ReactNative在Android上的通信机制的底层实现
com.facebook.react:react-native:0.60.4
initialization
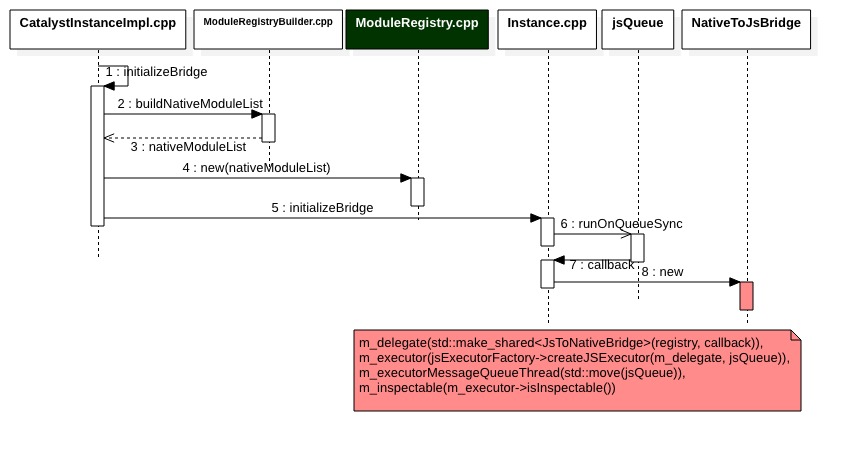
// ReactAndroid/src/main/jni/react/jni/CatalystInstanceImpl.cpp
void CatalystInstanceImpl::initializeBridge(
jni::alias_ref<ReactCallback::javaobject> callback,
// This executor is actually a factory holder.
JavaScriptExecutorHolder* jseh,
jni::alias_ref<JavaMessageQueueThread::javaobject> jsQueue,
jni::alias_ref<JavaMessageQueueThread::javaobject> nativeModulesQueue,
jni::alias_ref<jni::JCollection<JavaModuleWrapper::javaobject>::javaobject> javaModules,
jni::alias_ref<jni::JCollection<ModuleHolder::javaobject>::javaobject> cxxModules) {
// ...
moduleMessageQueue_ = std::make_shared<JMessageQueueThread>(nativeModulesQueue);
// ...
moduleRegistry_ = std::make_shared<ModuleRegistry>(
buildNativeModuleList(
std::weak_ptr<Instance>(instance_),
javaModules,
cxxModules,
moduleMessageQueue_));
instance_->initializeBridge(
std::make_unique<JInstanceCallback>(
callback,
moduleMessageQueue_),
jseh->getExecutorFactory(),
folly::make_unique<JMessageQueueThread>(jsQueue),
moduleRegistry_);
}
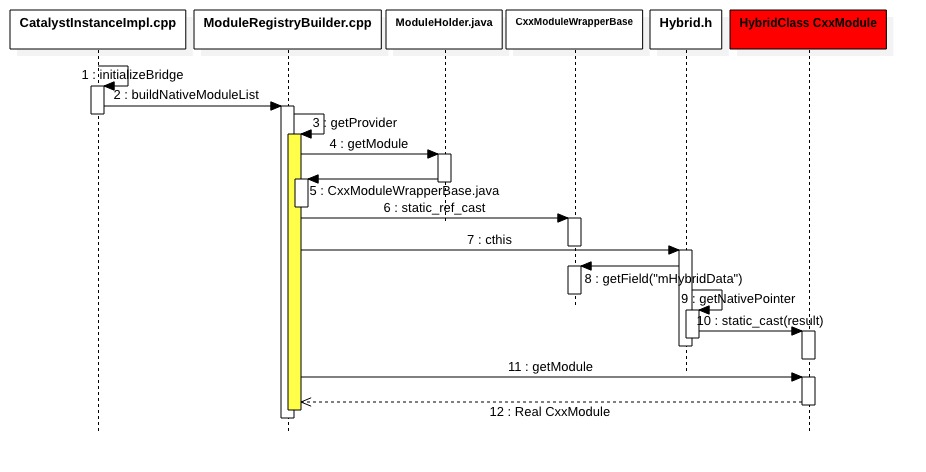
- buildNativeModuleList
- instance_->initializeBridge
创建Native模块列表
// ReactAndroid/src/main/jni/react/jni/ModuleRegistryBuilder.cpp
std::vector<std::unique_ptr<NativeModule>> buildNativeModuleList(
std::weak_ptr<Instance> winstance,
jni::alias_ref<jni::JCollection<JavaModuleWrapper::javaobject>::javaobject> javaModules,
jni::alias_ref<jni::JCollection<ModuleHolder::javaobject>::javaobject> cxxModules,
std::shared_ptr<MessageQueueThread> moduleMessageQueue) {
std::vector<std::unique_ptr<NativeModule>> modules;
if (javaModules) {
for (const auto& jm : *javaModules) {
modules.emplace_back(folly::make_unique<JavaNativeModule>(
winstance, jm, moduleMessageQueue));
}
}
if (cxxModules) {
for (const auto& cm : *cxxModules) {
modules.emplace_back(folly::make_unique<CxxNativeModule>(
winstance, cm->getName(), cm->getProvider(), moduleMessageQueue));
}
}
return modules;
}
- javaModules:JavaNativeModule
- cxxModules: CxxNativeModule
初始化Instance
// ReactCommon/cxxreact/Instance.cpp
void Instance::initializeBridge(
std::unique_ptr<InstanceCallback> callback,
