JVM 笔记:性能监控与分析工具
1. 概述
前面几篇文章分析了 JVM 的一些概念,大部分都是偏理论的,本文介绍一些可以实操的 JVM 性能监控与分析工具。
主要包括 JDK 自带的一些常用工具,以及阿里开源的 Java 诊断工具 Arthas。
2. 性能监控与故障处理工具
2.1 JDK 自带工具
JDK 自带的几个常用工具如下:
| 名称 | 主要作用 |
|---|---|
| jps | JVM Process Status Tool, 显示指定系统内所有的 HotSpot 虚拟机进程 |
| jstat | JVM Statistics Monitoring Tool, 用于收集 HotSpot 虚拟机各方面的运行数据 |
| jinfo | Configuration Info for Java, 显示虚拟机配置信息 |
| jmap | Memory Map for Java, 生成虚拟机的内存转储快照(heapdump 文件) |
| jhat | JVM Heap Analysis Tool, 用于分析 heapdump 文件(它会建立一个 HTTP/HTML 服务器,让用户可以在浏览器上查看分析结果) |
| jstack | Stack Trace for Java, 显示虚拟机的线程快照 |
这里只是少部分,其他更多命令可以参考官方文档:https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/technotes/tools/unix/toc.html
2.1.1 jps: 虚拟机进程状况工具
-
命令格式
jps [ options ] [ hostid ]
-
jps
$ jps
15236 Jps
14966 Example1
-
jps -l
$ jps -l
15249 sun.tools.jps.Jps
14966 com.jaxer.jvm.egs.Example1
-
jps -m
$ jps -m
15264 Jps -m
14966 Example1
-
jps -v
$ jps -v
14966 Example1 -Dvisualvm.id=44321340563858 -Xmx50m -Xms50m -XX:+PrintGCDetails -javaagent:/Applications/IntelliJ IDEA.app/Contents/lib/idea_rt.jar=61849:/Applications/IntelliJ IDEA.app/Contents/bin -Dfile.encoding=UTF-8
15278 Jps -Dapplication.home=/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_191.jdk/Contents/Home -Xms8m
-
jps -q
$ jps -q
9938
14966
15334
2.1.2 jstat: 虚拟机统计信息监视工具
-
命令格式
jstat [option vmid [interval[s|ms] [count]] ]
-
示例 1:监控堆内存信息
$ jstat -gc 14966
S0C S1C S0U S1U EC EU OC OU MC MU CCSC CCSU YGC YGCT FGC FGCT GCT
2048.0 2048.0 0.0 0.0 12800.0 9345.8 34304.0 26638.8 5248.0 4971.3 640.0 554.9 2 0.032 2 0.049 0.082
如图所示:
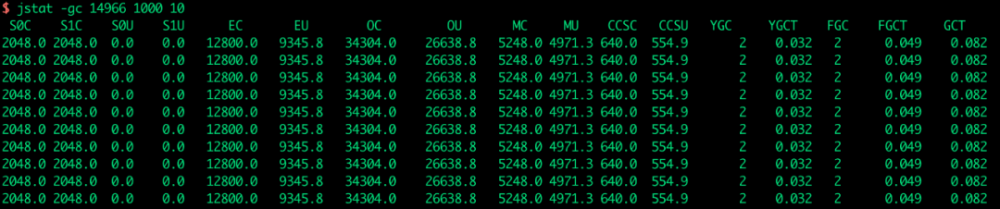
参数主要是新生代、老年代的内存空间占用情况以及 GC 的次数和时间,说明如下:
S0: Survivor space 0 utilization as a percentage of the space's current capacity.
S1: Survivor space 1 utilization as a percentage of the space's current capacity.
E: Eden space utilization as a percentage of the space's current capacity.
O: Old space utilization as a percentage of the space's current capacity.
M: Metaspace utilization as a percentage of the space's current capacity.
CCS: Compressed class space utilization as a percentage.
YGC: Number of young generation GC events.
YGCT: Young generation garbage collection time.
FGC: Number of full GC events.
FGCT: Full garbage collection time.
GCT: Total garbage collection time.
官方文档:https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/technotes/tools/unix/jstat.html#BEHHGFAE
-
示例 2:每隔 1000 毫秒打印堆内存信息,打印 10 次
$ jstat -gc 14966 1000 10
如图所示:
-
示例 3:查看类加载/卸载信息
$ jstat -class 14966
Loaded Bytes Unloaded Bytes Time
829 1604.4 0 0.0 0.37
2.1.3 jinfo: Java 配置信息工具
-
查看 JVM 启动参数
$ jinfo -flags 26472
VM Flags:
-XX:CICompilerCount=3 -XX:InitialHeapSize=52428800 -XX:MaxHeapSize=52428800 -XX:MaxNewSize=17301504 -XX:MinHeapDeltaBytes=524288 -XX:NewSize=17301504 -XX:OldSize=35127296 -XX:+PrintGCDetails -XX:+UseCompressedClassPointers -XX:+UseCompressedOops -XX:+UseFastUnorderedTimeStamps -XX:+UseParallelGC
值得注意的是,JDK 8 使用该命令时会抛出如下异常:
$ jinfo -flags 26284
Attaching to process ID 26284, please wait...
