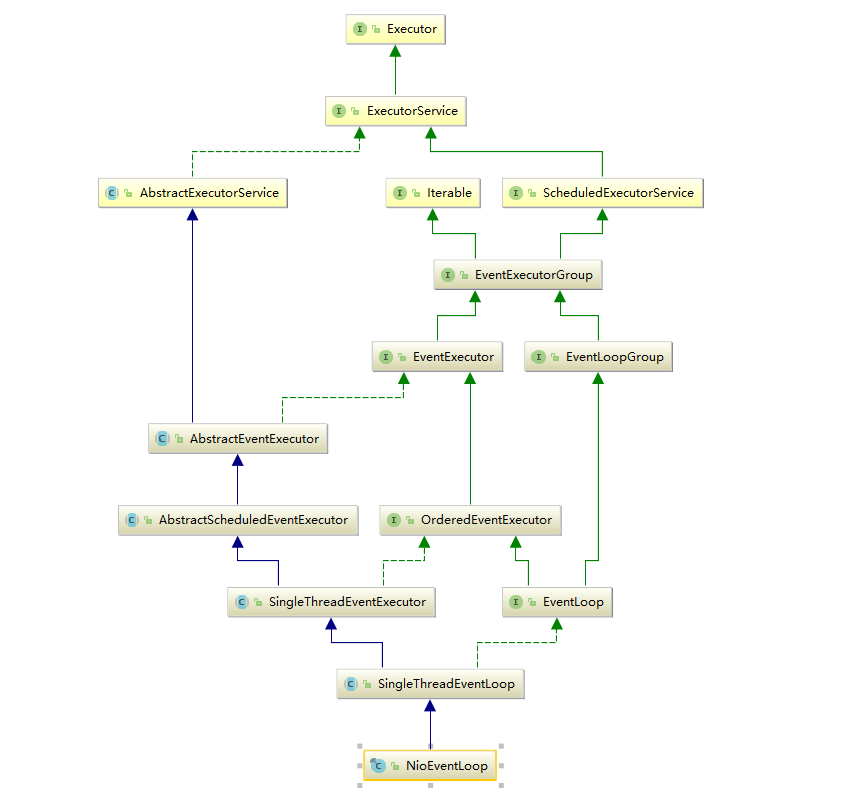
NioEventLoop 继承自
SingleThreadEventLoop ,而
SingleThreadEventLoop 又继承自
SingleThreadEventExecutor 。
SingleThreadEventExecutor 内部持有一个Thread对象,是
Netty 多线程的基础。 可以认为, 一个
NioEventLoop
与一个特定的线程进行了绑定,并且在其生命周期内,绑定的线程都不会再改变。
SingleThreadEventExecutor
从名字就可以看出来, SingleThreadEventExecutor 是一个单线程事件执行器。主要做的事情就是线程的管理和事件的执行。
线程管理
SingleThreadEventExecutor 中定义了五种线程状态:
/**
* 未开始
*/
private static final int ST_NOT_STARTED = 1;
/**
* 已开始
*/
private static final int ST_STARTED = 2;
/**
* 关闭中
*/
private static final int ST_SHUTTING_DOWN = 3;
/**
* 已关闭
*/
private static final int ST_SHUTDOWN = 4;
/**
* 已终止
*/
private static final int ST_TERMINATED = 5;
复制代码
这几种状态对应的方法有 startThread 、 shutdownGracefully 和 shutdown 。
startThread
private void startThread() {
if (state == ST_NOT_STARTED) {
if (STATE_UPDATER.compareAndSet(this, ST_NOT_STARTED, ST_STARTED)) {
try {
doStartThread();
} catch (Throwable cause) {
STATE_UPDATER.set(this, ST_NOT_STARTED);
PlatformDependent.throwException(cause);
}
}
}
}
复制代码
startThread 线程未开始时,尝试更新线程状态为一开始,更新成功,则调用 doStartThread 方法启动线程,子类的run方法就是在这里调用的,比如说接下来的 NioEventLoop 。
shutdownGracefully
public Future<?> shutdownGracefully(long quietPeriod, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) {
// 静待时间需要>=0
if (quietPeriod < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("quietPeriod: " + quietPeriod + " (expected >= 0)");
}
// 超时时间不能小于静待时间
if (timeout < quietPeriod) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"timeout: " + timeout + " (expected >= quietPeriod (" + quietPeriod + "))");
}
// 必须设置时间单位
if (unit == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("unit");
}
// 关闭中直接返回终止Future
if (isShuttingDown()) {
return terminationFuture();
}
boolean inEventLoop = inEventLoop();
boolean wakeup;
int oldState;
for (; ; ) {
// 关闭中直接返回终止Future
if (isShuttingDown()) {
return terminationFuture();
}
int newState;
wakeup = true;
oldState = state;
if (inEventLoop) {
newState = ST_SHUTTING_DOWN;
} else {
switch (oldState) {
case ST_NOT_STARTED:
case ST_STARTED:
newState = ST_SHUTTING_DOWN;
break;
default:
newState = oldState;
wakeup = false;
}
}
if (STATE_UPDATER.compareAndSet(this, oldState, newState)) {
