高性能 Netty 之初体验
Netty 是 what? Netty 是一个异步框架 。这是一句来自官网的介绍:
Netty is an asynchronous event-driven network application framework for rapid development of maintainable high performance protocol servers & clients.
Netty 是一个具备的特点是快速开发,事件驱动,网络应用框架,用于快速开发可维护的高性能协议服务端和客户端。
我们可以来看看架构图
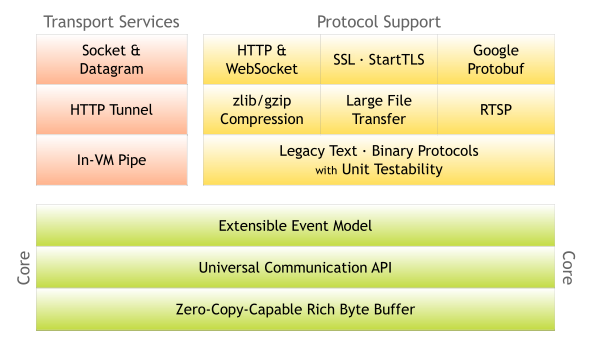
看起来很复杂。其实 Netty 在架构图分为三大块: Core , Protocol Support , Transport Services 。
Core Protocol Support Transport Services
上面是一个概图,我画了一张关于 Netty 的一些优点图。
demo 搭建
依赖
以下我们先来搭建一个简单的 demo。首先是环境的准备,可以新建一个 Spring Boot 的项目,然后在 pom.xml 里面加入依赖:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.netty</groupId>
<artifactId>netty-all</artifactId>
<version>4.1.50.Final</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
复制代码
服务端
首先是 TimeServer.java
public class TimeServer {
public void bind(int port) throws Exception {
//初始化两个 loopGroup
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
//服务端初始化的 bookstrap
ServerBootstrap s = new ServerBootstrap();
//加载两个 loopGroup
s.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 1024)
.childHandler(new ChildChannelHandler());
//异步监听端口,同步等待关闭
ChannelFuture f = s.bind(port).sync();
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}finally {
//关闭两个 loopGroup
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int port = 8080;
new TimeServer().bind(8080);
}
}
复制代码
上面的代码主要做几步
- 初始化两个
EventLoopGroup两个线程组。包含着一组NIO线程,专门用于网络事件的处理。(它们使用的Reactor模型) - 初始化服务器启动辅助配置类
ServerBootstrap,让你通过简单配置便可以启动 NIO 服务器。 - 设置
NioServerSocketChannel,对应了Java NIO的ServerSocketChannel。 - 设置
NioServerSocketChannel的TCP参数,设置backlog为 1024。 - 绑定
IO事件处理类ChildChannelHandler。
ChildChannelHandler 你可以简单粗暴理解为,这个是一个专门用于初始化子 handler 的地方,这样子的话看起来就整齐。我们仅仅需要在这里面加上需要初始化的 channelHandler 就行了。
public class ChildChannelHandler extends ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel> {
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
//获取 channel 的 pipeline,这里仅仅加进尾端
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new TimeServerHandler());
}
}
复制代码
Netty 是通过事件驱动的,所以上面的代码算是一个启动的配置文件。而 handler 是我们开发可以专注逻辑处理的地方。来看下 IO 事件的处理类 TimeServerHandler.java
public class TimeServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
//转换成对应的 ByteBuf
ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;
//设置长度
byte[] req = new byte[buf.readableBytes()];
//读取进 ByteBuf
buf.readBytes(req);
//转为字符串
String body = new String(req, "UTF-8");
System.out.println("the time server receive order : " + body);
//查看客户端命令是不是 QUERY ... ORDER
String currentTime = "QUERY TIME ORDER".equalsIgnoreCase(body)?