Error attaching to process: sun.jvm.hotspot.debugger.DebuggerException: Can't attach symbolicator to the process
sun.jvm.hotspot.debugger.DebuggerException: sun.jvm.hotspot.debugger.DebuggerException: Can't attach symbolicator to the process
at sun.jvm.hotspot.debugger.bsd.BsdDebuggerLocal$BsdDebuggerLocalWorkerThread.execute(BsdDebuggerLocal.java:169)
at sun.jvm.hotspot.debugger.bsd.BsdDebuggerLocal.attach(BsdDebuggerLocal.java:287)
at sun.jvm.hotspot.HotSpotAgent.attachDebugger(HotSpotAgent.java:671)
at sun.jvm.hotspot.HotSpotAgent.setupDebuggerDarwin(HotSpotAgent.java:659)
at sun.jvm.hotspot.HotSpotAgent.setupDebugger(HotSpotAgent.java:341)
at sun.jvm.hotspot.HotSpotAgent.go(HotSpotAgent.java:304)
at sun.jvm.hotspot.HotSpotAgent.attach(HotSpotAgent.java:140)
at sun.jvm.hotspot.tools.Tool.start(Tool.java:185)
at sun.jvm.hotspot.tools.Tool.execute(Tool.java:118)
at sun.jvm.hotspot.tools.JInfo.main(JInfo.java:138)
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method)
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(NativeMethodAccessorImpl.java:62)
at sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:43)
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:498)
at sun.tools.jinfo.JInfo.runTool(JInfo.java:108)
at sun.tools.jinfo.JInfo.main(JInfo.java:76)
Caused by: sun.jvm.hotspot.debugger.DebuggerException: Can't attach symbolicator to the process
at sun.jvm.hotspot.debugger.bsd.BsdDebuggerLocal.attach0(Native Method)
at sun.jvm.hotspot.debugger.bsd.BsdDebuggerLocal.access$100(BsdDebuggerLocal.java:65)
at sun.jvm.hotspot.debugger.bsd.BsdDebuggerLocal$1AttachTask.doit(BsdDebuggerLocal.java:278)
at sun.jvm.hotspot.debugger.bsd.BsdDebuggerLocal$BsdDebuggerLocalWorkerThread.run(BsdDebuggerLocal.java:144)
查资料说是 JVM 的 bug(链接:https://bugs.java.com/bugdatabase/view_bug.do?bug_id=8160376),在 JDK 9 b129 修复了。
因此,这里测试该命令使用了 JDK 11,版本信息如下:
$ java -version
java version "11.0.5" 2019-10-15 LTS
Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment 18.9 (build 11.0.5+10-LTS)
Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM 18.9 (build 11.0.5+10-LTS, mixed mode)
2.1.4 jstack: Java 堆栈跟踪工具
-
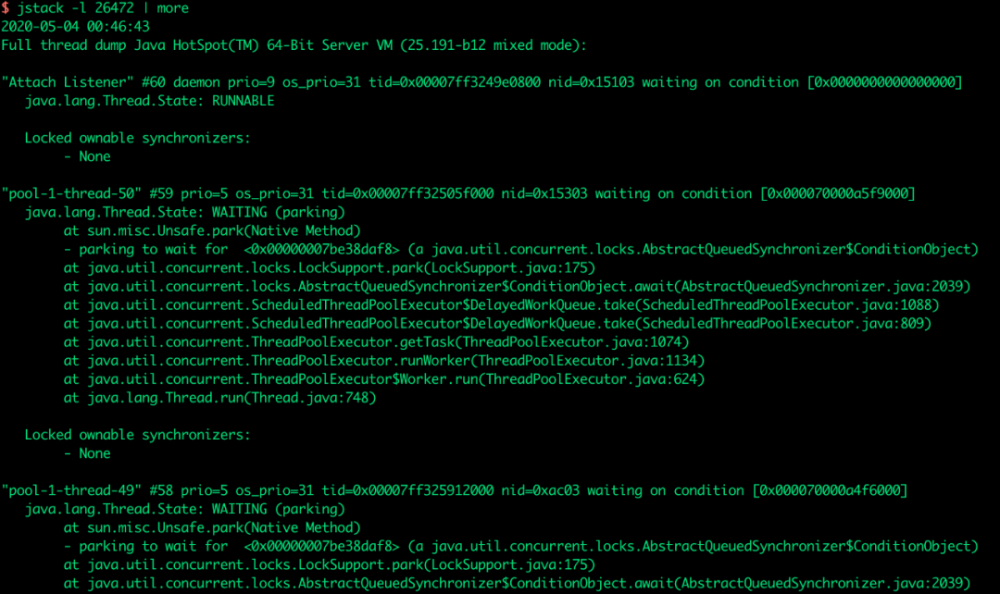
jstack (Stack Trace for Java) 命令用于生成虚拟机当前时刻的线程快照(一般称为 threaddump 或 javacore 文件)。
-
线程快照就是当前虚拟机内每一条线程正在执行的方法堆栈的集合,生成堆栈快照的主要目的是定位线程出现长时间停顿的原因,如线程死锁、死循环、请求外部资源导致的长时间等待等都是导致线程长时间停顿的常见原因。
$ jstack -l 26472 | more
如图所示:
2.1.5 jmap: Java 内存映像工具
-
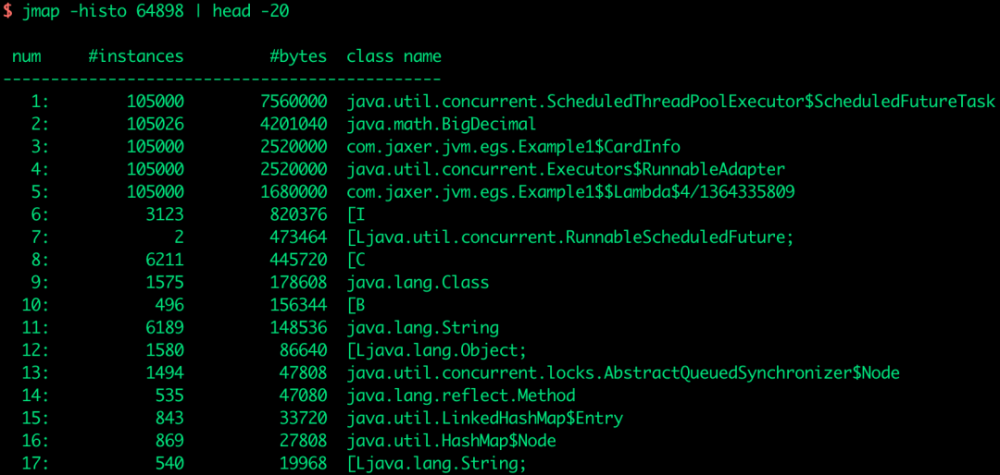
查看对象信息
可以使用 jmap 查看内存中的对象数量及内存空间占用:
jmap [option] <pid>
例如:
-
导出堆转储快照
$ jmap -dump:live,format=b,file=/Users/jaxer/Desktop/dump.hprof 26472
Dumping heap to /Users/jaxer/Desktop/dump.hprof ...