break;
}
}
gracefulShutdownQuietPeriod = unit.toNanos(quietPeriod);
gracefulShutdownTimeout = unit.toNanos(timeout);
if (oldState == ST_NOT_STARTED) {
try {
doStartThread();
} catch (Throwable cause) {
STATE_UPDATER.set(this, ST_TERMINATED);
terminationFuture.tryFailure(cause);
if (!(cause instanceof Exception)) {
PlatformDependent.throwException(cause);
}
return terminationFuture;
}
}
if (wakeup) {
wakeup(inEventLoop);
}
return terminationFuture();
}
复制代码
shutdownGracefully 目的是让正在执行的任务再执行一会儿,同时拒绝新任务。 quietPeriod 和 timeout 这两个时间会在 confirmShutdown 方法中用到,当然单位已经转为纳秒了。
事件的执行
public void execute(Runnable task) {
if (task == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("task");
}
boolean inEventLoop = inEventLoop();
if (inEventLoop) {
addTask(task);
} else {
startThread();
addTask(task);
if (isShutdown() && removeTask(task)) {
reject();
}
}
if (!addTaskWakesUp && wakesUpForTask(task)) {
wakeup(inEventLoop);
}
}
复制代码
NioEventLoop
NioEventLoop 的核心操作都在它的run方法里面:
protected void run() {
for (; ; ) {
try {
switch (selectStrategy.calculateStrategy(selectNowSupplier, hasTasks())) {
case SelectStrategy.CONTINUE:
continue;
case SelectStrategy.SELECT:
// 重置wakenUp为false并选择任务
select(wakenUp.getAndSet(false));
if (wakenUp.get()) {
selector.wakeup();
}
default:
}
cancelledKeys = 0;
needsToSelectAgain = false;
final int ioRatio = this.ioRatio;
// 当处理io用时占比为100%时
if (ioRatio == 100) {
try {
processSelectedKeys();
} finally {
runAllTasks();
}
} else {
final long ioStartTime = System.nanoTime();
try {
processSelectedKeys();
} finally {
final long ioTime = System.nanoTime() - ioStartTime;
runAllTasks(ioTime * (100 - ioRatio) / ioRatio);
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
// 处理Loop异常
handleLoopException(t);
}
try {
// 处于关闭状态
if (isShuttingDown()) {
// 关闭所有
closeAll();
if (confirmShutdown()) {
return;
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
// 处理Loop异常
handleLoopException(t);
}
}
}
复制代码
该方法主要是处理流程的控制,包括选择、处理和关闭这几种。
文中帖的代码注释全在: KAMIJYOUDOUMA , 有兴趣的童鞋可以关注一下。
本篇到此结束,如果读完觉得有收获的话,欢迎点赞、关注、加公众号【贰级天災】,查阅更多精彩历史!!!

正文到此结束
热门推荐
相关文章
Loading...











![[HBLOG]公众号](http://www.liuhaihua.cn/img/qrcode_gzh.jpg)

