HashMap 实现原理与源码分析
public class Array {
/**
* 删除 插入 慢 O(n)
* 找到下标的查找 O(1)
* java.util.ArrayList
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer[] integers = new Integer[10];
integers[0] = 0;
integers[1] = 1;
integers[2] = 2;
integers[3] = 3;
integers[4] = 4;
}
}
复制代码
数组:采用一段连续的存储单元来存储数据。对于指定下标的查找,时间复杂度为O(1); 对于一般的插入删除操作,涉及到数组元素的移动,其平均复杂度为O(n)。
2、线性链表
public class Node {
public Node next;
private Object data;
public Node(Object data){
this.data = data;
}
/**
* 新增、插入 时间复杂度O(1)
* 查找时间复杂度O(n)
* java.util.LinkedList
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node node = new Node(1);
node.next = new Node(2);
node.next.next = new Node(3);
}
}
复制代码
线性链表:对于链表的新增、删除等操作(在找到指定操作位置后),仅需要处理结点间的引用即可,时间复杂度为O(1),而查找操作需要遍历链表逐一进行比对,复杂度为O(n)。
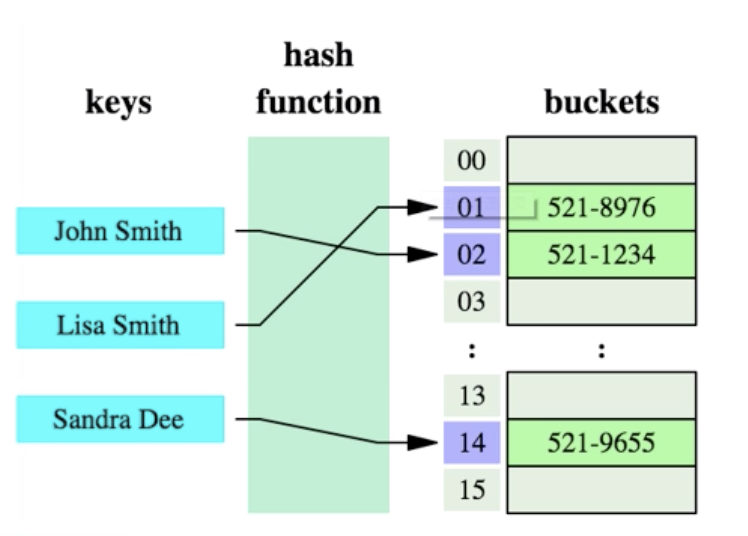
3、哈希hash
哈希算法(也叫散列),就是把任意长度值(key)通过散列算法变成固定长度的key地址,通过这个地址进行访问的数据结构。
它通过把关键码值映射到表中一个位置来访问记录,以加快查找的速度。
这个映射的函数也叫做散列函数,存放记录的数组叫做散列表。
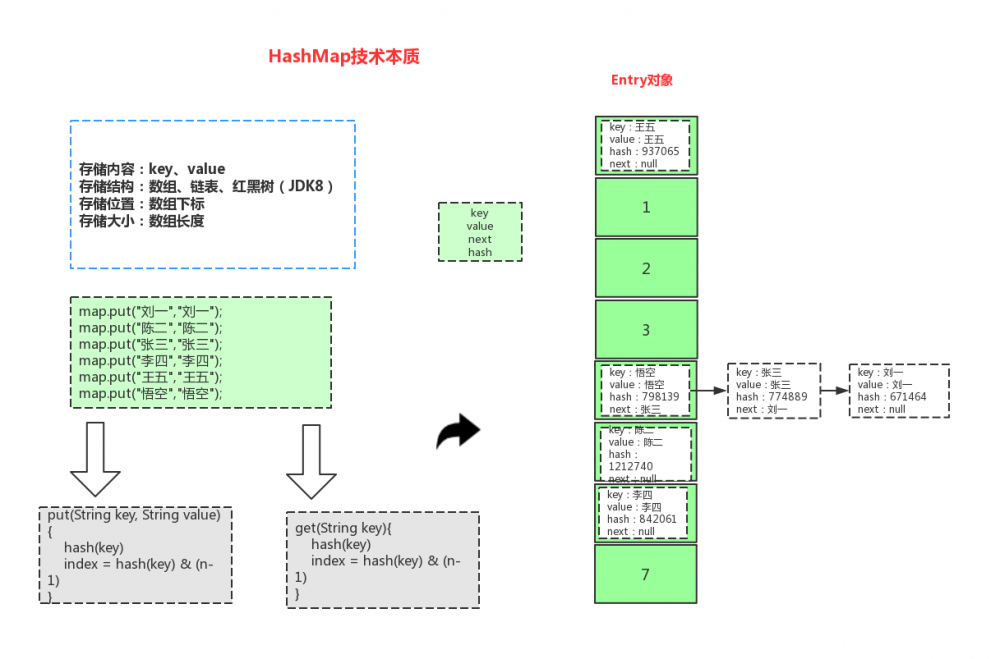
4、理解HashMap 技术本质
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Map<String,String> map = new HashMap();
App map = new App();
map.put("刘一","刘一");
map.put("陈二","陈二");
map.put("张三","张三");
map.put("李四","李四");
map.put("王五","张一");
map.put("悟空","悟空");
}
/**
* hash 算法 山寨
* @param key
* @param value
*/
public void put(String key, String value){