std::shared_ptr<JSExecutorFactory> jsef,
std::shared_ptr<MessageQueueThread> jsQueue,
std::shared_ptr<ModuleRegistry> moduleRegistry) {
callback_ = std::move(callback);
moduleRegistry_ = std::move(moduleRegistry);
jsQueue->runOnQueueSync([this, &jsef, jsQueue]() mutable {
nativeToJsBridge_ = folly::make_unique<NativeToJsBridge>(
jsef.get(), moduleRegistry_, jsQueue, callback_);
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(m_syncMutex);
m_syncReady = true;
m_syncCV.notify_all();
});
CHECK(nativeToJsBridge_);
}
-
创建 NativeToJsBridge
-
runOnQueueSync
NativeToJsBridge创建过程
// ReactCommon/cxxreact/NativeToJsBridge.cpp
NativeToJsBridge::NativeToJsBridge(
JSExecutorFactory *jsExecutorFactory,
std::shared_ptr<ModuleRegistry> registry,
std::shared_ptr<MessageQueueThread> jsQueue,
std::shared_ptr<InstanceCallback> callback)
: m_destroyed(std::make_shared<bool>(false)),
m_delegate(std::make_shared<JsToNativeBridge>(registry, callback)),
m_executor(jsExecutorFactory->createJSExecutor(m_delegate, jsQueue)),
m_executorMessageQueueThread(std::move(jsQueue)),
m_inspectable(m_executor->isInspectable()) {}
- JsToNativeBridge:JS到Native调用的Bridge
- createJSExecutor:JS执行器,充当JSRuntime和JsToNativeBridge的桥梁。
CxxModule函数列表获取过程
ReactCommon/cxxreact/SampleCxxModule.cpp
auto SampleCxxModule::getMethods() -> std::vector<Method> {
return {
Method("hello", [this] {
sample_->hello();
}),
// ...
Method("addIfPositiveAsAsync", [](dynamic args, Callback cb, Callback cbError) {
auto a = jsArgAsDouble(args, 0);
auto b = jsArgAsDouble(args, 1);
if (a < 0 || b < 0) {
cbError({"Negative number!"});
} else {
cb({a + b});
}
}, AsyncTag),
};
}
Native 2 JS
Native对于js的调用如下图所示:

以上可以看出。上层所有的入口都是CatalystInstanceImpl的jniCallJSFunction,之后通过Instance即可到达NativeToJsBridge。
而NativeToJsBridge就是Native到JS的通信桥了,从这里所有的调用首先会在初始化时定义的jsQueue线程中运行,从而可以保证所有对JS的调用都是在同一线程中运行的。
在NativeToJsBridge中可以拿到对于JSExecutor的实现类(目前默认的是JSIExecutor),调用JSExecutor中的callFunction可以真正直达js Runtime,完成对js函数调用。如下:
// react-native/ReactCommon/jsiexecutor/jsireact/JSIExecutor.cpp
void JSIExecutor::callFunction(
const std::string &moduleId,
const std::string &methodId,
const folly::dynamic &arguments) {
// ...
if (!callFunctionReturnFlushedQueue_) {
bindBridge();
}
// ...
