配置文件@ConfigurationProperties读取List、Map参数
在SpringBoot环境中,我们有“使用不完的”注解。这也是SpringBoot替代了传统的Spring项目中的xml配置的原因。在使用这些annotation的时候,我们一定要了解这些注解背后的原理以及约定。
package org.springframework.boot.context.properties;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AliasFor;
@Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface ConfigurationProperties {
......
}
复制代码
支持的类型
List
custom.config.config1.folders[0]=/root custom.config.config1.folders[1]=/home/user1 custom.config.config1.folders[2]=/home/user2 复制代码
对应的Java实现
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "custom.config.config1")
public class Config1Properties{
private List<String> folders;
...
}
复制代码
Map
custom.config.config1.map.key1=value1 custom.config.config1.map.key2=value2 custom.config.config1.map.key3=value3 custom.config.config1.map.key4=value4 custom.config.config1.map.key5=value5 复制代码
对应的Java实现
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "custom.config.config1")
public class Config1Properties{
private Map<String, String> map;
...
}
复制代码
Object
custom.config.config1.server.host=host1 custom.config.config1.server.port=22 custom.config.config1.server.username=username1 custom.config.config1.server.password=password1 复制代码
对应的Java实现
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "custom.config.config1")
public class Config1Properties{
private ServerProperties server;
...
public static class ServerProperties {
private String host;
private int port;
private String username;
private String password;
...
}
}
复制代码
Object List
custom.config.config1.servers[0].host=host1 custom.config.config1.servers[0].port=22 custom.config.config1.servers[0].username=username1 custom.config.config1.servers[0].password=password1 custom.config.config1.servers[1].host=host2 custom.config.config1.servers[1].port=22 custom.config.config1.servers[1].username=username2 custom.config.config1.servers[1].password=password2 复制代码
对应的Java实现
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "custom.config.config1")
public class Config1Properties{
private List<ServerProperties> servers;
...
public static class ServerProperties {
private String host;
private int port;
private String username;
private String password;
...
}
}
复制代码
Map的使用案例
比如,我们同时需要连接多个OSS(阿里对象存储),那我们就可以利用ConfigurationProperties的方式来配置多个。而且可以通过Spring的加载动态的注入到容器中去。
配置中心的配置:
# OSS1配置 oss.multi.clients.accout.accessKeyId=xxx oss.multi.clients.accout.accessKeySecret=xxx oss.multi.clients.accout.privateEndpoint=xxx oss.multi.clients.accout.bucketName=bucket-b-test # OSS2配置 oss.multi.enabled=true oss.multi.clients.xdtrans.accessKeyId=xxx oss.multi.clients.xdtrans.accessKeySecret=xxx oss.multi.clients.xdtrans.privateEndpoint=xxx oss.multi.clients.xdtrans.bucketName=bucket-a-test 复制代码
对应的Java实现
@Data
@EqualsAndHashCode(callSuper = false)
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = OssConstants.MULTI_CONFIG_PREFIX)
public class MultiOssProperties {
private Map<String, OssProperties> clients;
@Data
public static class OssProperties {
