ActionCable 源码阅读笔记-前端部分-2
本节将会阐述 ActionCable 浏览器端是如何建立连接、以及收发消息的。
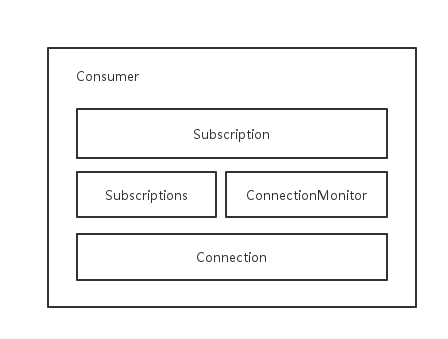
Cable.Consumer
Cable.Consumer 维护了下面三个类的实例对象
1、 Cable.Subscriptions
维护多个 subscription,是消息的发布者和消费者。
2、 Cable.Connection
维护与服务端的连接,给 subscription 提供基础的服务。
3、 Cable.ConnectionMonitor
用来监控连接的健康状态。
具体源码如下
class Cable.Consumer constructor: (@url) -> @subscriptions = new Cable.Subscriptions this @connection = new Cable.Connection this @connectionMonitor = new Cable.ConnectionMonitor this send: (data) -> @connection.send(data) inspect: -> JSON.stringify(this, null, 2) toJSON: -> {@url, @subscriptions, @connection, @connectionMonitor}
架构
建立 WebSocket 连接
创建一个 Connection 实例
new Cable.Connection(this)
调用构造方法
constructor: (@consumer) -> @open()
打开 WebSocket 连接
open: => if @webSocket and not @isState('closed') throw new Error('Existing connection must be closed before opening') else @webSocket = new WebSocket(@consumer.url) @installEventHandlers() true
注册事件处理器
installEventHandlers: -> for eventName of @events handler = @events[eventName].bind(this) @webSocket["on#{eventName}"] = handler return
我们来看看 @events 究竟是哪些
events: message: (event) -> {identifier, message, type} = JSON.parse(event.data) switch type when message_types.confirmation @consumer.subscriptions.notify(identifier, "connected") when message_types.rejection @consumer.subscriptions.reject(identifier) else @consumer.subscriptions.notify(identifier, "received", message) open: -> @disconnected = false @consumer.subscriptions.reload() close: -> @disconnect() error: -> @disconnect()
从上面的源码可以看到,最后 @webSocket 注册的事件回调有
onmessage onopen onclose onerror
这些回调,本身就是浏览器 WebSocket 实例对象所提供的, 可以从这里查询到 。
发送消息
从上一篇的例子可以知道,通过 @perform('appear', { message: "Hello, John" }) 可以发送消息到服务器并调用服务器相应的 AppearanceChannel 类的实例对象的 appear 方法。
所以我们来看看 Cable.Subscription 相关的函数体
perform: (action, data = {}) -> data.action = action @send(data) send: (data) -> @consumer.send(command: "message", identifier: @identifier, data: JSON.stringify(data))
继续看 Cable.Consumer 里的 send 函数体
send: (data) -> @connection.send(data)
所以它是通过 Cable.Connection 的实例对象 @connection 来发送数据的
send: (data) -> if @isOpen() @webSocket.send(JSON.stringify(data)) true else false
到此已经结束,通过浏览器 WebSocket 实例对象的 send 方法来发送消息到服务端。
正文到此结束
热门推荐
相关文章
Loading...











![[HBLOG]公众号](http://www.liuhaihua.cn/img/qrcode_gzh.jpg)