Value ret = Value::undefined();
try {
scopedTimeoutInvoker_(
[&] {
ret = callFunctionReturnFlushedQueue_->call(
*runtime_,
moduleId,
methodId,
valueFromDynamic(*runtime_, arguments));
},
std::move(errorProducer));
} catch (...) {
std::throw_with_nested(
std::runtime_error("Error calling " + moduleId + "." + methodId));
}
callNativeModules(ret, true);
}
这里其实是三个逻辑:
- bindBridge:即获取对js层相关对象/方法的持有,这是一个初始化的过程。
- Call JS Function:即执行callFunctionReturnFlushedQueue_函数,这里会执行到js的MessageQueue中,完成对js函数的真正执行。
- callNativeModules:上一步的结果其实是js内部缓存的对于native调用的Queue。
bindBridge
// ReactCommon/jsiexecutor/jsireact/JSIExecutor.cpp
void JSIExecutor::bindBridge() {
std::call_once(bindFlag_, [this] {
SystraceSection s("JSIExecutor::bindBridge (once)");
Value batchedBridgeValue = runtime_->global().getProperty(*runtime_, "__fbBatchedBridge");
if (batchedBridgeValue.isUndefined()) {
throw JSINativeException("Could not get BatchedBridge, make sure your bundle is packaged correctly");
}
Object batchedBridge = batchedBridgeValue.asObject(*runtime_);
callFunctionReturnFlushedQueue_ = batchedBridge.getPropertyAsFunction(*runtime_, "callFunctionReturnFlushedQueue");
invokeCallbackAndReturnFlushedQueue_ = batchedBridge.getPropertyAsFunction( *runtime_, "invokeCallbackAndReturnFlushedQueue");
flushedQueue_ = batchedBridge.getPropertyAsFunction(*runtime_, "flushedQueue");
callFunctionReturnResultAndFlushedQueue_ = batchedBridge.getPropertyAsFunction( *runtime_, "callFunctionReturnResultAndFlushedQueue");
});
}
这里并不会每次都执行,如上在每次调用之前都会校验是否初始化过,如果没有则进行初始化。
这里主要的逻辑,就是在C++层完成对js层相关对象等的持有,以便直接对js层访问。
大概持有如下对象(函数):
- flushedQueue : JS层缓存的对于Native调用的Queue。
- callFunctionReturnFlushedQueue : 调用js函数并返回flushedQueue
- invokeCallbackAndReturnFlushedQueue : 执行callback并返回flushedQueue
- callFunctionReturnResultAndFlushedQueue : 调用js函数并返回执行结果以及flushedQueue
这里我们只关注callFunctionReturnFlushedQueue即可。如下:
MessageQueue
这里是callFunctionReturnFlushedQueue在js层的实现:
// Libraries/BatchedBridge/MessageQueue.js
callFunctionReturnFlushedQueue(module: string, method: string, args: any[]) {
this.__guard(() => {
this.__callFunction(module, method, args);
});
return this.flushedQueue();
}
__callFunction(module: string, method: string, args: any[]): any {
// ...
const moduleMethods = this.getCallableModule(module);
// ...
const result = moduleMethods[method].apply(moduleMethods, args);
Systrace.endEvent();
return result;
}
通过module可以拿到这个模块对应的函数列表,并通过函数名找到目标函数并配合参数执行js代码即可。
callNativeMethod
callNativeMethod是JsToNativeBridge内部的实现,最终会进入ModuleRegistry.cpp调用对应method,这就是js到native层的通信了。
为什么会有这种操作?其实RN中所有的事件都是异步的,js层到native的通信依赖与多种异步的触发点。比如这里说的native调用js时会触发调用js到native的缓存事件。
JS 2 Native
- 加载js代码
- js代码初始化
- js调用NativeMothod过程
- 执行flushedQueue
加载js代码: runJSBundle
CatalystInstanceImpl对象build之后紧接着执行runJSBundle()用于加载JS代码。最终通过JSBunlderLoader会走到如下三个jni函数:
// ReactAndroid/src/main/java/com/facebook/react/bridge/CatalystInstanceImpl.java private native void jniLoadScriptFromAssets(AssetManager assetManager, String assetURL, boolean loadSynchronously); private native void jniLoadScriptFromFile(String fileName, String sourceURL, boolean loadSynchronously); private native void jniLoadScriptFromDeltaBundle(String sourceURL, NativeDeltaClient deltaClient, boolean loadSynchronously);
