OkHttp - CacheInterceptor源码简析
Github: okhttp 分析版本: 930d4d0
Serves requests from the cache and writes responses to the cache
HTTP 缓存
Expires (强制缓存)
Expires 的值为服务端返回的到期时间,即下一次请求时请求时间小于服务端返回的到期时间则直接使用缓存数据
Expires 是 HTTP 1.0 的产物,在 HTTP 1.1 中用 Cache-Control 替代
Cache-Control (强制缓存)
Cache-Control 的取值有 private、public、no-cache、max-age,no-store 等,默认为private
| 指令 | 意义 |
|---|---|
| private | 表明响应只能被单个用户缓存,不能作为共享缓存(即代理服务器不能缓存它) |
| public | 表明响应可以被任何对象(包括:发送请求的客户端,代理服务器,等等)缓存 |
| no-cache | 在发布缓存副本之前,强制要求缓存把请求提交给原始服务器进行验证 |
| no-store | 缓存不应存储有关客户端请求或服务器响应的任何内容 |
| max-age=
|
设置缓存存储的最大周期,超过这个时间缓存被认为过期 |
| s-maxage=
|
覆盖 max-age 或者 Expires 头,但是仅适用于共享缓存 |
| max-stale[=
|
表明客户端愿意接收一个已经过期的资源。可以设置一个可选的秒数,表示响应不能已经过时超过该给定的时间 |
| min-fresh=
|
表示客户端希望获取一个能在指定的秒数内保持其最新状态的响应 |
Last-Modified (对比缓存)
服务器在响应请求时,告诉浏览器资源的最后修改时间
If-Modified-Since (对比缓存)
再次请求服务器时,通过此字段通知服务器上次请求时间,服务器返回的资源最后修改时间,服务器收到请求后发现有头If-Modified-Since 则与被请求资源的最后修改时间进行比对
- 若资源的最后修改时间大于 If-Modified-Since ,说明资源又被改动过,则响应整片资源内容,返回状态码 200
- 若资源的最后修改时间小于或等于 If-Modified-Since ,说明资源无新修改,则响应 HTTP 304,告知浏览器继续使用所保存的 Cache
Etag (对比缓存)
服务器响应请求时,告诉浏览器当前资源在服务器的唯一标识(生成规则由服务器决定)
If-None-Match (对比缓存)
再次请求服务器时,通过此字段通知服务器客户段缓存数据的唯一标识,服务器收到请求后发现有头 If-None-Match 则与被请求资源的唯一标识进行比对
- 不同,说明资源又被改动过,则响应整片资源内容,返回状态码 200
- 相同,说明资源无新修改,则响应 HTTP 304,告知浏览器继续使用所保存的 Cache
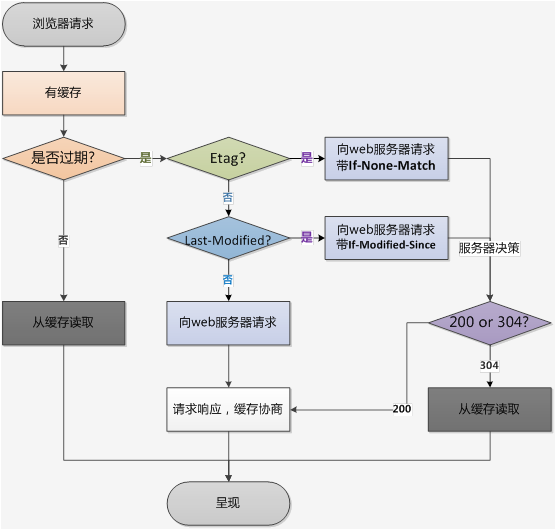
源码解析
intercept(chain: Interceptor.Chain)
class CacheInterceptor(internal val cache: InternalCache?) : Interceptor {
// ...
