Shiro 快速指南
认证
/* 收集实体+凭据 */
//Example using most common scenario of username/password pair:
UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken(username, password);
//”Remember Me” built-in:
token.setRememberMe(true);
/* 提交实体+凭据 */
Subject currentUser = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
currentUser.login(token);
/* 认证处理 */
try {
currentUser.login(token);
} catch ( UnknownAccountException uae ) { ...
} catch ( IncorrectCredentialsException ice ) { ...
} catch ( LockedAccountException lae ) { ...
} catch ( ExcessiveAttemptsException eae ) { ...
} ... catch your own ...
} catch ( AuthenticationException ae ) {
//unexpected error?
}
currentUser.logout(); //removes all identifying information and invalidates their session too.
如果login方法执行完毕且没有抛出任何异常信息,那么便认为用户认证通过。之后在应用程序任意地方调用SecurityUtils.getSubject() 都可以获取到当前认证通过的用户实例,使用subject.isAuthenticated()判断用户是否已验证都将返回true.
相反,如果login方法执行过程中抛出异常,那么将认为认证失败。Shiro有着丰富的层次鲜明的异常类来描述认证失败的原因,如代码示例。
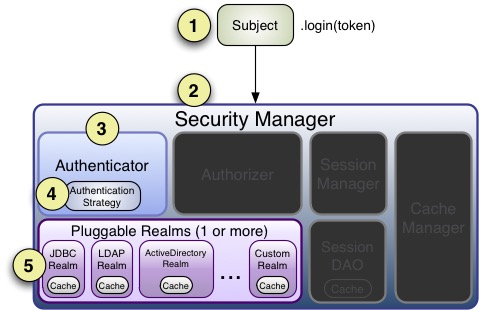
Realm将调用getAuthenticationInfo(token); getAuthenticationInfo 方法就是实际认证处理,我们通过覆盖Realm的doGetAuthenticationInfo方法来编写我们自定义的认证处理。
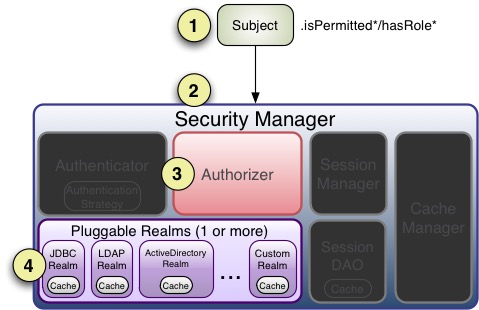
授权
/* 编程方式 */
/* 对象 */
Permission printPermission = new PrinterPermission("laserjet4400n", "print");
Subject currentUser = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
if (currentUser.isPermitted(printPermission)) {
//show the Print button
} else {
//don't show the button? Grey it out?
}
/* 字符串 */
Subject currentUser = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
if (currentUser.isPermitted("printer:print:laserjet4400n")) {
//show the Print button
} else {
//don't show the button? Grey it out?
}
/* 断言:对象 */
Subject currentUser = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
//guarantee that the current user is permitted
//to open a bank account:
Permission p = new AccountPermission("open");
currentUser.checkPermission(p);
openBankAccount();
/* 断言:字符串 */
Subject currentUser = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
//guarantee that the current user is permitted
//to open a bank account:
currentUser.checkPermission("account:open");
openBankAccount();
/* 注解方式 */
@RequiresAuthentication
public void updateAccount(Account userAccount) {
//this method will only be invoked by a
//Subject that is guaranteed authenticated
...
}
@RequiresPermissions("account:create")
public void createAccount(Account account) {
//this method will only be invoked by a Subject
//that is permitted to create an account
...
}
Realm 实现
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken authcToken) throws AuthenticationException {
UsernamePasswordToken token = (UsernamePasswordToken) authcToken;
User user = accountManager.findUserByUserName(token.getUsername());
if (user != null) {
return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(user.getUserName(), user.getPassword(), getName());
} else {
return null;
}
}
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principals) {
String userName = (String) principals.fromRealm(getName()).iterator().next();
User user = accountManager.findUserByUserName(userName);
if (user != null) {
SimpleAuthorizationInfo info = new SimpleAuthorizationInfo();
for (Group group : user.getGroupList()) {
info.addStringPermissions(group.getPermissionList());
}
return info;
} else {
return null;
}
}
Shiro 配置
<bean id="securityManager" class="org.apache.shiro.mgt.DefaultSecurityManager">
<property name="cacheManager" ref="cacheManager"/>
<property name="sessionMode" value="native"/>
<!-- Single realm app. If you have multiple realms, use the 'realms' property instead. -->
<property name="realm" ref="myRealm"/>
<property name="sessionManager" ref="sessionManager"/>
</bean>
<bean id="shiroFilter" class="org.apache.shiro.spring.web.ShiroFilterFactoryBean">
<property name="securityManager" ref="securityManager"/>
<property name="loginUrl" value="/login.jsp"/>
<property name="successUrl" value="/home.jsp"/>
<property name="unauthorizedUrl" value="/unauthorized.jsp"/> -->
<property name="filterChainDefinitions">
<value>
# some example chain definitions:
/admin/** = authc, roles[admin]
/docs/** = authc, perms[document:read]
/** = authc
# more URL-to-FilterChain definitions here
</value>
</property>
</bean>
Shiro可以通过配置文件实现基于URL的授权验证。FilterChain定义格式:
URL_Ant_Path_Expression = Path_Specific_Filter_Chain
URL表达式说明
1、URL目录是基于HttpServletRequest.getContextPath()此目录设置
2、URL可使用通配符,**代表任意子目录
3、Shiro验证URL时,URL匹配成功便不再继续匹配查找。所以要注意配置文件中的URL顺序,尤其在使用通配符时。
Filter Chain定义说明
1、一个URL可以配置多个Filter,使用逗号分隔
2、当设置多个过滤器时,全部验证通过,才视为通过
3、部分过滤器可指定参数,如perms,roles
Shiro内置的FilterChain
| Filter Name | Class |
|---|---|
| anon | org.apache.shiro.web.filter.authc.AnonymousFilter |
| authc | org.apache.shiro.web.filter.authc.FormAuthenticationFilter |
| authcBasic | org.apache.shiro.web.filter.authc.BasicHttpAuthenticationFilter |
| perms | org.apache.shiro.web.filter.authz.PermissionsAuthorizationFilter |
| port | org.apache.shiro.web.filter.authz.PortFilter |
| rest | org.apache.shiro.web.filter.authz.HttpMethodPermissionFilter |
| roles | org.apache.shiro.web.filter.authz.RolesAuthorizationFilter |
| ssl | org.apache.shiro.web.filter.authz.SslFilter |
| user | org.apache.shiro.web.filter.authc.UserFilter |
Apache Shiro 使用手册(二)Shiro 认证
正文到此结束
- 本文标签: 代码 logo example cache authenticate cat 实例 update Authorization token https NSA 参数 ORM 认证 find Document spring Word id ip IDE REST bean ssl tar App rmi http Collection servlet UI list web Property CTO 目录 src IO tab 配置 value apache Security session js
- 版权声明: 本文为互联网转载文章,出处已在文章中说明(部分除外)。如果侵权,请联系本站长删除,谢谢。
- 本文海报: 生成海报一 生成海报二
热门推荐
相关文章
Loading...










![[HBLOG]公众号](https://www.liuhaihua.cn/img/qrcode_gzh.jpg)