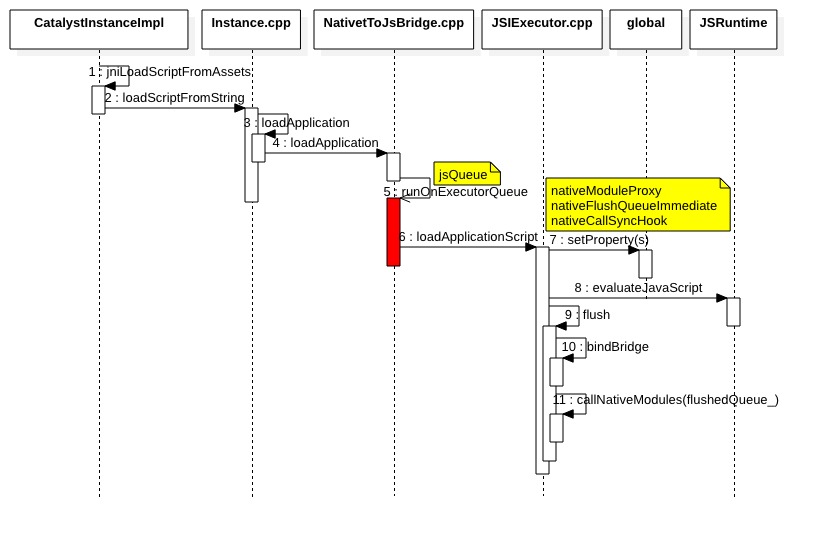
Java层的CatalystInstanceImpl在调用jniLoadScriptFromAssets时最终会进到CatalystInstanceImpl.cpp对应的函数中,如上图。
之后调用到Instance的loadApplication中,如下:
// ReactCommon/cxxreact/Instance.cpp
void Instance::loadScriptFromString(std::unique_ptr<const JSBigString> string,
std::string sourceURL,
bool loadSynchronously) {
if (loadSynchronously) {
loadApplicationSync(nullptr, std::move(string), std::move(sourceURL));
} else {
loadApplication(nullptr, std::move(string), std::move(sourceURL));
}
}
void Instance::loadApplication(std::unique_ptr<RAMBundleRegistry> bundleRegistry,
std::unique_ptr<const JSBigString> string,
std::string sourceURL) {
callback_->incrementPendingJSCalls();
nativeToJsBridge_->loadApplication(std::move(bundleRegistry), std::move(string),std::move(sourceURL));
}
此时会首先调用incrementPendingJSCalls,这时java层的ReactCallback会收到对应回调。接着还是会进入万能的NativeToJsBridge里:
// ReactCommon/cxxreact/NativeToJsBridge.cpp
void NativeToJsBridge::loadApplication(
std::unique_ptr<RAMBundleRegistry> bundleRegistry,
std::unique_ptr<const JSBigString> startupScript,
std::string startupScriptSourceURL) {
runOnExecutorQueue(
[this,
bundleRegistryWrap=folly::makeMoveWrapper(std::move(bundleRegistry)),
startupScript=folly::makeMoveWrapper(std::move(startupScript)),
startupScriptSourceURL=std::move(startupScriptSourceURL)]
(JSExecutor* executor) mutable {
auto bundleRegistry = bundleRegistryWrap.move();
if (bundleRegistry) {
executor->setBundleRegistry(std::move(bundleRegistry));
}
try {
executor->loadApplicationScript(std::move(*startupScript),
std::move(startupScriptSourceURL));
} catch (...) {
m_applicationScriptHasFailure = true;
throw;
}
});
}
同样的,所有对于js层的调用会都在jsQueue中执行,确保所有调用在同一线程运行。之后调用JSExecutor的loadApplicationScript真正加载js代码。
下面看看具体加载过程:
// ReactCommon/jsiexecutor/jsireact/JSIExecutor.cpp
void JSIExecutor::loadApplicationScript(
std::unique_ptr<const JSBigString> script,
std::string sourceURL) {
// ...
runtime_->global().setProperty(
*runtime_,
"nativeModuleProxy",
Object::createFromHostObject(
*runtime_, std::make_shared<NativeModuleProxy>(*this)));
runtime_->global().setProperty(
*runtime_,
"nativeFlushQueueImmediate",
Function::createFromHostFunction(
*runtime_,
PropNameID::forAscii(*runtime_, "nativeFlushQueueImmediate"),
1,
[this](
jsi::Runtime &,
const jsi::Value &,
const jsi::Value *args,
size_t count) {
if (count != 1) {
throw std::invalid_argument(
"nativeFlushQueueImmediate arg count must be 1");
}
callNativeModules(args[0], false);
return Value::undefined();
}));
runtime_->global().setProperty(
*runtime_,
"nativeCallSyncHook",
Function::createFromHostFunction(
*runtime_,
PropNameID::forAscii(*runtime_, "nativeCallSyncHook"),
1,
[this](
jsi::Runtime &,
const jsi::Value &,
const jsi::Value *args,
size_t count) { return nativeCallSyncHook(args, count); }));
// ...
if (runtimeInstaller_) {
runtimeInstaller_(*runtime_);
}
// ...
runtime_->evaluateJavaScript(std::make_unique<BigStringBuffer>(std::move(script)), sourceURL);
flush();
// ...
