Spring Boot之ImportSelector
ImportSelector这个接口不是有了springboot之后才有的,它是在org.springframework.context.annotation这个包下,随着spring-context包3.1版本发布的时候出现的。
用法和用途
其用途比较简单,可以根据启动的相关环境配置来决定让哪些类能够被Spring容器初始化。
举个例子:
一个是事务配置相关的TransactionManagementConfigurationSelector,其实现如下:
@Override
protected String[] selectImports(AdviceMode adviceMode) {
switch (adviceMode) {
case PROXY:
return new String[] {AutoProxyRegistrar.class.getName(),
ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration.class.getName()};
case ASPECTJ:
return new String[] {determineTransactionAspectClass()};
default:
return null;
}
}
复制代码
总结下来的用法应该是这样:
- 定义一个Annotation, Annotation中定义一些属性,到时候会根据这些属性的不同返回不同的class数组。
- 在selectImports方法中,获取对应的Annotation的配置,根据不同的配置来初始化不同的class。
- 实现ImportSelector接口的对象应该是在Annotation中由@Import Annotation来引入。这也就意味着,一旦启动了注解,那么就会实例化这个对象。
实践
比如我有一个需求,要根据当前环境是测试还是生产来决定我们的日志是输出到本地还是阿里云。
假设我定义两个logger : LoggerA 和 LoggerB ,两个logger实现 Logger接口。我们再定义一个Annotation。
Annotation( @EnableMyLogger )的定义:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Import({LoggerSelector.class})
public @interface EnableMyLogger {
}
复制代码
LoggerSelector 的定义:
public class LoggerSelector implements ImportSelector {
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata) {
List<String> classNames = new ArrayList<>();
if (testEnv()) {
classNames.add(LoggerA.class.getName());
} else {
classNames.add(LoggerB.class.getName());
}
return classNames.toArray(new String[0]);
}
private boolean testEnv() {
return false;
}
}
复制代码
配置类定义:
@Configuration
@EnableMyLogger
public class SelectorConfig {
}
复制代码
测试类定义:
public class MainTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SelectorConfig.class);
System.out.println(applicationContext.getBean(Logger.class));
}
}
复制代码
测试结果:
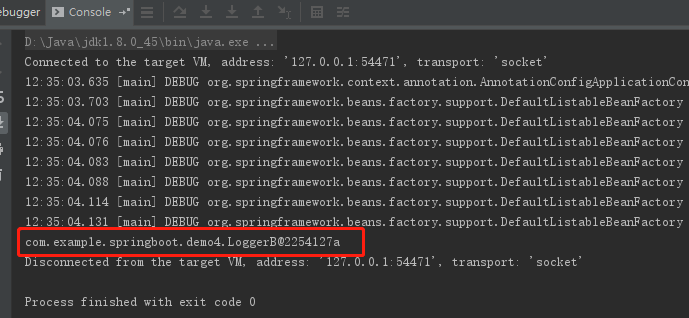
事实证明, testEnv() 方法返回值为false,确实 LoggerA 没有注入到容器, LoggerB 注入到容器。
正文到此结束
热门推荐
相关文章
Loading...











![[HBLOG]公众号](https://www.liuhaihua.cn/img/qrcode_gzh.jpg)