Heap dump file created
可以在对应路径下看到堆转储快照文件 dump.hprof。导出来之后,就可以用其它工具分析快照文件了。
2.1.6 jhat: 堆转储快照分析工具
分析 jmap 生成的快照文件,命令如下:
$ jhat dump.hprof
Reading from dump.hprof...
Dump file created Sun May 03 17:09:07 CST 2020
Snapshot read, resolving...
Resolving 42293 objects...
Chasing references, expect 8 dots........
Eliminating duplicate references........
Snapshot resolved.
Started HTTP server on port 7000
Server is ready.
Server 启动后,在浏览器打开 http://localhost:7000/,可以看到如下信息:
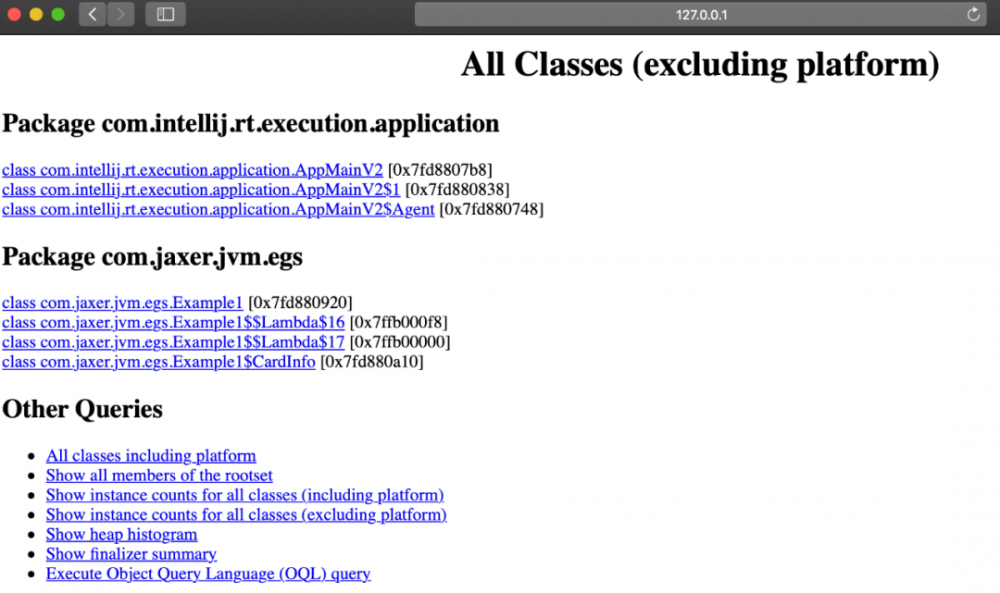
实际工作中,一般不会直接使用 jhat 命令来分析 dump 文件,主要原因:
-
一般不会在部署应用程序的服务器上直接分析 dump 文件(分析工作一般比较耗时,而且消耗硬件资源,在其他机器上进行时则没必要受到命令行工具的限制);
-
jhat 分析功能相对简陋,VisualVM 等更工具功能强大。
2.1.7 jvisualvm & VisualVM: 堆转储快照分析工具
jvisualvm 也是 JDK 自带的命令,虽然后面独立发展了。这两种方式都可以使用。
VisualVM 链接:https://visualvm.github.io/
使用 VisualVM 分析上面 jmap 导出的堆栈转储文件,导入后如下:
-
概览
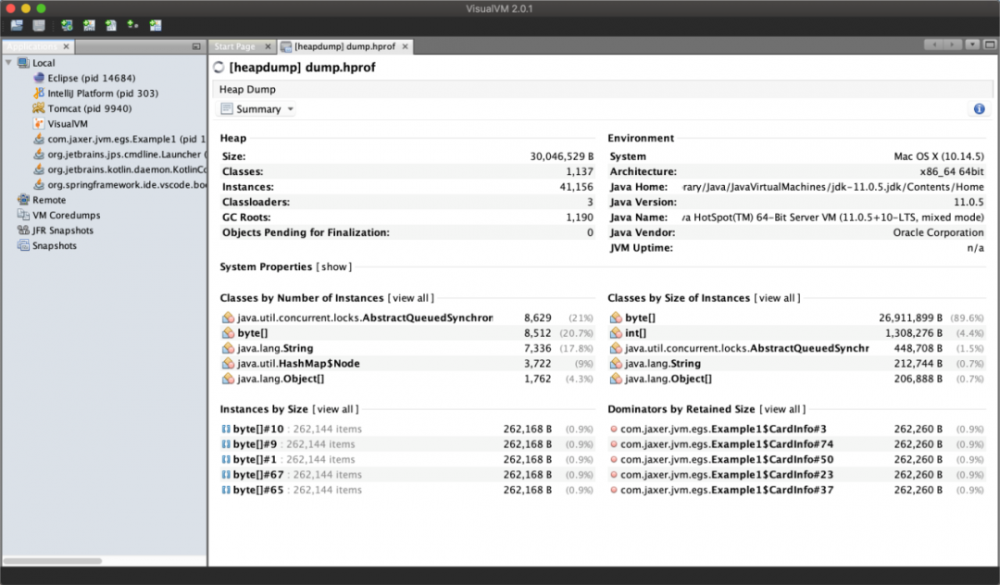
-
对象信息
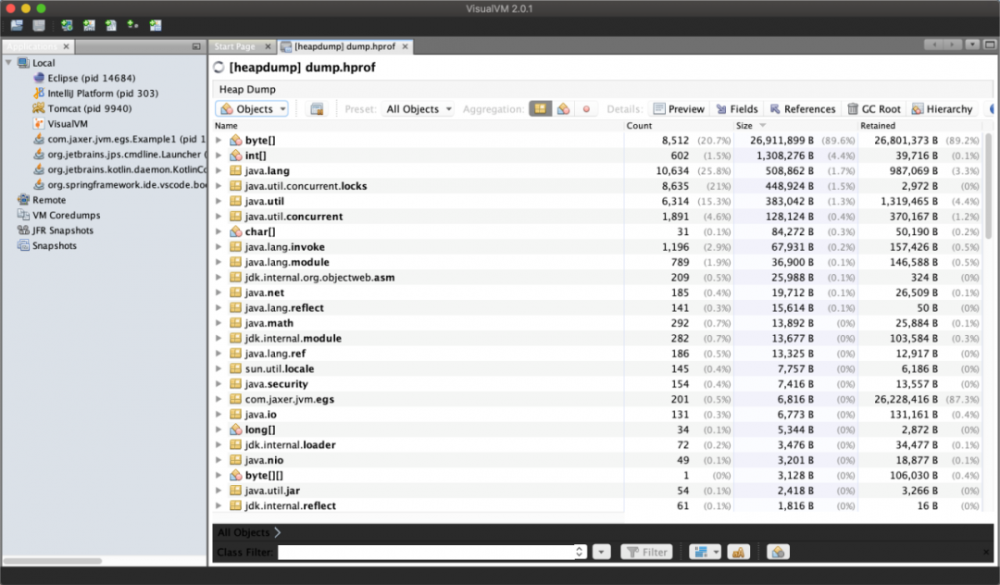
-
线程信息
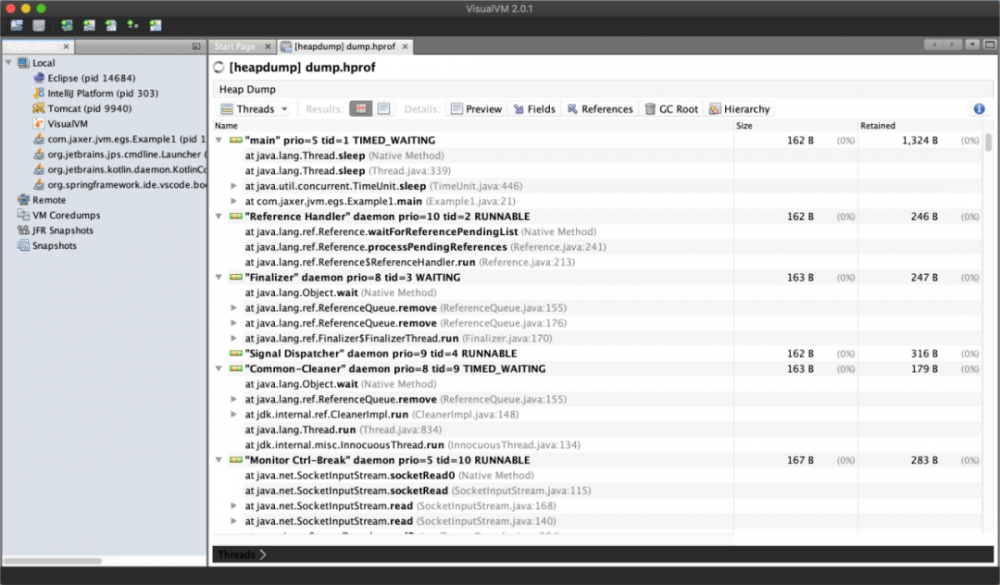
这个工具使用起来比 jhat 舒服多了。
2.1.8 jconsole: JVM 性能监控