}
首先,这里实际上会在js runtime中注册global的回调。如:
- nativeCallSyncHook :用于同步调用NativeMethod
- nativeFlushQueueImmediate : 用于原本准备异步调用但是因等待过久而进行主动调用NativeMethod。
前者直接执行JSIExecutor的 nativeCallSyncHook ,后者对应的是 callNativeModules 。
其次,js runtime中进行evaluateJavaScript,对js代码进行载入。
最后,调用flush()。这里实际上是将缓存的native call拿出来执行。
下面先看一下js的初始化过程:
js代码初始化

初始化时通过读取全局的remoteModuleConfig,获取当前支持的NativeModule。
之后通过loadModule函数,完成对Module的读取。注意,由上图可知这一步并不立即发生,而是lazy的方式。在这过程中,会读取module所包含的所有的Method并加入到缓存,如下:
// Libraries/BatchedBridge/NativeModules.js
function loadModule(name: string, moduleID: number): ?Object {
// ...
const config = global.nativeRequireModuleConfig(name);
const info = genModule(config, moduleID);
return info && info.module;
}
function genModule(
config: ?ModuleConfig,
moduleID: number,
): ?{name: string, module?: Object} {
if (!config) {
return null;
}
const [moduleName, constants, methods, promiseMethods, syncMethods] = config;
// ...
if (!constants && !methods) {
// Module contents will be filled in lazily later
return {name: moduleName};
}
const module = {};
methods && methods.forEach((methodName, methodID) => {
const isPromise = promiseMethods && arrayContains(promiseMethods, methodID);
const isSync = syncMethods && arrayContains(syncMethods, methodID);
// ...
const methodType = isPromise ? 'promise' : isSync ? 'sync' : 'async';
module[methodName] = genMethod(moduleID, methodID, methodType);
});
Object.assign(module, constants);
if (module.getConstants == null) {
module.getConstants = () => constants || Object.freeze({});
}
// ...
return {name: moduleName, module};
}
可以看到 genModule 中会遍历config中的所有声明的函数信息,根据函数名 映射由 模块ID/函数ID/函数类型 生成的函数结构。函数生成过程如下:
// Libraries/BatchedBridge/NativeModules.js
function genMethod(moduleID: number, methodID: number, type: MethodType) {
let fn = null;
if (type === 'promise') {
fn = function(...args: Array<any>) {
// In case we reject, capture a useful stack trace here.
const enqueueingFrameError: ExtendedError = new Error();
enqueueingFrameError.framesToPop = 1;
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
BatchedBridge.enqueueNativeCall(
moduleID,
methodID,
args,
data => resolve(data),
errorData =>
reject(updateErrorWithErrorData(errorData, enqueueingFrameError)),
);
});
};
} else {
fn = function(...args: Array<any>) {
const lastArg = args.length > 0 ? args[args.length - 1] : null;
const secondLastArg = args.length > 1 ? args[args.length - 2] : null;
const hasSuccessCallback = typeof lastArg === 'function';
const hasErrorCallback = typeof secondLastArg === 'function';
hasErrorCallback &&
invariant(
hasSuccessCallback,
'Cannot have a non-function arg after a function arg.',
);
const onSuccess = hasSuccessCallback ? lastArg : null;
const onFail = hasErrorCallback ? secondLastArg : null;
const callbackCount = hasSuccessCallback + hasErrorCallback;
args = args.slice(0, args.length - callbackCount);
if (type === 'sync') {
return BatchedBridge.callNativeSyncHook(