// HashMap默认数组长度为16
System.out.printf("key:%s,hash值:%s,存储位置:%s/r/n",key,key.hashCode(),Math.abs(key.hashCode() % 6));
}
复制代码
输出结果:
key:刘一,hash值:671464,存储位置:4 key:陈二,hash值:1212740,存储位置:5 key:张三,hash值:774889,存储位置:4 key:李四,hash值:842061,存储位置:6 key:王五,hash值:937065,存储位置:0 key:悟空,hash值:798139,存储位置:4 复制代码
分析HashMap 技术本质:
5、手写实现
定义接口:
/**
* 定义一个接口
* @param <K>
* @param <V>
*/
public interface Map<K,V> {
public V put(K k,V v);
public V get(K k);
public int size();
public interface Entry<K,V>{
public K getKey();
public V getValue();
}
}
复制代码
接口实现:
/**
* <p>
* 实现HashMap
* </p>
*
* @author: org_hejianhui@163.com
* @create: 2019-04-26 22:52
* @see HashMap
* @since JDK1.8
*/
public class HashMap<K, V> implements Map<K, V> {
private Entry<K, V>[] tables = null;
private static int defaultLengh = 16;
private int size = 0;
public HashMap() {
this.tables = new Entry[defaultLengh];
}
public V put(K k, V v) {
// hash 出来的hash值
int index = hash(k);
// 数组的长度 index 值 下标的位置
Entry entry = tables[index];
if (entry == null) {
tables[index] = new Entry<>(k, v, null, index);
size++;
} else {
tables[index] = new Entry<>(k, v, entry, index);
}
// 通过位置找到我们的table对应的Entry
return tables[index].getValue();
}
public V get(K k) {
if (size == 0)
return null;
// hash 出来的值
int index = hash(k);