private String accessKeyId;
private String accessKeySecret;
private String publicEndpoint;
private String privateEndpoint;
private String bucketName;
private String object;
}
复制代码
动态的定义我们需要的BeanDefinition。
public class MultiOssScannerConfigurer implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor, InitializingBean, ApplicationContextAware, BeanNameAware {
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@Setter
private MultiOssProperties multiOssProperties;
@Override
public void setBeanName(String name) {
log.info("init bean {}", name);
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
Objects.requireNonNull(this.multiOssProperties, "multiOssProperties不能为空");
Objects.requireNonNull(this.applicationContext, "applicationContext不能为空");
}
// 动态的定义Bean
@Override
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry beanDefinitionRegistry) throws BeansException {
String beanSuffixName = StringUtils.capitalize(OssConstants.BEAN_SUFFIX_NAME);
// productCodes实际与oss.multi.clients.xdtrans的xdtrans保持一致
multiOssProperties.getClients().forEach((productCode, ossProperties) -> {
AbstractBeanDefinition beanDefinition = BeanDefinitionBuilder.genericBeanDefinition(OssClient.class,
() -> OssClientUtils.buildOssClient(ossProperties))
.getRawBeanDefinition();
beanDefinition.setInitMethodName("init");
beanDefinition.setDestroyMethodName("shutDown");
beanDefinitionRegistry.registerBeanDefinition(productCode + beanSuffixName, beanDefinition);
});
}
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory configurableListableBeanFactory) throws BeansException {
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
}
复制代码
通过binder来让配置与对应的Java代码产生关系:
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties(MultiOssProperties.class)
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = OssConstants.MULTI_CONFIG_PREFIX, value = "enabled")
public class MultiOssAutoConfiguration {
/**
* 初始化多个 ossClient 自动配置
*
* @param environment 环境变量属性
* @return OssClient 自动扫描注册器
*/
@Bean
public MultiOssScannerConfigurer multiOssScannerConfigurer(Environment environment) {
Binder binder = Binder.get(environment);
MultiOssProperties properties = binder.bind(OssConstants.MULTI_CONFIG_PREFIX, MultiOssProperties.class).get();
MultiOssScannerConfigurer multiOssScannerConfigurer = new MultiOssScannerConfigurer();
multiOssScannerConfigurer.setMultiOssProperties(properties);
return multiOssScannerConfigurer;
}
}
复制代码
如何使用?
@Getter
@AllArgsConstructor
public enum OssTypeEnum {
// 注意一下这里的beanName,要跟上面的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry保持一致
XDtransOssClient("xdtransOssClient", "oss1"),
DianDianOssClient("ddacctOssClient", "oss2"),
;
private final String beanName;
private final String desc;
// 根据BeanName来Spring容器中获取即可
public OssClient getBean() {
return SpringContextHolder.getBean(beanName, OssClient.class);
}
复制代码
Binder是如何映射的?
通过上面的代码 binder.bind(OssConstants.MULTI_CONFIG_PREFIX, MultiOssProperties.class).get(); 来进行bind。
