AbstractQueuedSynchronizer AQS锁原理及ReentrantLock非公平锁的实现
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer AQS锁原理及ReentrantLock非公平锁的实现
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer是基于一个FIFO双向链队列 ==CLH队列==,用于构建锁或者同步装置的类,也称为Java同步器,ReentrantLock的公平锁与非公平锁就是由该同步器构成,链队列结构图如下。
你可以理解为银行ATM机取钱,一个人先去取,获取到了锁,在这个时间内其他线程处于阻塞状态,只有等他取完钱了,他走了,释放了锁,排在它后面的人才可以获取到释放的锁并进行取钱。
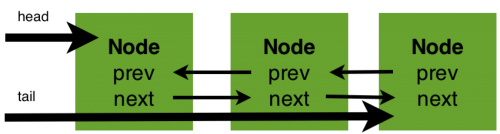
该同步器利用一个int值表示状态,实现方式是==使用内部类继承该同步器的方式==实现它的tryRelease、tryAcquire等方法管理状态,管理状态使用以下三个方法:
- getState() 获取状态
- setState() 基本设置状态
- compareAndSetSate(int,int) 基于CAS实现的原子性设置状态
AQS节点
节点包含的状态有:
- CANCELLED,值为1,表示当前的线程被取消;
- SIGNAL,值为-1,表示当前节点的后继节点包含的线程需要运行,也就是unpark;
- CONDITION,值为-2,表示当前节点在等待condition,也就是在condition队列中;
- PROPAGATE,值为-3,表示当前场景下后续的acquireShared能够得以执行;
- 值为0,表示当前节点在sync队列中,等待着获取锁。
节点其他信息:
| Node prev | 前驱节点 |
|---|---|
| Node next | 后继节点 |
| Node nextWaiter | 存储condition队列中的后继节点 |
| Thread thread | 入队列时的当前线程 |
独占锁
锁在一个时间点只能被一个线程锁占有,AQS实现的ReentrantLock,又分为公平锁和非公平锁
-
公平锁
保障了多线程下各线程获取锁的顺序,先到的线程优先获取锁
-
非公平锁
加锁时不考虑排队等待问题,直接尝试获取锁,获取不到自动到队尾等待
共享锁
锁在一个时间点可以被多个线程同时获取,AQS实现的CountDownLatch、ReadWriteLock
一、AQS实现ReentrantLock非公平锁
ReentrantLock非公平锁获取锁
1、lock()
final void lock() {
if (compareAndSetState(0, 1))
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());
else
acquire(1);
}
2、acquire()
根据指定状态获取,能获取到 执行compareAndSetState方法设置新状态
public final void acquire(int arg) {
//tryAcquire成功的话 acquire结束;
if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&
//AcquireQueued方法进行阻塞等待,直到获取锁为止
//addWaiter把当前线程添加到队列尾部
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
//tryAcquire失败并且acquiredQueued成功的话把当前线程中断
selfInterrupt();
}
- 尝试获取锁;
- 如果获取不到,将当前线程构造成节点Node并加入队列;
addWaiter方法把节点加入队列,每个线程都是一个节点Node,从而形成了一个双向队列,类似CLH队列。 - 再次尝试获取,如果没有获取到那么将当前线程从线程调度器上摘下,进入等待状态。
3、tryAcquire()
final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
//获取状态
int c = getState();
//如果该锁未被任何线程占有,该锁能被当前线程获取
if (c == 0) {
if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
//若被获取到 查看是否被当前线程
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
//是当前线程的话再次获取,计数+1
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
在tryAcquire方法中使用了同步器提供的对state操作的方法,利用CAS原理保证只有一个线程能够对状态进行成功修改,而没有成功修改的线程将进入队列排队。
4、acquireQueued()
AcquireQueued方法进行阻塞等待,直到获取锁为止
//node为null,排他方式阻塞等待
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
//p为当前节点的前一个节点
final Node p = node.predecessor();
//如果p为头结点并且获取成功就把当前线节点设置为头结点
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return interrupted;
}
//如果线程需要被阻塞 则interrputr为true
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
- 获取当前节点的前驱节点;
- 当前驱节点是头结点并且能够获取状态,代表该当前节点占有锁;
- 否则进入等待状态。
5、shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire()
判断线程是否需要阻塞
private static boolean shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(Node pred, Node node) {
int ws = pred.waitStatus;
//线程需要运行
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL)
return true;
//ws>0 处于CANCEL状态的线程
if (ws > 0) {
//把这些线程从队列中清除
do {
node.prev = pred = pred.prev;
} while (pred.waitStatus > 0);
pred.next = node;
} else {
//把等待的设置为运行状态
compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL);
}
return false;
}
- 先判断线程是否处于运行状态
- 如果处于CANCEL状态则把他们都从队列中清除
- 把当前节点下一个节点等待状态设置为准备运行
6、parkAndCheckInterrupt()
// park方法让其他线程处于等待状态
private final boolean parkAndCheckInterrupt() {
LockSupport.park(this);
return Thread.interrupted();
}
- 调用阻塞线程本地方法park
- 返回线程是否被阻塞
ReentrantLock非公平锁释放锁
1、unlock()
调用release释放一个锁
public void unlock() {
//释放一个锁
sync.release(1);
}
2、release()
释放锁
public final boolean release(int arg) {
//调用tryRelease尝试释放一个锁
if (tryRelease(arg)) {
Node h = head;
//释放成功后
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)
unparkSuccessor(h);
return true;
}
return false;
}
- 调用tryRelease方法尝试释放锁,失败返回false
- 释放成功判断头结点不为null并且状态不为等待获取锁状态
- 满足条件则唤醒线程并返回true