moduleID,
methodID,
args,
onFail,
onSuccess,
);
} else {
BatchedBridge.enqueueNativeCall(
moduleID,
methodID,
args,
onFail,
onSuccess,
);
}
};
}
fn.type = type;
return fn;
}
由上可知,如果时同步方式那么直接调用BatchedBridge.callNativeSyncHook,这里对应的是上面的nativeCallSyncHook。
否则默认都是BatchedBridge.enqueueNativeCall,即异步方式,如下:
js调用NativeMothod过程
enqueueNativeCall是异步调用native method的入口,流程如下:
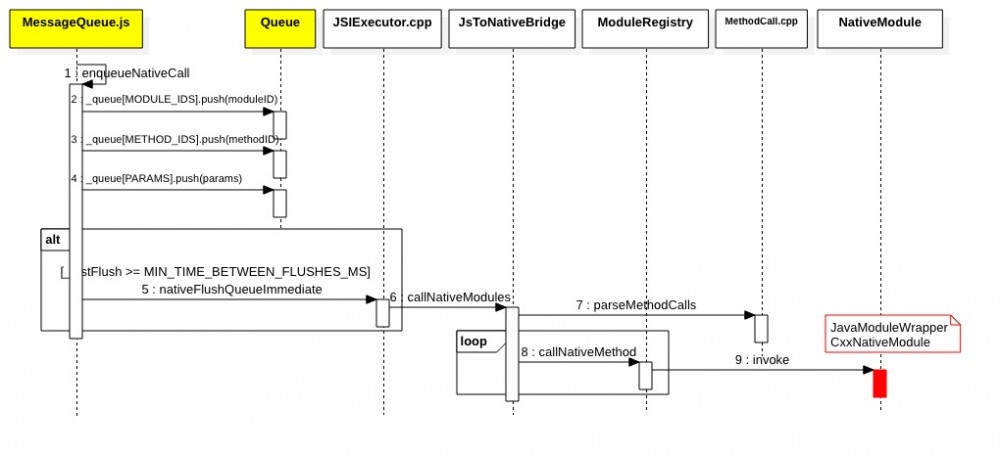
// Libraries/BatchedBridge/MessageQueue.js
enqueueNativeCall(
moduleID: number,
methodID: number,
params: any[],
onFail: ?Function,
onSucc: ?Function,
) {
this.processCallbacks(moduleID, methodID, params, onFail, onSucc);
this._queue[MODULE_IDS].push(moduleID);
this._queue[METHOD_IDS].push(methodID);
// ...
this._queue[PARAMS].push(params);
const now = Date.now();
if (
global.nativeFlushQueueImmediate &&
now - this._lastFlush >= MIN_TIME_BETWEEN_FLUSHES_MS
) {
const queue = this._queue;
this._queue = [[], [], [], this._callID];
this._lastFlush = now;
global.nativeFlushQueueImmediate(queue);
}
// ...
}
- 加入_queue,对应的是flushedQueue
- 如果_lastFlush >= MIN_TIME_BETWEEN_FLUSHES_MS:nativeFlushQueueImmediate。这是一个来自C++层的函数,最终调用到JSExecutor的
callNativeModules执行native模块,如图步骤5所示。具体callNativeModules的实现,后面再说。
如果_lastFlush没有超过对应时间(MIN_TIME_BETWEEN_FLUSHES_MS),那么就会静静等待被临幸。
临幸flushedQueue
来自JS的调用大概会有如下三种被临幸的方式:
- flush() -> flushedQueue_
flush()在加载js bundle之后会直接被调用到,由上层runJSBundle()触发,直接获取flushedQueue_一一执行。
- callFunction() -> callFunctionReturnFlushedQueue_
callFunction()来自jniCallJsFunction(),即来自native对js函数的调用。即先执行js的funcation之后返回flushedQueue_。
- invokeCallback() -> invokeCallbackAndReturnFlushedQueue_
invokeCallback()来自native层对js callback的调用(来自JavaMethodWrapper.java,即Native被js调用时注册了的Callback),同上面类似都是native to js。之后返回flushedQueue_等触发js对native的调用。
上面三个函数最后都通过拿到的flushedQueue_,跑到callNativeModules完成对native的调用。
下面是对应上面三个变量对应的js实现:
// Libraries/BatchedBridge/MessageQueue.js
callFunctionReturnFlushedQueue(module: string, method: string, args: any[]) {
this.__guard(() => {
this.__callFunction(module, method, args);
});
return this.flushedQueue();
}
callFunctionReturnResultAndFlushedQueue(
module: string,
method: string,
args: any[],
) {
let result;
this.__guard(() => {
result = this.__callFunction(module, method, args);
});
return [result, this.flushedQueue()];
}
invokeCallbackAndReturnFlushedQueue(cbID: number, args: any[]) {
this.__guard(() => {
this.__invokeCallback(cbID, args);
});
return this.flushedQueue();
}
flushedQueue() {
this.__guard(() => {
this.__callImmediates();
});
const queue = this._queue;
this._queue = [[], [], [], this._callID];
return queue[0].length ? queue : null;
}
JS 对 Native的调用到这里就结束了。下面再来看看JSI调用Native的具体方式。
JSI到Native
异步调用Native函数:callNativeModules
由上面可知,最终js调用native会在callNativeModules实现,大概过程如上如示。下面看看具体代码:
// ReactCommon/jsiexecutor/jsireact/JSIExecutor.cpp
void JSIExecutor::callNativeModules(const Value &queue, bool isEndOfBatch) {
delegate_->callNativeModules(