protected final <T> T bind(ConfigurationPropertyName name, Bindable<T> target, BindHandler handler, Context context, boolean allowRecursiveBinding) {
context.clearConfigurationProperty();
try {
target = handler.onStart(name, target, context);
if (target == null) {
return null;
}
Object bound = bindObject(name, target, handler, context,allowRecursiveBinding);
return handleBindResult(name, target, handler, context, bound);
} catch (Exception ex) {
return handleBindError(name, target, handler, context, ex);
}
}
复制代码
如果我们的key是:oss.multi.clients.accout.xxx
实际上对应的是Map,那么它的引用名字就是clients。具体的key就是accout,那么对应的value就是OssProperties。
private Object bindBean(ConfigurationPropertyName name, Bindable<?> target,
BindHandler handler, Context context, boolean allowRecursiveBinding) {
if (containsNoDescendantOf(context.getSources(), name)
|| isUnbindableBean(name, target, context)) {
return null;
}
BeanPropertyBinder propertyBinder = (propertyName, propertyTarget) -> bind(
name.append(propertyName), propertyTarget, handler, context, false);
Class<?> type = target.getType().resolve(Object.class);
if (!allowRecursiveBinding && context.hasBoundBean(type)) {
return null;
}
return context.withBean(type, () -> {
Stream<?> boundBeans = BEAN_BINDERS.stream()
.map((b) -> b.bind(name, target, context, propertyBinder));
return boundBeans.filter(Objects::nonNull).findFirst().orElse(null);
});
}
复制代码
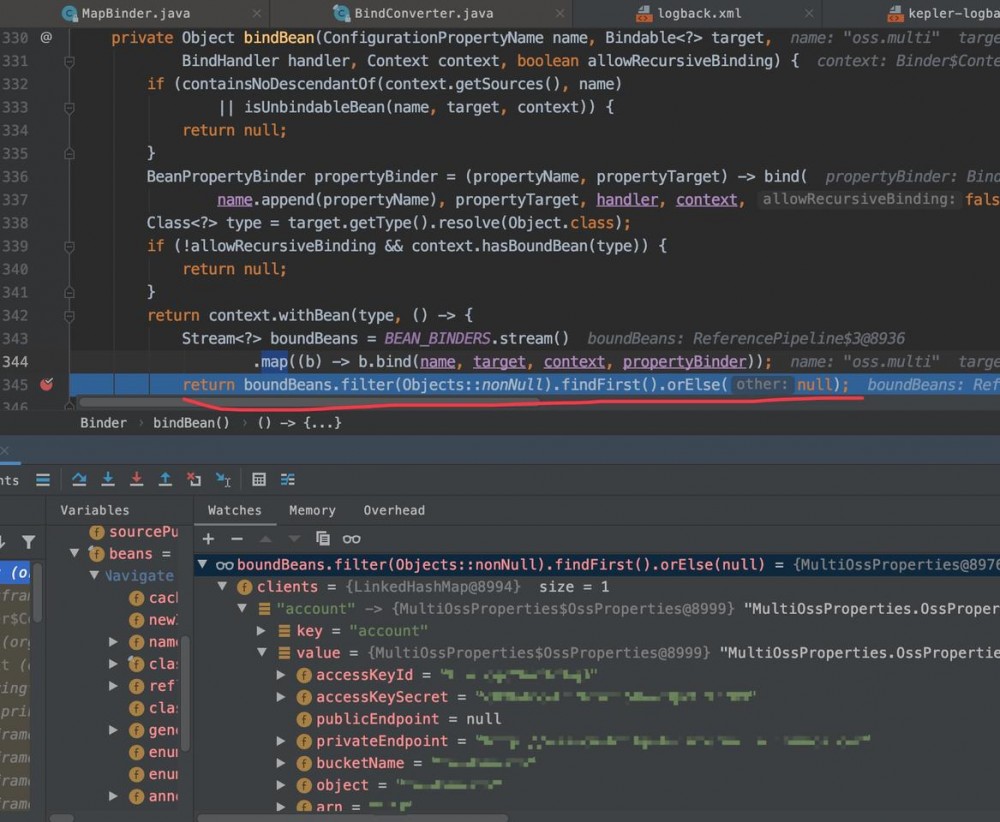
具体的一个bind情况。
private static final List<BeanBinder> BEAN_BINDERS;
static {
List<BeanBinder> binders = new ArrayList<>();
binders.add(new JavaBeanBinder());
BEAN_BINDERS = Collections.unmodifiableList(binders);
}
public <T> T bind(ConfigurationPropertyName name, Bindable<T> target, Context context,
BeanPropertyBinder propertyBinder) {
boolean hasKnownBindableProperties = hasKnownBindableProperties(name, context);
Bean<T> bean = Bean.get(target, hasKnownBindableProperties);
if (bean == null) {
return null;
}
BeanSupplier<T> beanSupplier = bean.getSupplier(target);
boolean bound = bind(propertyBinder, bean, beanSupplier);
return (bound ? beanSupplier.get() : null);
}
// 返回对应的对象
public BeanSupplier<T> getSupplier(Bindable<T> target) {
return new BeanSupplier<>(() -> {
T instance = null;
if (target.getValue() != null) {
instance = target.getValue().get();
}
if (instance == null) {
instance = (T) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(this.resolvedType);
}
return instance;
});
}
复制代码
参考地址
- blog.csdn.net/sayyy/artic…
如果大家喜欢我的文章,可以关注个人订阅号。欢迎随时留言、交流。如果想加入微信群的话一起讨论的话,请加管理员简栈文化-小助手(lastpass4u),他会拉你们进群。

正文到此结束
- 本文标签: struct IDE Collections build 文章 id UI Document final ACE Collection db 配置 App 参数 Word IO node map CTO BeanUtils http bean stream tab cat 代码 list ask constant equals root find SDN value core Property ArrayList java tar API key src BeanDefinition 配置中心 spring https 管理 XML client IOS springboot
- 版权声明: 本文为互联网转载文章,出处已在文章中说明(部分除外)。如果侵权,请联系本站长删除,谢谢。
- 本文海报: 生成海报一 生成海报二
热门推荐
相关文章
Loading...











![[HBLOG]公众号](http://www.liuhaihua.cn/img/qrcode_gzh.jpg)