使用 jconsole 命令会启动一个用户界面,如下:
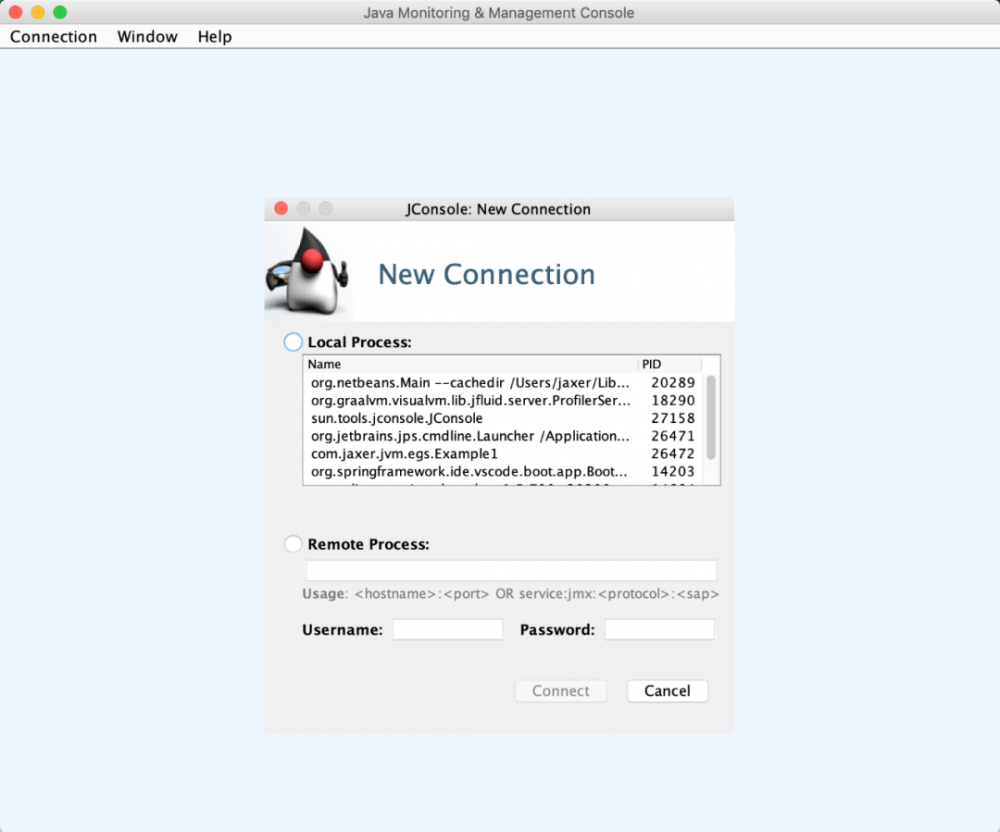
可以选择本地或者远程的 JVM 进程进行连接。
本人测试连接时报错,描述及解决方案详见:https://blog.csdn.net/u010551118/article/details/105907403
连接成功之后如下:
-
概览
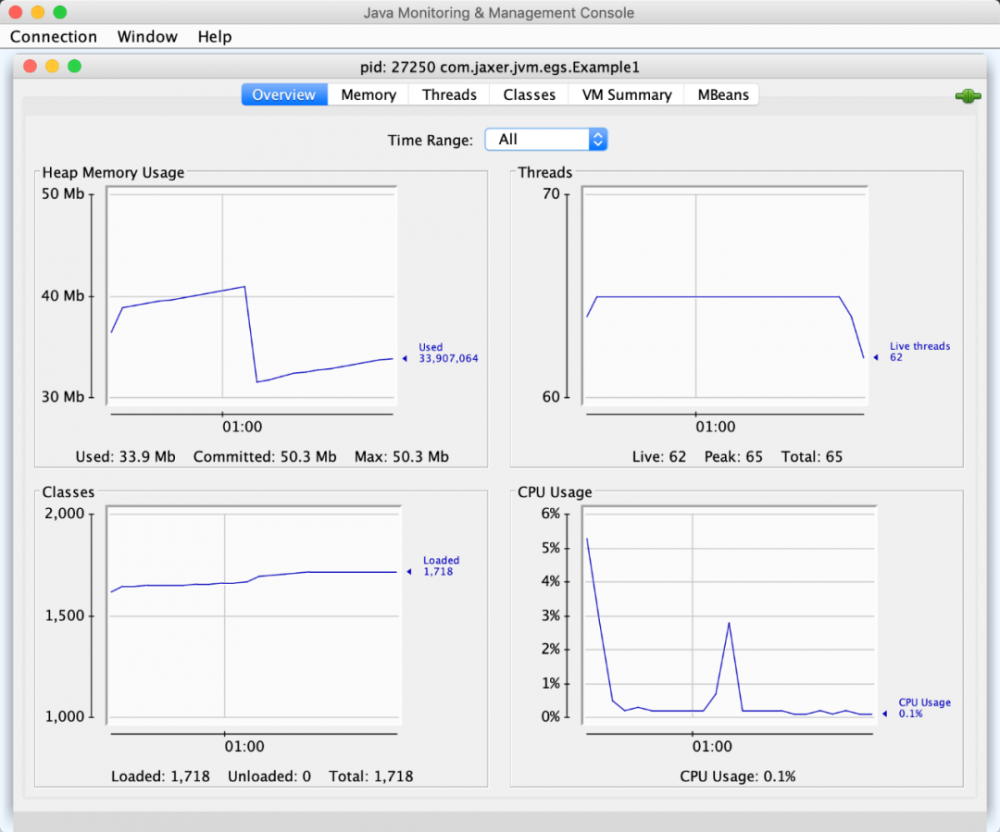
-
死锁检测

除了上面 JDK 自带的工具,还有个很好用的阿里开源的 Arthas。
2.2 Arthas
官方文档:
中:https://alibaba.github.io/arthas/
英:https://alibaba.github.io/arthas/en/
2.2.0 准备代码
为了演示部分功能,这里准备了一些简单的示例代码:
-
Hello.java
package com.jaxer.jvm.arthas;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
public class Hello {
public void sayHello() {
System.out.println(LocalDateTime.now() + " hello");
}
}
-
ArthasTest.java
package com.jaxer.jvm.arthas;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class ArthasTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
while (true) {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
new Hello().sayHello();
}
}
}
代码比较简单,这里不再赘述。
2.2.1 启动 Arthas
Arthas 其实是一个 jar 包,下载后运行:
$ java -jar arthas-boot.jar
启动成功后:
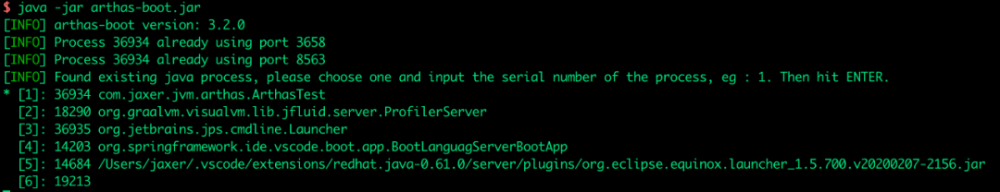