@Throws(IOException::class)
override fun intercept(chain: Interceptor.Chain): Response {
// 从本地获取
val cacheCandidate = cache?.get(chain.request())
val now = System.currentTimeMillis()
// 根据 response 中 header 缓存信息返回策略,判断是使用缓存还是请求网络获取新的数据
val strategy = CacheStrategy.Factory(now, chain.request(), cacheCandidate).compute()
val networkRequest = strategy.networkRequest // 若是不为 null ,表示需要进行网络请求
val cacheResponse = strategy.cacheResponse // 若是不为 null ,表示可以使用本地缓存
cache?.trackResponse(strategy)
// 缓存的 response 不适用
if (cacheCandidate != null && cacheResponse == null) {
// The cache candidate wasn't applicable. Close it.
cacheCandidate.body()?.closeQuietly()
}
// 如果不允许使用网络并且缓存为空,新建一个 504 的 Resposne 返回
// If we're forbidden from using the network and the cache is insufficient, fail.
if (networkRequest == null && cacheResponse == null) {
return Response.Builder()
.request(chain.request())
.protocol(Protocol.HTTP_1_1)
.code(HTTP_GATEWAY_TIMEOUT)
.message("Unsatisfiable Request (only-if-cached)")
.body(EMPTY_RESPONSE)
.sentRequestAtMillis(-1L)
.receivedResponseAtMillis(System.currentTimeMillis())
.build()
}
// 不需要网络访问,返回 cache response
// If we don't need the network, we're done.
if (networkRequest == null) {
return cacheResponse!!.newBuilder()
.cacheResponse(stripBody(cacheResponse))
.build()
}
// 丢给下一个拦截器
var networkResponse: Response? = null
try {
networkResponse = chain.proceed(networkRequest)
} finally {
// If we're crashing on I/O or otherwise, don't leak the cache body.
if (networkResponse == null && cacheCandidate != null) {
cacheCandidate.body()?.closeQuietly()
}
}
// 当缓存响应和网络响应同时存在的时候
// If we have a cache response too, then we're doing a conditional get.
if (cacheResponse != null) {
if (networkResponse?.code() == HTTP_NOT_MODIFIED) { // 返回 304
// 使用缓存的响应
val response = cacheResponse.newBuilder()
.headers(combine(cacheResponse.headers(), networkResponse.headers()))
.sentRequestAtMillis(networkResponse.sentRequestAtMillis())
.receivedResponseAtMillis(networkResponse.receivedResponseAtMillis())
.cacheResponse(stripBody(cacheResponse))
.networkResponse(stripBody(networkResponse))
.build()
networkResponse.body()!!.close()
// Update the cache after combining headers but before stripping the
// Content-Encoding header (as performed by initContentStream()).
cache!!.trackConditionalCacheHit()
cache.update(cacheResponse, response)
return response
} else {
cacheResponse.body()?.closeQuietly()
}
}
// 使用网络响应
val response = networkResponse!!.newBuilder()
.cacheResponse(stripBody(cacheResponse))
.networkResponse(stripBody(networkResponse))
.build()
// 缓存 response
if (cache != null) {
if (response.promisesBody() && CacheStrategy.isCacheable(response, networkRequest)) {
// Offer this request to the cache.
val cacheRequest = cache.put(response)
return cacheWritingResponse(cacheRequest, response)
}
// 只缓存GET....不然移除request
if (HttpMethod.invalidatesCache(networkRequest.method)) {
try {
cache.remove(networkRequest)
} catch (_: IOException) {
// The cache cannot be written.
}
}
}
return response
}
// ...
}
- 通过 Request 尝试到 cache 中拿缓存
- 根据 response , time , request 创建一个缓存策略,用于判断怎样使用缓存
- 如果缓存策略中设置禁止使用网络,并且缓存又为空,则构建一个 504 的 Resposne 直接返回
- 缓存策略中设置不使用网络但有缓存,直接返回缓存
- 接着走后续拦截器的流程,chain.proceed(networkRequest)
- 当缓存存在的时候,如果网络返回的 304 Resposne,则使用缓存的 Resposne
- 构建网络请求的 Response
- 将 Response 缓存起来
- 返回 Response
这里的 cache 是 InternalCache 类型
InternalCache
interface InternalCache {
@Throws(IOException::class)
fun get(request: Request): Response?
