netty极简教程(三): nio Channel意义以及FileChannel使用
上一章接单介绍了jdk nio中的容器 Buffer 的原理及使用: (netty极简教程(二): nio Buffer的原理及使用)[ www.jianshu.com/p/9a9feee60… ], 接下来我们继续聊聊jdk nio中的Channel
示例源码: github.com/jsbintask22…
Channel介绍
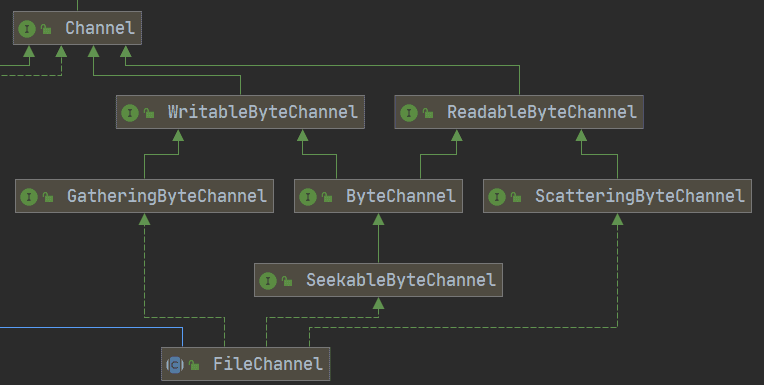
在nio中,所有channel继承自*Channel(java.nio.channels.Channel)*接口,它代表一个可以进行io操作的连接,可以是硬件设备,文件,网络等等.
我们以FileChannel为例,介绍下Channel的使用以及接口实现作用
int write(ByteBuffer src) int read(ByteBuffer dst) long write(ByteBuffer[] srcs) long read(ByteBuffer[] dsts)
FileChannel使用
写入数据
FileChannel fileChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("", "file_channel_example.txt"), // 1
StandardOpenOption.WRITE,
StandardOpenOption.READ);
String src = "hello from jsbintask.cn zh中文/n...test";
// write
ByteBuffer writeBuffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(src.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
fileChannel.write(writeBuffer); // 2
复制代码
- 通过FileChannel open方法获取代表该文件连接的channel
- 从buffer中向channel写入数据(写入到对应的文件)
这里值得注意的是,对于获取channel的步骤,改写法需要文件已经事先存在,如若文件不存在,可换另一种写法: fileChannel = new FileOutputStream("file_channel_example.txt");.getChannel(); 通过bio进行转换
读取数据
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("file_channel_example.txt");
FileChannel fileChannel = fis.getChannel();
// read
ByteBuffer readBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(100);
int length = fileChannel.read(readBuffer); // 1
// method 1
System.out.println(new String(readBuffer.array())); // 2
// method 2
readBuffer.flip();
byte[] data = new byte[length];
int index = 0;
while (readBuffer.hasRemaining()) {
data[index++] = readBuffer.get();
}
System.out.println(new String(data)); // 3
复制代码
- 将channel的数据读取都buffer
- 直接获取buffer中的字节数据打印
- 利用buffer的position指针获取有效数据然后打印
值得注意的是,这里调用了buffer的flip方法,因为上面的channel.read()方法已经移动了buffer中的指针
拷贝
有了上面的写,读 已经知道了拷贝的写法,这里我们假设分配的buffer很小,则需要分多次才能copy完成
// copy: file_1.txt => file_2.txt
FileChannel fileChannel = new FileInputStream("file_channel_example.txt").getChannel();
// write
FileChannel writeChannel = new FileOutputStream("file_channel_example_copy.txt").getChannel();
// 只分配一块很小的 缓存 分多次读
ByteBuffer readBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(3); // 1
int len = -1;
while ((len = fileChannel.read(readBuffer)) != -1) { // 2
readBuffer.flip(); // 3
writeChannel.write(readBuffer);
readBuffer.clear(); // 4
}
复制代码
零拷贝
FileChannel有一个省去中间buffer的方法,即我们所谓的 零拷贝
readChannel.transferTo(0, fis.available(), writeChannel); writeChannel.transferFrom(readChannel, fis.available(), fis.available()); 复制代码
总结
- channel的意义以及作用
- writable, readable, gatherting, Scattering 接口中新增的方法
- FileChannel的使用以及零拷贝
正文到此结束
热门推荐
相关文章
Loading...











![[HBLOG]公众号](https://www.liuhaihua.cn/img/qrcode_gzh.jpg)

