ThreadLocal 源码解析
ThreadLocal 为每个使用变得的线程保存一个副本,这样每个线程操作的就是自己的副本. 简述 : 每个 Thread 都有一个 ThreadLocalMap 的变量,当在线程中调用 ThreadLocal.set() 的时候初始化。 ThreadLocalMap 存储键值对 key = ThreadLacal value = “用户设置的变量” 。 这里的key是一个 WeakRefrences 意味着key可能被GC回收。 对应的 get() 从Thread.ThreadLocalMap从取。这里可能存在几种情况 没有值,key被GC回收了 有值。具体看下面的代码逻辑
/**
取到Thread 的threadLocals 如果 = null 初始化 将value put进去 ,
已经初始化过了 ,直接put
**/
public void set(T value) {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
// Thread.threadLocals
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value); (1)
else
// 初始化 Thead.threadLocals 这里逻辑很简单
createMap(t, value); (2)
}
//-------------------------------------------------------
//ThreadLocalmMap.set
private void set(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value) {
// We don't use a fast path as with get() because it is at
// least as common to use set() to create new entries as
// it is to replace existing ones, in which case, a fast
// path would fail more often than not.
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
// 散列取得key映射到数据的位置 i 这里 相当于
// key.threadLocalHashCode % (len) 但用位运算效率更高
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);
// 当前i位置不为空 说明 hash 碰撞了 向后线性探索 遇到e = null 停止
for (Entry e = tab[i];
e != null;
e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
if (k == key) {
//找到匹配的key
e.value = value;
return;
}
if (k == null) {
// 这key = null key别GC回收了
replaceStaleEntry(key, value, i);
return;
}
}
// 位置上没有Entry
tab[i] = new Entry(key, value);
int sz = ++size;
if (!cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) && sz >= threshold)
rehash();
}
复制代码
一个简单的图 说明 set 过程

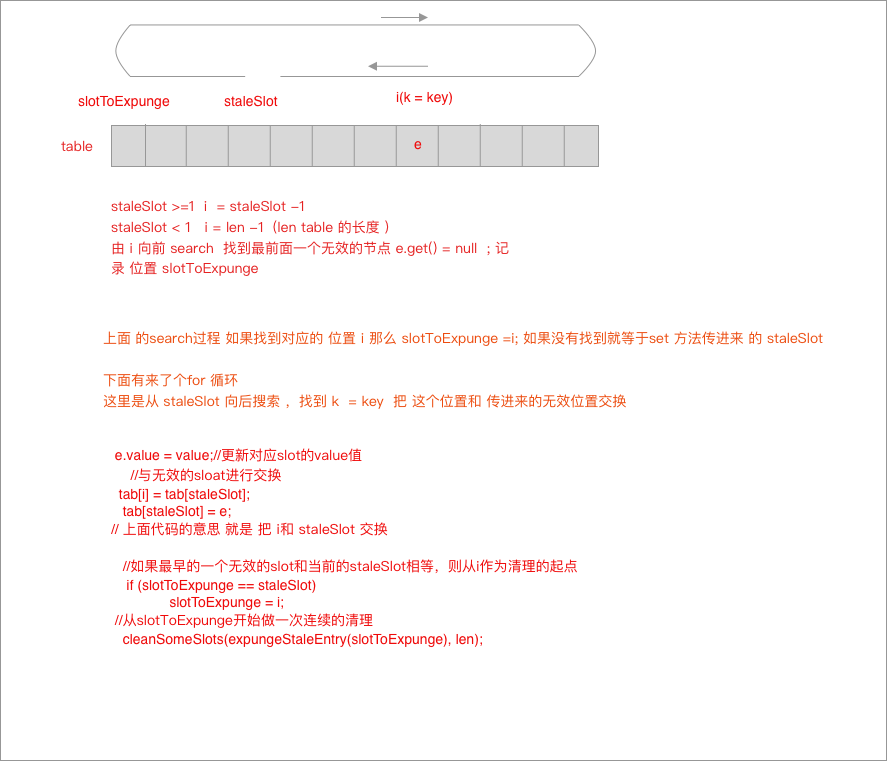
private void replaceStaleEntry(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value,
int staleSlot) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
Entry e;
//从 staleSlot 位置 向前搜索stale 节点位置 (连续空间因为这里遇到e = null 会停止 )
int slotToExpunge = staleSlot;
for (int i = prevIndex(staleSlot, len);
(e = tab[i]) != null;
i = prevIndex(i, len))
if (e.get() == null)
slotToExpunge = i;
// 向后搜索
for (int i = nextIndex(staleSlot, len);
(e = tab[i]) != null;
i = nextIndex(i, len)) {
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
// If we find key, then we need to swap it
// with the stale entry to maintain hash table order.