@Throws(IOException::class)
fun put(response: Response): CacheRequest?
/**
* Remove any cache entries for the supplied [request]. This is invoked when the client
* invalidates the cache, such as when making POST requests.
*/
@Throws(IOException::class)
fun remove(request: Request)
/**
* Handles a conditional request hit by updating the stored cache response with the headers from
* [network]. The cached response body is not updated. If the stored response has changed
* since [cached] was returned, this does nothing.
*/
fun update(cached: Response, network: Response)
/** Track an conditional GET that was satisfied by this cache. */
fun trackConditionalCacheHit()
/** Track an HTTP response being satisfied with [cacheStrategy]. */
fun trackResponse(cacheStrategy: CacheStrategy)
}
InternalCache 是一个接口,利用了面向接口编程的方式,接着查找哪个实现了或者说使用了这个接口,对应找到了 Cache 这个类
Cache
class Cache internal constructor(
directory: File,
maxSize: Long,
fileSystem: FileSystem
) : Closeable, Flushable {
internal val internalCache: InternalCache = object : InternalCache {
override fun get(request: Request): Response? {
return this@Cache.get(request)
}
override fun put(response: Response): CacheRequest? {
return this@Cache.put(response)
}
override fun remove(request: Request) {
this@Cache.remove(request)
}
override fun update(cached: Response, network: Response) {
this@Cache.update(cached, network)
}
override fun trackConditionalCacheHit() {
this@Cache.trackConditionalCacheHit()
}
override fun trackResponse(cacheStrategy: CacheStrategy) {
this@Cache.trackResponse(cacheStrategy)
}
}
internal val cache: DiskLruCache
/** Create a cache of at most `maxSize` bytes in `directory`. */
constructor(directory: File, maxSize: Long) : this(directory, maxSize, FileSystem.SYSTEM)
init {
this.cache = DiskLruCache.create(fileSystem, directory, VERSION, ENTRY_COUNT, maxSize)
}
// ...
}
内部现实是 DiskLruCache
CacheStrategy
CacheStrategy 是一个策略器,负责判断是使用缓存还是请求网络获取新的数据,通过工厂创建
class CacheStrategy internal constructor(
/** The request to send on the network, or null if this call doesn't use the network. */
val networkRequest: Request?,
/** The cached response to return or validate; or null if this call doesn't use a cache. */
val cacheResponse: Response?
) {
class Factory(
private val nowMillis: Long,
internal val request: Request,
private val cacheResponse: Response?
) {
/** The server's time when the cached response was served, if known. */
private var servedDate: Date? = null
private var servedDateString: String? = null
/** The last modified date of the cached response, if known. */
private var lastModified: Date? = null
private var lastModifiedString: String? = null
/**
* The expiration date of the cached response, if known. If both this field and the max age are
* set, the max age is preferred.
*/
private var expires: Date? = null
/**
* Extension header set by OkHttp specifying the timestamp when the cached HTTP request was
* first initiated.
*/
private var sentRequestMillis = 0L
/**
* Extension header set by OkHttp specifying the timestamp when the cached HTTP response was
* first received.
*/
private var receivedResponseMillis = 0L
/** Etag of the cached response. */
private var etag: String? = null
/** Age of the cached response. */
private var ageSeconds = -1
/**
* Returns true if computeFreshnessLifetime used a heuristic. If we used a heuristic to serve a
* cached response older than 24 hours, we are required to attach a warning.