*this, dynamicFromValue(*runtime_, queue), isEndOfBatch);
}
这里的delegate就是JsToNativeBridge(这个类在NativeToJsBridge.cpp内部,一不小心就混淆了)。其内部的callNativeModules实现如下:
// ReactCommon/cxxreact/NativeToJsBridge.cpp
class JsToNativeBridge : public react::ExecutorDelegate {
void callNativeModules(
__unused JSExecutor& executor, folly::dynamic&& calls, bool isEndOfBatch) override {
m_batchHadNativeModuleCalls = m_batchHadNativeModuleCalls || !calls.empty();
for (auto& call : parseMethodCalls(std::move(calls))) {
m_registry->callNativeMethod(call.moduleId, call.methodId, std::move(call.arguments), call.callId);
}
if (isEndOfBatch) {
if (m_batchHadNativeModuleCalls) {
m_callback->onBatchComplete();
m_batchHadNativeModuleCalls = false;
}
m_callback->decrementPendingJSCalls();
}
}
}
这里会将MessageQueue.js中的flushQueue解析成一个由MethodCall组成的向量。之后遍历这个向量,对单个MethodCall一个一个调用。解析过程如下:
解析js参数: parseMethodCalls
// ReactCommon/cxxreact/MethodCall.cpp
std::vector<MethodCall> parseMethodCalls(folly::dynamic&& jsonData) {
// ...
auto& moduleIds = jsonData[REQUEST_MODULE_IDS];
auto& methodIds = jsonData[REQUEST_METHOD_IDS];
auto& params = jsonData[REQUEST_PARAMSS];
int callId = -1;
// ...
if (jsonData.size() > REQUEST_CALLID) {
callId = (int)jsonData[REQUEST_CALLID].asInt();
}
std::vector<MethodCall> methodCalls;
for (size_t i = 0; i < moduleIds.size(); i++) {
// ...
methodCalls.emplace_back(
moduleIds[i].asInt(),
methodIds[i].asInt(),
std::move(params[i]),
callId);
callId += (callId != -1) ? 1 : 0;
}
return methodCalls;
}
函数调用参数是以json数据进行封装的,模块/函数/参数等分别在对应的json字段中作为单独的数组存在。
模块仓库:ModuleRegistry
// ReactCommon/cxxreact/ModuleRegistry.cpp
void ModuleRegistry::callNativeMethod(unsigned int moduleId, unsigned int methodId, folly::dynamic&& params, int callId) {
if (moduleId >= modules_.size()) {
throw std::runtime_error(
folly::to<std::string>("moduleId ", moduleId, " out of range [0..", modules_.size(), ")"));
}
modules_[moduleId]->invoke(methodId, std::move(params), callId);
}
这里的modules_在CatalystInstanceImpl初始化时生成,所有的NativeModule(包括JavaModule和CxxModule)共享相同的模块命名(因此写Native模块时需要主要命名)。
这里所做的事就是通过moduleId找到对应模块,并且给相应模块传递所需要的函数id以及参数等。
下面分别介绍一下java和Cxx模块是如何被调用的。
- 执行Java模块
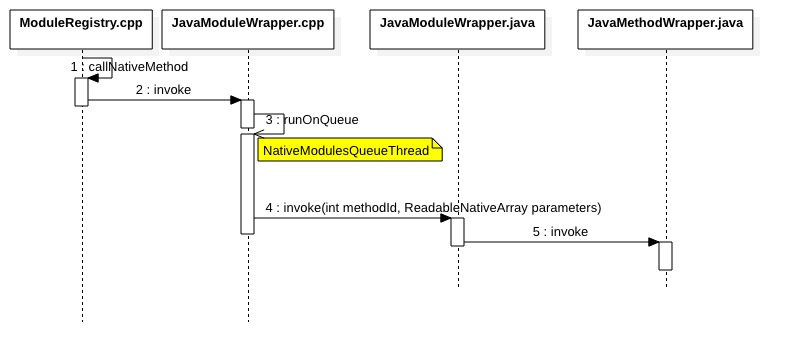
void JavaNativeModule::invoke(unsigned int reactMethodId, folly::dynamic&& params, int callId) {
messageQueueThread_->runOnQueue([this, reactMethodId, params=std::move(params), callId] {
static auto invokeMethod = wrapper_->getClass()->getMethod<void(jint, ReadableNativeArray::javaobject)>("invoke");
#ifdef WITH_FBSYSTRACE
if (callId != -1) {
fbsystrace_end_async_flow(TRACE_TAG_REACT_APPS, "native", callId);
}
#endif
invokeMethod(
wrapper_,
static_cast<jint>(reactMethodId),
ReadableNativeArray::newObjectCxxArgs(std::move(params)).get());
});
}
- 执行Cxx模块

// ReactCommon/cxxreact/CxxNativeModule.cpp
void CxxNativeModule::invoke(unsigned int reactMethodId, folly::dynamic&& params, int callId) {
// ...