// The newly stale slot, or any other stale slot
// encountered above it, can then be sent to expungeStaleEntry
// to remove or rehash all of the other entries in run.
// 找到对应的key,与 stale entity 交换
if (k == key) {
e.value = value;
tab[i] = tab[staleSlot];
tab[staleSlot] = e;
// Start expunge at preceding stale entry if it exists
if (slotToExpunge == staleSlot)
slotToExpunge = i;
cleanSomeSlots(expungeStaleEntry(slotToExpunge), len);
return;
}
// If we didn't find stale entry on backward scan, the
// first stale entry seen while scanning for key is the
// first still present in the run.
if (k == null && slotToExpunge == staleSlot)
slotToExpunge = i;
}
// If key not found, put new entry in stale slot
tab[staleSlot].value = null;
tab[staleSlot] = new Entry(key, value);
// If there are any other stale entries in run, expunge them
// 清除别的 stale entity
if (slotToExpunge != staleSlot)
cleanSomeSlots(expungeStaleEntry(slotToExpunge), len);
}
复制代码
说明下 replaceStatleEntity 的流程
private boolean cleanSomeSlots(int i, int n) {
boolean removed = false;
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
do {
// i 用永远不能是一个无效的位置
i = nextIndex(i, len);
Entry e = tab[i];
if (e != null && e.get() == null) {
n = len;
removed = true;
i = expungeStaleEntry(i);
}
} while ( (n >>>= 1) != 0);
return removed;
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------
private int expungeStaleEntry(int staleSlot) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
// expunge entry at staleSlot
// 擦除staleSlot 位置的entry
tab[staleSlot].value = null;
tab[staleSlot] = null;
size--;
// Rehash until we encounter null
Entry e;
int i;
for (i = nextIndex(staleSlot, len);
(e = tab[i]) != null;
i = nextIndex(i, len)) {
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
// 从staleSlot 位置向后搜索
// key = null 擦除
// key != null rehash 如果位置变了 向后搜索找到一个空位置放
if (k == null) {
e.value = null;
tab[i] = null;
size--;
} else {
int h = k.threadLocalHashCode & (len - 1);
if (h != i) {
tab[i] = null;
// Unlike Knuth 6.4 Algorithm R, we must scan until
// null because multiple entries could have been stale.
while (tab[h] != null)
h = nextIndex(h, len);
tab[h] = e;
}
}
}
return i;
}
复制代码
remove
private void remove(ThreadLocal<?> key) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);
for (Entry e = tab[i];
e != null;
e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {
if (e.get() == key) {
// 擦除key 相同的位置
e.clear();
expungeStaleEntry(i);
return;
}
}
}
复制代码
rehash
private void rehash() {
expungeStaleEntries();
// Use lower threshold for doubling to avoid hysteresis
if (size >= threshold - threshold / 4)
resize();
}
/**
从头到尾 清除一下无效Entity
**/
private void expungeStaleEntries() {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
for (int j = 0; j < len; j++) {
Entry e = tab[j];
if (e != null && e.get() == null)
expungeStaleEntry(j);
}
}
private void resize() {
Entry[] oldTab = table;
int oldLen = oldTab.length;
int newLen = oldLen * 2;
Entry[] newTab = new Entry[newLen];
int count = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < oldLen; ++j) {
Entry e = oldTab[j];
if (e != null) {
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
if (k == null) {
e.value = null; // Help the GC
} else {
// 重新hash 找到扩容后的table 位置
int h = k.threadLocalHashCode & (newLen - 1);
while (newTab[h] != null)
h = nextIndex(h, newLen);
newTab[h] = e;
count++;
}
}
}
setThreshold(newLen);
size = count;
table = newTab;
}
复制代码
总结: 代码大概都能看懂,但是设计中为什么这么设计,为什么选择了这样的算法,我也不懂,可能是基础太差
正文到此结束
热门推荐
相关文章
Loading...











![[HBLOG]公众号](https://www.liuhaihua.cn/img/qrcode_gzh.jpg)