new java.util.Date(System.currentTimeMillis()).toString():"BAD ORDER";
//通过对currentTime 直接转为 ByteBuf
ByteBuf resp = Unpooled.copiedBuffer(currentTime.getBytes());
ctx.write(resp);
}
@Override
public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.flush();
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
ctx.close();
}
}
复制代码
上面主要实现了三个方法 channelRead , channelReadComplete , exceptionCaught 。简单说一下, channelRead 是当有链接进来的时候,Netty 会将客户端请求数据作为参数调用的; channelReadComplete 是当 channel 都读取完数据后调用的周期方法; exceptionCaught 是当 channel 调用链发生异常的时候,Netty 也会将异常封装成 Throwable 然后在调用链上传递。
客户端
客户端和服务端类似,只不过客户端对于服务端是 1:n 的关系,客户端发送请求和处理请求仅仅是需要关心自己就行了,所以只需要一个 EventLoopGroup 来处理即可。
TimeClient.java
public class TimeClient {
public void connect(int port, String host) {
// 创建客户端处理 IO 读写的 NioEventLoopGroup 线程组
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
// 创建客户端辅助启动类
Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap();
b.group(group).channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new TimeClientHandler());
}
});
//调用connect发起异步请求,调用同步方法等待成功
ChannelFuture f = b.connect(host, port).sync();
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}catch (Exception e ) {
}finally {
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int port = 8080;
new TimeClient().connect(port, "127.0.0.1");
}
}
复制代码
客户端与服务端的步骤类似,如
- 创建处理
IO读写的EventLoopGroup - 创建客户端启动配置辅助类
Bootstrap -
Bookstrap配置为NioSocketChannel.class - 添加处理
IO的处理器NioSocketChannel,并添加到ChannelPipeline。
我们来看看 TimeClientHandler 的实现逻辑。TimeClientHandler 和 TimeServerHandler 一样,仅仅是负责串行化处理从服务端返回的数据。
public class TimeClientHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
//日志记录
private static final Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(TimeClientHandler.class.getName());
private final ByteBuf firstMessage;
//实例化,赋值 firstMessage
public TimeClientHandler() {
byte[] req = "QUERY TIME ORDER".getBytes();
firstMessage = Unpooled.buffer(req.length);
firstMessage.writeBytes(req);
}
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.writeAndFlush(firstMessage);
}
//当客户端和服务端tcp链路建立成功之后,netty的nio线程会调用channelActive方法
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;
byte[] req = new byte[buf.readableBytes()];
buf.readBytes(req);
String body = new String(req, "UTF-8");
System.out.println("now is : " + body);
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
logger.warning("unexpected exception from downstream: " + cause.getMessage());
ctx.close();
}
}
复制代码
上面和 TimeServerHandler 类似,都是有 channelActive / channelRead / exceptionCaught 。我们说一下 channelRead 里面的逻辑:
- 由于服务端是写入
ByteBuf的,客户端也是转变成ByteBuf - 将
ByteBuf读取进字节数组 - 通过
String来将字典数组以UTF-8编码格式转成字符串 - 输出字符串
结尾
其实这篇文章主要是记录一些 Netty 相对于 NIO 的一些优势点/高性能的原因,以及一个最简单的 demo 是如何跑出来的。但是其实我们还有很多东西都没用上的,例如说编解码/自定义序列化/如何理解零拷贝/半包读写等等。下篇文章会继续写我们在网络经常遇到的一个拦路石 - Netty 在 TCP 粘包/拆包的问题 !
- 本文标签: stream TCP 同步 pom message Spring Boot IDE XML 服务器 DDL ORM 线程 Reactor 代码 final db IOS id 数据 实例 java core Service equals Netty 开发 node 文章 服务端 UI App spring src https 处理器 专注 API dependencies 端口 ACE IO 配置 CTO client ip Transport 模型 Bootstrap 参数 协议 http NIO cat
- 版权声明: 本文为互联网转载文章,出处已在文章中说明(部分除外)。如果侵权,请联系本站长删除,谢谢。
- 本文海报: 生成海报一 生成海报二











![[HBLOG]公众号](https://www.liuhaihua.cn/img/qrcode_gzh.jpg)