3、tryRelease()
尝试释放当前锁
protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {
int c = getState() - releases;
if (Thread.currentThread() != getExclusiveOwnerThread())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
boolean free = false;
if (c == 0) {
free = true;
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
}
setState(c);
return free;
}
- 释放锁必需是当前线程,如果不是当前线程抛出异常
- 如果获取锁的线程为当前线程则判断释放后的状态是否为0,即释放前为CANCEL状态,如果是,则设置独占模式线程为null,并设置状态为0,返回true。
4、unparkSuccessor()
锁释放后唤醒线程,一同竞争CPU资源
private void unparkSuccessor(Node node) {
//获取当前节点状态
int ws = node.waitStatus;
//把状态设置为等待获取锁状态
if (ws < 0)
compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, ws, 0);
//如果没有下一个节点或者下一个节点状态为CANCEL,则把它们清除
Node s = node.next;
if (s == null || s.waitStatus > 0) {
s = null;
for (Node t = tail; t != null && t != node; t = t.prev)
if (t.waitStatus <= 0)
s = t;
}
//否则调用LockSupport中unpark方法,唤醒后一个节点
if (s != null)
LockSupport.unpark(s.thread);
}
- 获取当前节点状态
- 判断如果状态<0,即不为等待获取锁状态,则把状态设置为等待获取锁状态
- 如果没有下一个节点或者下一个节点状态为CANCEL,则把它们清除
- 当当前节点下一个节点不为null时,调用LockSupport中unpark方法,唤醒后一个节点
5、unpark()
调用UNSAFE的本地方法unpark唤醒线程
public static void unpark(Thread thread) {
if (thread != null)
UNSAFE.unpark(thread);
}
二、AQS实现ReentrantLock公平锁
AQS实现ReentrantLock公平锁与非公平锁最大的区别在下面这段代码:

源码如下:
public final boolean hasQueuedPredecessors() {
// The correctness of this depends on head being initialized
// before tail and on head.next being accurate if the current
// thread is first in queue.
Node t = tail; // Read fields in reverse initialization order
Node h = head;
Node s;
return h != t &&
((s = h.next) == null || s.thread != Thread.currentThread());
}
==判断"当前线程"是不是在CLH队列的队首,来实现公平性==。
三、AQS实现的自定义锁
public class MyAQSLock implements Lock {
private final Sync sync;
public MyAQSLock() {
sync = new Sync();
}
@Override
public void lock() {
sync.acquire(1);
}
@Override
public void lockInterruptibly() throws InterruptedException {
sync.acquireInterruptibly(1);
}
@Override
public boolean tryLock() {
return sync.tryAcquire(1);
}
@Override
public boolean tryLock(long time, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
return sync.tryAcquireNanos(1,unit.toNanos(time));
}
@Override
public void unlock() {
sync.release(1);
}
@Override
public Condition newCondition() {
return sync.newCondition();
}
/**
* 把lock、unlock实现使用AQS构建为内部类
*/
private class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer{
Condition newCondition(){
return new ConditionObject();
}
@Override
protected boolean tryAcquire(int arg) {
//第一个线程进来拿到锁
int state = getState();
//用于重入锁判断
Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
if(state==0){
if(compareAndSetState(0,arg)){
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());
return true;
}
}
//重入锁判断 当前线程和独占锁线程相同,则再次获取
else if(current==getExclusiveOwnerThread()){
int next = state+arg;
if(next<0){
throw new RuntimeException();
}
setState(next);
return true;
}
return false;
}
/**
* 可重入释放锁
* @param arg
* @return
*/
@Override
protected boolean tryRelease(int arg) {
if(Thread.currentThread()!=getExclusiveOwnerThread()){
throw new RuntimeException();
}
int state = getState()-arg;
if(state==0){
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
setState(0);
return true;
}
setState(0);
return false;
}
}
}
测试(可重入锁)
public class TestAQSLock2 {
MyAQSLock myLock = new MyAQSLock();
private int value;
private int value2;
public int a(){
myLock.lock();
try {
b();
return value++;
}finally {
myLock.unlock();
}
}
public void b(){
myLock.lock();
try {
System.out.println(++value2);
}finally {
myLock.unlock();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestAQSLock2 myLock = new TestAQSLock2();
for(int i=0;i<50;i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + myLock.a());
}).start();
}
}
}











![[HBLOG]公众号](https://www.liuhaihua.cn/img/qrcode_gzh.jpg)