Entry<K, V> entry = getEntry(k, index);
return entry == null ? null : entry.getValue();
}
public int size() {
return size;
}
class Entry<K, V> implements Map.Entry<K, V> {
private K k;
private V v;
private Entry next;
private int hash;
public Entry(K k, V v, Entry next, int hash) {
this.k = k;
this.v = v;
this.next = next;
this.hash = hash;
}
public K getKey() {
return k;
}
public V getValue() {
return v;
}
}
private int hash(K k) {
int index = k.hashCode() & (defaultLengh - 1);
return Math.abs(index);
}
private Entry<K, V> getEntry(K k, int index) {
for (Entry e = tables[index]; e != null; e = e.next) {
if (e.hash == index && (e.getKey() == k || e.getKey().equals(k))) {
return e;
}
}
return null;
}
}
复制代码
测试验证:
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Map<String,String> map = new HashMap();
//App map = new App();
com.nuih.map.Map map = new com.nuih.map.HashMap();
map.put("刘一","刘一");
map.put("陈二","陈二");
map.put("张三","张三");
map.put("李四","李四");
map.put("王五","张一");
map.put("悟空","悟空");
System.out.println(map.get("悟空"));
}
复制代码
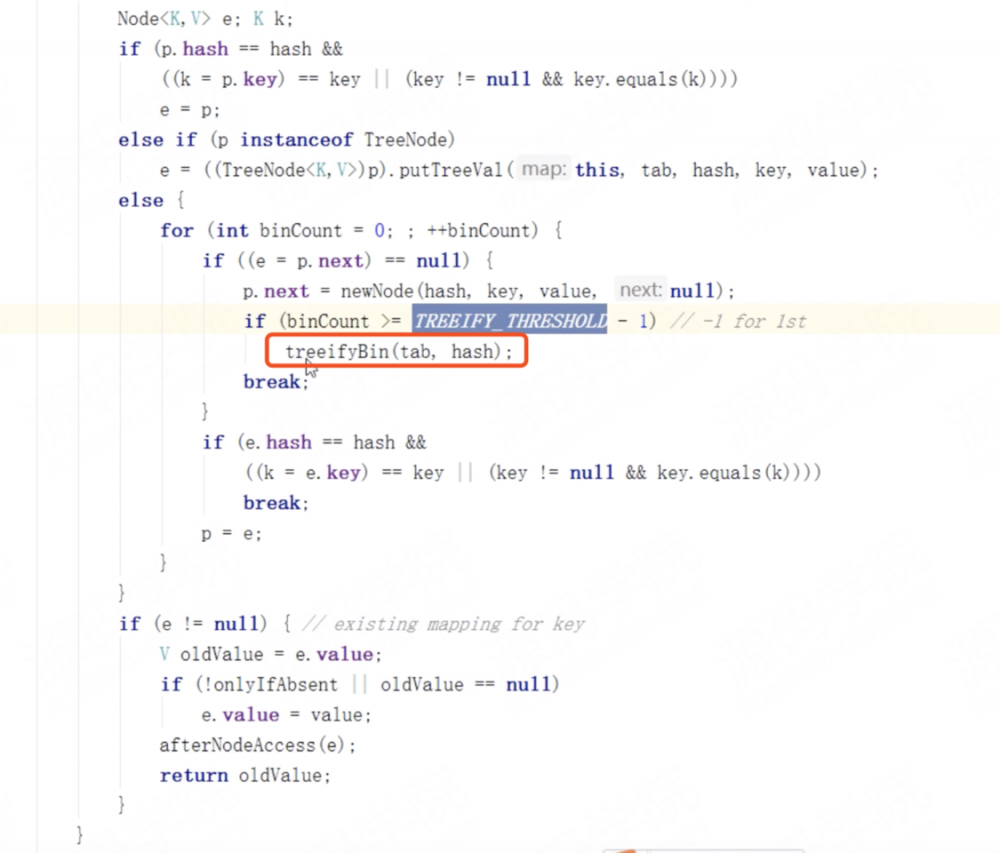
6、现在回答一下JDK8 对 HashMap 优化了哪块,为何要优化?
- 原因是因为链表过长,解决平衡性,JDK8 引入红黑树来解决链表查找的速度,但同样也带来一个问题:插入变慢,它默认有个阀值默认8才会转变成红黑树,源码如下:

正文到此结束
热门推荐
相关文章
Loading...











![[HBLOG]公众号](https://www.liuhaihua.cn/img/qrcode_gzh.jpg)