Arthas 会检测本地 JVM 进程并列出来(参见上面的 jps 命令),选择前面的序号就能附着到对应的进程。这里选择 1,然后回车:
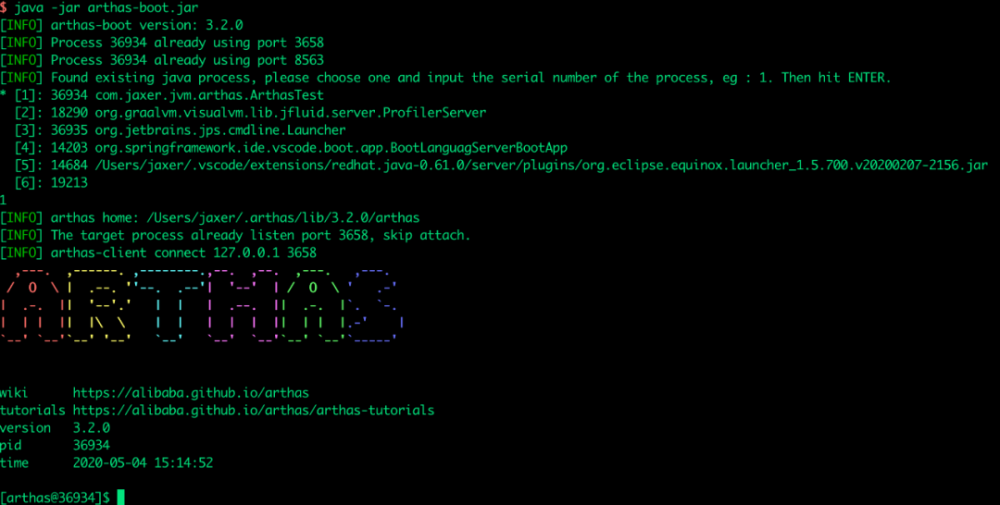
这样就成功 附着 到了该进程。接下来就可以执行各种命令来分析 JVM 了。
2.2.2 help
使用 help 命令可以看到 Arthas 的命令概览:
[arthas@36934]$ help
NAME DESCRIPTION
help Display Arthas Help
keymap Display all the available keymap for the specified connection.
sc Search all the classes loaded by JVM
sm Search the method of classes loaded by JVM
classloader Show classloader info
jad Decompile class
getstatic Show the static field of a class
monitor Monitor method execution statistics, e.g. total/success/failure count, average rt, fail rate, etc.
stack Display the stack trace for the specified class and method
thread Display thread info, thread stack
trace Trace the execution time of specified method invocation.
watch Display the input/output parameter, return object, and thrown exception of specified method invocation
tt Time Tunnel
jvm Display the target JVM information
perfcounter Display the perf counter infornation.
ognl Execute ognl expression.
mc Memory compiler, compiles java files into bytecode and class files in memory.
redefine Redefine classes. @see Instrumentation#redefineClasses(ClassDefinition...)
dashboard Overview of target jvm's thread, memory, gc, vm, tomcat info.
dump Dump class byte array from JVM
heapdump Heap dump
options View and change various Arthas options
cls Clear the screen
reset Reset all the enhanced classes
version Display Arthas version
session Display current session information
sysprop Display, and change the system properties.
sysenv Display the system env.
vmoption Display, and update the vm diagnostic options.
logger Print logger info, and update the logger level
history Display command history
cat Concatenate and print files
echo write arguments to the standard output
pwd Return working directory name
mbean Display the mbean information
grep grep command for pipes.
tee tee command for pipes.
profiler Async Profiler. https://github.com/jvm-profiling-tools/async-profiler
stop Stop/Shutdown Arthas server and exit the console.