CxxModule::Callback first;
CxxModule::Callback second;
const auto& method = methods_[reactMethodId];
// ...
if (method.callbacks == 1) {
first = convertCallback(makeCallback(instance_, params[params.size() - 1]));
} else if (method.callbacks == 2) {
first = convertCallback(makeCallback(instance_, params[params.size() - 2]));
second = convertCallback(makeCallback(instance_, params[params.size() - 1]));
}
params.resize(params.size() - method.callbacks);
messageQueueThread_->runOnQueue([method, params=std::move(params), first, second, callId] () {
#ifdef WITH_FBSYSTRACE
if (callId != -1) {
fbsystrace_end_async_flow(TRACE_TAG_REACT_APPS, "native", callId);
}
#else
(void)(callId);
#endif
SystraceSection s(method.name.c_str());
try {
method.func(std::move(params), first, second);
}
// ....
});
}
同步调用Native函数:nativeCallSyncHook
// ReactCommon/cxxreact/NativeToJsBridge.cpp
MethodCallResult callSerializableNativeHook(
__unused JSExecutor& executor, unsigned int moduleId, unsigned int methodId,
folly::dynamic&& args) override {
return m_registry->callSerializableNativeHook(moduleId, methodId, std::move(args));
}
// ReactCommon/cxxreact/ModuleRegistry.cpp
MethodCallResult ModuleRegistry::callSerializableNativeHook(unsigned int moduleId, unsigned int methodId, folly::dynamic&& params) {
if (moduleId >= modules_.size()) {
throw std::runtime_error(
folly::to<std::string>("moduleId ", moduleId, "out of range [0..", modules_.size(), ")"));
}
return modules_[moduleId]->callSerializableNativeHook(methodId, std::move(params));
}
// ReactCommon/cxxreact/CxxNativeModule.cpp
MethodCallResult CxxNativeModule::callSerializableNativeHook(unsigned int hookId, folly::dynamic&& args) {
if (hookId >= methods_.size()) {
throw std::invalid_argument(
folly::to<std::string>("methodId ", hookId, " out of range [0..", methods_.size(), "]"));
}
const auto& method = methods_[hookId];
if (!method.syncFunc) {
throw std::runtime_error(
folly::to<std::string>("Method ", method.name,
" is asynchronous but invoked synchronously"));
}
return method.syncFunc(std::move(args));
}
// ReactCommon/cxxreact/MethodCall.cppBy@hyongbai 共23741个字
本文链接
- 本文标签: message ip Collection IDE parse lib java Property tar 缓存 CTO 参数 ACE db IO 数据 遍历 client JavaScript Proxy 时间 list strace remote executor UI 2019 解析 build queue js Lua 代码 value http tab ORM cat tag Android 同步 producer https id Facebook json src update constant 线程 zab App provider
- 版权声明: 本文为互联网转载文章,出处已在文章中说明(部分除外)。如果侵权,请联系本站长删除,谢谢。
- 本文海报: 生成海报一 生成海报二










![[HBLOG]公众号](https://www.liuhaihua.cn/img/qrcode_gzh.jpg)