*/
private fun isFreshnessLifetimeHeuristic(): Boolean {
return cacheResponse!!.cacheControl().maxAgeSeconds == -1 && expires == null
}
init {
// 在 cacheResponse 缓存不为空的请求,将头信息取出
if (cacheResponse != null) {
this.sentRequestMillis = cacheResponse.sentRequestAtMillis()
this.receivedResponseMillis = cacheResponse.receivedResponseAtMillis()
val headers = cacheResponse.headers()
for (i in 0 until headers.size) {
val fieldName = headers.name(i)
val value = headers.value(i)
when {
// Date
fieldName.equals("Date", ignoreCase = true) -> {
servedDate = HttpDate.parse(value)
servedDateString = value
}
// Expires
fieldName.equals("Expires", ignoreCase = true) -> {
expires = HttpDate.parse(value)
}
// Last-Modified
fieldName.equals("Last-Modified", ignoreCase = true) -> {
lastModified = HttpDate.parse(value)
lastModifiedString = value
}
// ETag
fieldName.equals("ETag", ignoreCase = true) -> {
etag = value
}
// Age
fieldName.equals("Age", ignoreCase = true) -> {
ageSeconds = value.toNonNegativeInt(-1)
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
在 CacheStrategy.Factory 的构造函数中
CacheStrategy.Factory#compute()
class CacheStrategy internal constructor(
/** The request to send on the network, or null if this call doesn't use the network. */
val networkRequest: Request?,
/** The cached response to return or validate; or null if this call doesn't use a cache. */
val cacheResponse: Response?
) {
class Factory(
private val nowMillis: Long,
internal val request: Request,
private val cacheResponse: Response?
) {
/** Returns a strategy to satisfy [request] using [cacheResponse]. */
fun compute(): CacheStrategy {
val candidate = computeCandidate()
// We're forbidden from using the network and the cache is insufficient.
if (candidate.networkRequest != null && request.cacheControl.onlyIfCached) {
return CacheStrategy(null, null)
}
return candidate
}
/** Returns a strategy to use assuming the request can use the network. */
private fun computeCandidate(): CacheStrategy {
// 没有缓存 Response 的话返回没有 response 的 CacheStrategy
// No cached response.
if (cacheResponse == null) {
return CacheStrategy(request, null)
}
// 若是 Https 且没有经过 handshake 的话,返回没有 response 的 CacheStrategy
// Drop the cached response if it's missing a required handshake.
if (request.isHttps && cacheResponse.handshake() == null) {
return CacheStrategy(request, null)
}
// 是否可缓存,若 cacheResponse 是不可缓存的(通过 response code 以及 cache-control 等判断),则返回没有 response 的 CacheStrategy
// If this response shouldn't have been stored, it should never be used as a response source.
// This check should be redundant as long as the persistence store is well-behaved and the
// rules are constant.
if (!isCacheable(cacheResponse, request)) {
return CacheStrategy(request, null)
}
// request 请求要求不带缓存,则返回没有 response 的 CacheStrategy
val requestCaching = request.cacheControl
if (requestCaching.noCache || hasConditions(request)) {
return CacheStrategy(request, null)
}
val responseCaching = cacheResponse.cacheControl()
val ageMillis = cacheResponseAge()
var freshMillis = computeFreshnessLifetime()
if (requestCaching.maxAgeSeconds != -1) {
freshMillis = minOf(freshMillis, SECONDS.toMillis(requestCaching.maxAgeSeconds.toLong()))
}
var minFreshMillis: Long = 0
if (requestCaching.minFreshSeconds != -1) {
minFreshMillis = SECONDS.toMillis(requestCaching.minFreshSeconds.toLong())
}
var maxStaleMillis: Long = 0
if (!responseCaching.mustRevalidate && requestCaching.maxStaleSeconds != -1) {
maxStaleMillis = SECONDS.toMillis(requestCaching.maxStaleSeconds.toLong())
}
// 满足缓存时间条件,返回没有 reqeust 的 CacheStrategy
if (!responseCaching.noCache && ageMillis + minFreshMillis < freshMillis + maxStaleMillis) {
val builder = cacheResponse.newBuilder()
if (ageMillis + minFreshMillis >= freshMillis) {
builder.addHeader("Warning", "110 HttpURLConnection /"Response is stale/"")
}
val oneDayMillis = 24 * 60 * 60 * 1000L
if (ageMillis > oneDayMillis && isFreshnessLifetimeHeuristic()) {
builder.addHeader("Warning", "113 HttpURLConnection /"Heuristic expiration/"")
}
return CacheStrategy(null, builder.build())
}
// 进行缓存 header 判断
// Find a condition to add to the request. If the condition is satisfied, the response body
// will not be transmitted.