此外,还可以查看每个命令的用法举例,命令后面加 -help,例如:
[arthas@36934]$ help -help
USAGE:
help [-h] [cmd]
SUMMARY:
Display Arthas Help
Examples:
help
help sc
help sm
help watch
OPTIONS:
-h, --help this help
<cmd> command name
2.2.3 dashboard
dashboard 命令可以总览 JVM 状况(默认 5 秒刷新一次):
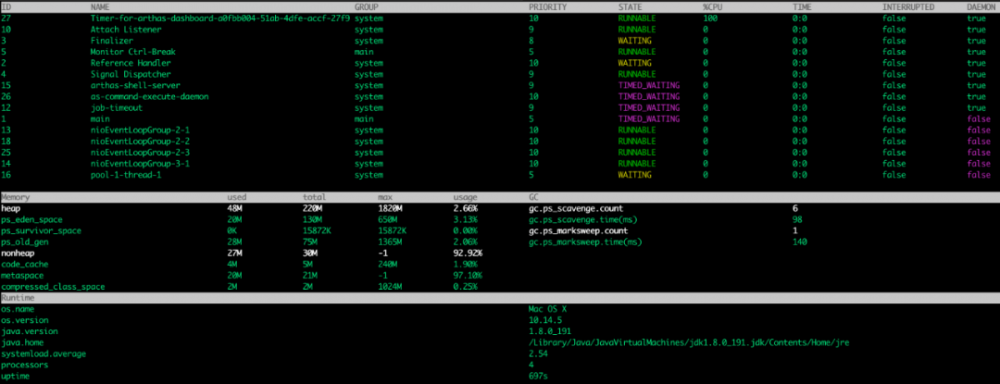
2.2.4 jvm
jvm 可以查看当前 JVM 的运行时信息,比如机器信息、JVM 版本、启动参数、ClassPath 等:
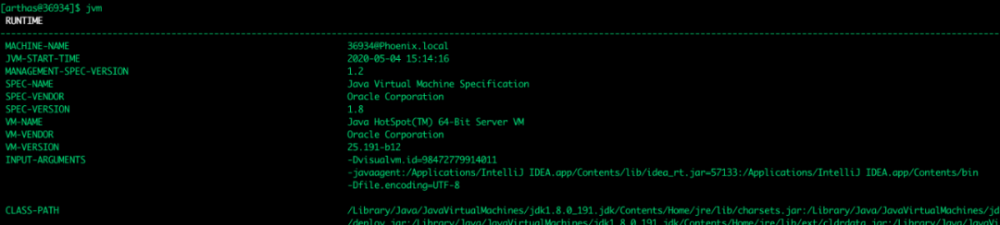
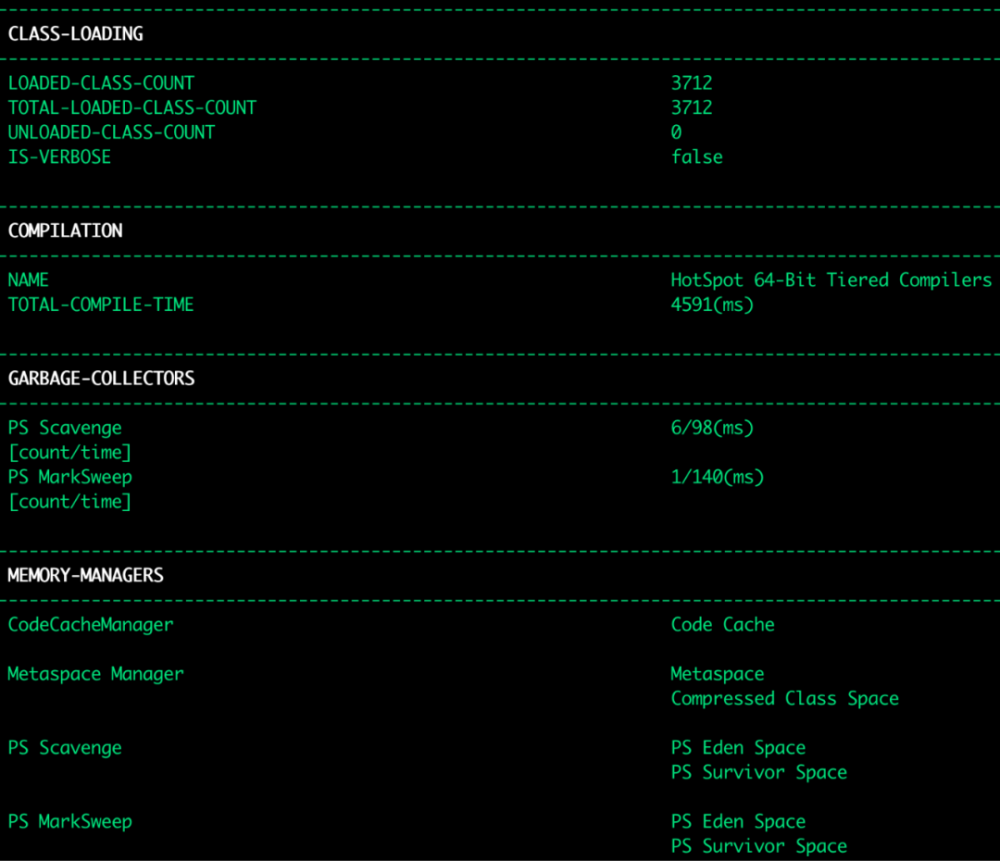
还有类加载信息、编译信息、垃圾收集器、内存相关信息:
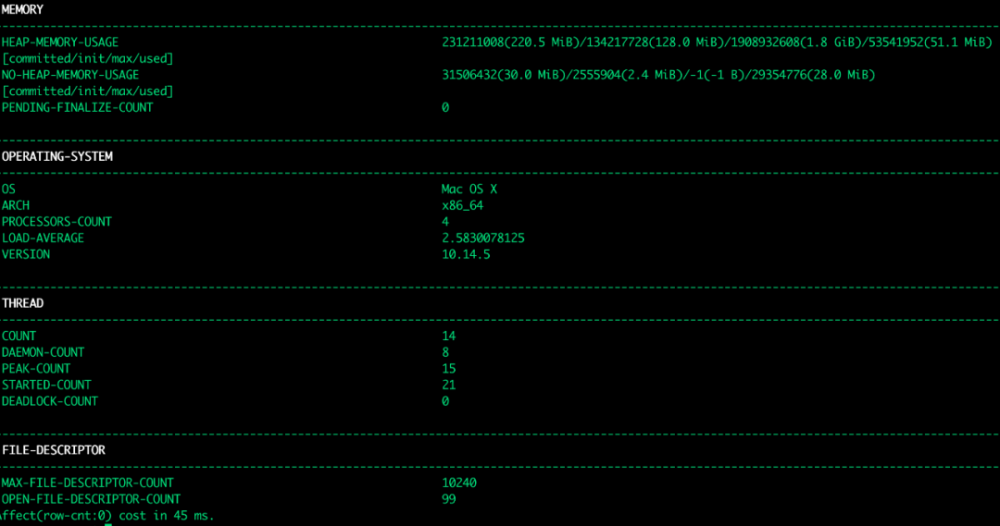
以及操作系统信息、死锁等:
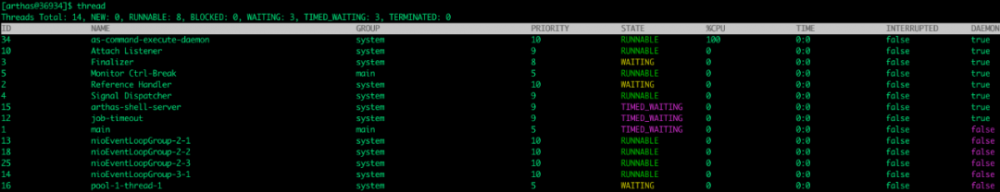
2.2.5 thread
线程信息、线程堆栈:
2.2.6 sc & sm
sc 可以查看类加载信息:
[arthas@36934]$ sc com.jaxer.*
com.jaxer.jvm.arthas.ArthasTest
com.jaxer.jvm.arthas.Hello
Affect(row-cnt:2) cost in 36 ms.