val conditionName: String
val conditionValue: String?
when {
etag != null -> {
conditionName = "If-None-Match"
conditionValue = etag
}
lastModified != null -> {
conditionName = "If-Modified-Since"
conditionValue = lastModifiedString
}
servedDate != null -> {
conditionName = "If-Modified-Since"
conditionValue = servedDateString
}
else -> return CacheStrategy(request, null) // No condition! Make a regular request.
}
val conditionalRequestHeaders = request.headers.newBuilder()
addHeaderLenient(conditionalRequestHeaders, conditionName, conditionValue!!)
val conditionalRequest = request.newBuilder()
.headers(conditionalRequestHeaders.build())
.build()
return CacheStrategy(conditionalRequest, cacheResponse)
}
/**
* Returns true if the request contains conditions that save the server from sending a response
* that the client has locally. When a request is enqueued with its own conditions, the built-in
* response cache won't be used.
*/
private fun hasConditions(request: Request): Boolean =
request.header("If-Modified-Since") != null || request.header("If-None-Match") != null
}
companion object {
/** Returns true if `response` can be stored to later serve another request. */
fun isCacheable(response: Response, request: Request): Boolean {
// Always go to network for uncacheable response codes (RFC 7231 section 6.1), This
// implementation doesn't support caching partial content.
when (response.code()) {
HTTP_OK, // 200
HTTP_NOT_AUTHORITATIVE, // 203
HTTP_NO_CONTENT, // 204
HTTP_MULT_CHOICE, // 300
HTTP_MOVED_PERM, // 301
HTTP_NOT_FOUND, // 404
HTTP_BAD_METHOD, // 405
HTTP_GONE, // 410
HTTP_REQ_TOO_LONG, // 414
HTTP_NOT_IMPLEMENTED, // 501
StatusLine.HTTP_PERM_REDIRECT -> { // 308
// These codes can be cached unless headers forbid it.
}
HTTP_MOVED_TEMP, // 302
StatusLine.HTTP_TEMP_REDIRECT -> {
// These codes can only be cached with the right response headers.
// http://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7234#section-3
// s-maxage is not checked because OkHttp is a private cache that should ignore s-maxage.
if (response.header("Expires") == null &&
response.cacheControl().maxAgeSeconds == -1 &&
!response.cacheControl().isPublic &&
!response.cacheControl().isPrivate) {
return false
}
}
else -> {
// All other codes cannot be cached.
return false
}
}
// A 'no-store' directive on request or response prevents the response from being cached.
return !response.cacheControl().noStore && !request.cacheControl.noStore
}
}
}
isCacheable()
正文到此结束
- 本文标签: id CTO client cache tab tag 数据 parse message 服务端 https 时间 build ORM 源码 stream UI 解析 ACE 希望 git GitHub Connection constant ssl 缓存 cat HTML http IO struct NSA final Persistence 服务器 equals find App src NIO ip 2019 IDE value queue update
- 版权声明: 本文为互联网转载文章,出处已在文章中说明(部分除外)。如果侵权,请联系本站长删除,谢谢。
- 本文海报: 生成海报一 生成海报二
热门推荐
相关文章
Loading...











![[HBLOG]公众号](https://www.liuhaihua.cn/img/qrcode_gzh.jpg)