sm 可以查看类的方法信息:
[arthas@36934]$ sm com.jaxer.jvm.arthas.ArthasTest
com.jaxer.jvm.arthas.ArthasTest <init>()V
com.jaxer.jvm.arthas.ArthasTest main([Ljava/lang/String;)V
Affect(row-cnt:2) cost in 14 ms.
2.2.7 jad
jad 可以对类进行反编译,例如反编译上面的 Hello 类,结果如下:
[arthas@36934]$ jad com.jaxer.jvm.arthas.Hello
ClassLoader:
+-sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader@18b4aac2
+-sun.misc.Launcher$ExtClassLoader@14612fee
Location:
/Users/jaxer/GitHub-JiaoXR/Java-Learning/jvm-learning/target/classes/
/*
* Decompiled with CFR.
*/
package com.jaxer.jvm.arthas;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
public class Hello {
public void sayHello() {
System.out.println(LocalDateTime.now() + " hello");
}
}
Affect(row-cnt:1) cost in 260 ms.
2.2.8 redefine
redefine 就是热部署,通俗来讲就是「开着飞机换引擎」。比如上述代码的运行结果是每隔 5 秒打印一行代码,如下:
2020-05-04T16:07:04.242 hello
2020-05-04T16:07:09.247 hello
...
在不停止该程序的情况下,可以改变输出内容吗?答案是肯定的!
怎么做呢?
首先在本地新建一个与 Hello.java 内容完全一样的文件(名字也完全一样),然后修改方法内容,新的 Hello.java 文件内容如下(修改了方法输出内容):
package com.jaxer.jvm.arthas;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
public class Hello {
public void sayHello() {
System.out.println(LocalDateTime.now() + " I'm hungry");
}
}
然后在本地执行 javac 将其编译为 class 文件(注意该文件的路径为 /Users/jaxer/Desktop/Hello.class),然后运行 redefine 命令:
[arthas@36934]$ redefine /Users/jaxer/Desktop/Hello.class
redefine success, size: 1
这时候去观察输出结果,神奇的事情发生了:
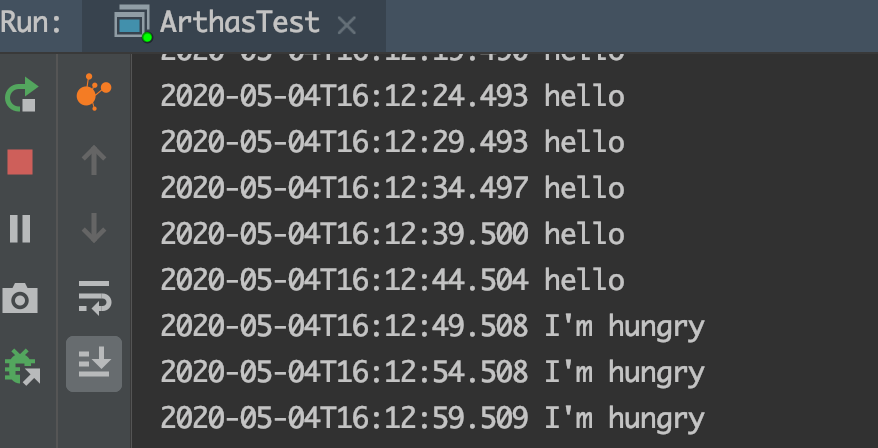
注意:直到现在,原先的程序还是一直运行的,并没有停下来。
有木有开着飞机换引擎的感觉?nubility!
其他还有很多命令,小伙伴们可以自行尝试。 不知道怎 么 用 ? 别忘了 -help。
3. 小结
本文主要介绍了 JDK 性能分析与监测的一些工具,主要包括 JDK 自带的 jps、jinfo、jstack、jmap 等,以及 很好用的阿里开源工具 Arthas。
对于这种实操类的东西,当然还是要多动手练一练咯!
本文内容就到这里,希望对大家有所帮助~

- 本文标签: 服务器 mina grep UI CTO jvisualvm ask IO JVM update cmd tar 配置 空间 开源 统计 ORM session java tab map 时间 锁 core bean Dashboard 2019 unix js cat 代码 操作系统 src 下载 javaagent 部署 classpath https 进程 GitHub 参数 lib 文章 bug CST 测试 git 线程 SDN key build ACE id tag 编译 ip Oracle IDE HTML example jstack 希望 Agent ssl tomcat description 数据 App Connection http Collection Full GC
- 版权声明: 本文为互联网转载文章,出处已在文章中说明(部分除外)。如果侵权,请联系本站长删除,谢谢。
- 本文海报: 生成海报一 生成海报二











![[HBLOG]公众号](http://www.liuhaihua.cn/img/qrcode_gzh.jpg)

