深入了解Netty【六】Netty工作原理

引言
前面学习了NIO与零拷贝、IO多路复用模型、Reactor主从模型。
服务器基于IO模型管理连接,获取输入数据,又基于线程模型,处理请求。
下面来学习Netty的具体应用。
1、Netty线程模型
Netty线程模型是建立在Reactor主从模式的基础上,主从 Rreactor 多线程模型:
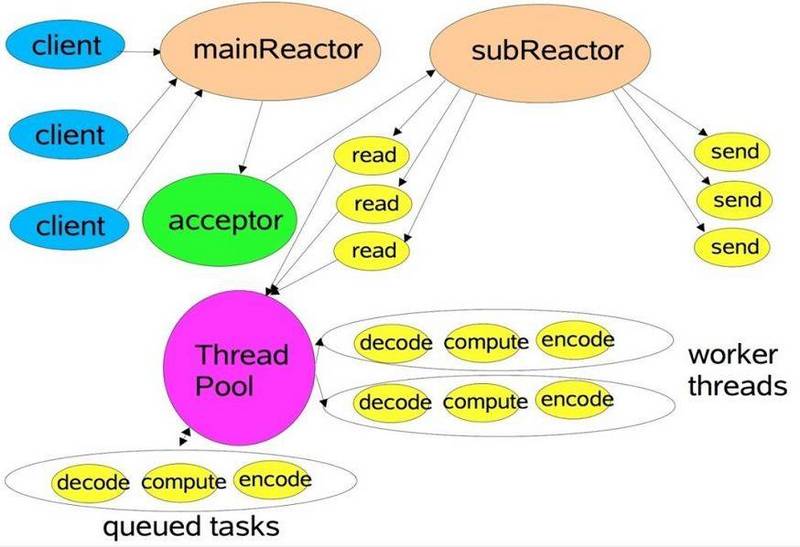
但是在Netty中,bossGroup相当于mainReactor,workerGroup相当于SubReactor与Worker线程池的合体。如:
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
ServerBootstrap server = new ServerBootstrap();
server.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class);
- bossGroup
bossGroup线程池负责监听端口,获取一个线程作为MainReactor,用于处理端口的Accept事件。
- workerGroup
workerGroup线程池负责处理Channel(通道)的I/O事件,并处理相应的业务。
在启动时,可以初始化多个线程。
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(2); EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(3);
2、Netty示例(客户端、服务器)
下面的例子演示了Netty的简单使用。
2.1、服务端
2.1.1、 EchoServerHandler
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFutureListener;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandler;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.util.CharsetUtil;
/**
* EchoServerHandler
*/
// 标识这类的实例之间可以在 channel 里面共享
@ChannelHandler.Sharable
public class EchoServerHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) {
ByteBuf in = (ByteBuf) msg;
System.out.println("Server received: " + in.toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
ctx.write(in);
}
@Override
public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.EMPTY_BUFFER)
.addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE);
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
}
2.1.2、 EchoServer
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
/**
* Echo服务端
*/
public class EchoServer {
private final int port;
private EchoServer(int port) {
this.port = port;
}
private void start() throws Exception {
//创建 EventLoopGroup
NioEventLoopGroup boss = new NioEventLoopGroup();
NioEventLoopGroup work = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
//创建 ServerBootstrap
ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();
b.group(boss, work)
//指定使用 NIO 的传输 Channel
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
//设置 socket 地址使用所选的端口
.localAddress(new InetSocketAddress(port))
//添加 EchoServerHandler 到 Channel 的 ChannelPipeline
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new EchoServerHandler());
}
});
//绑定的服务器;sync 等待服务器关闭
ChannelFuture f = b.bind().sync();
System.out.println(EchoServer.class.getName() + " started and listen on " + f.channel().localAddress());
//关闭 channel 和 块,直到它被关闭
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
//关机的 EventLoopGroup,释放所有资源。
group.shutdownGracefully().sync();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//设置端口值(抛出一个 NumberFormatException 如果该端口参数的格式不正确)
int port = 9999;
//服务器start()
new EchoServer(port).start();
}
}
2.2、客户端
2.2.1、EchoClientHandler
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler;
import io.netty.util.CharsetUtil;
public class EchoClientHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<ByteBuf> {
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("Netty rocks!", CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
@Override
protected void messageReceived(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf msg) {
System.out.println("Client received: " + msg.toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
}
}
2.2.2、EchoClient
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
public class EchoClient {
private final String host;
private final int port;
private EchoClient(String host, int port) {
this.host = host;
this.port = port;
}
private void start() throws Exception {
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
//创建 Bootstrap
Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap();
//指定 EventLoopGroup 来处理客户端事件。
//由于使用 NIO 传输,所以用到了 NioEventLoopGroup 的实现
b.group(group)
//使用的 channel 类型是一个用于 NIO 传输
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
//设置服务器的 InetSocketAddress
.remoteAddress(new InetSocketAddress(host, port))
//当建立一个连接和一个新的通道时,创建添加到 EchoClientHandler 实例 到 channel pipeline
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new EchoClientHandler());
}
});
//连接到远程;等待连接完成
ChannelFuture f = b.connect().sync();
//阻塞直到 Channel 关闭
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
//调用 shutdownGracefully() 来关闭线程池和释放所有资源
group.shutdownGracefully().sync();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//服务器地址及端口
String host = "localhost";
int port = 9999;
new EchoClient(host, port).start();
}
}
3、Netty工作原理
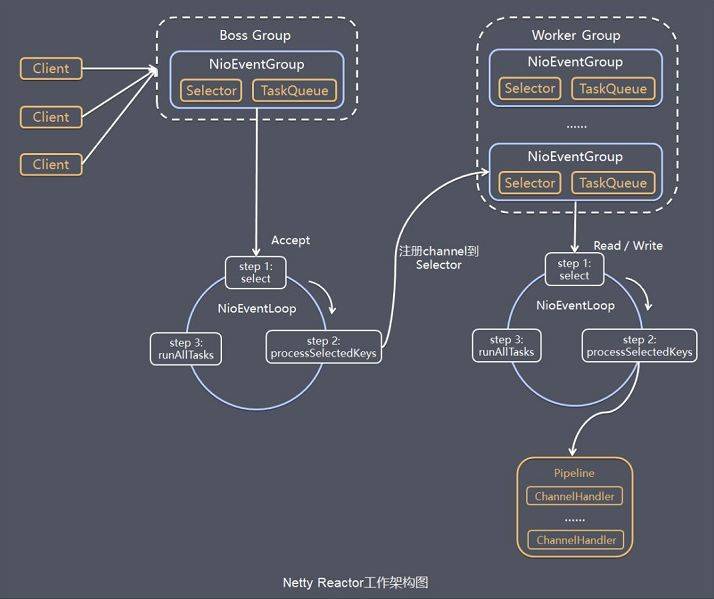
服务端包含了1个boss NioEventLoopGroup和1个work NioEventLoopGroup。
NioEventLoopGroup相当于1个事件循环组,组内包含多个事件循环(NioEventLoop),每个NioEventLoop包含1个Selector和1个事件循环线程。
3.1、boss NioEventLoop循环任务
- 轮询Accept事件。
- 处理Accept IO事件,与Client建立连接,生成NioSocketChannel,并将NioSocketChannel注册到某个work NioEventLoop的Selector上。
- 处理任务队列中的任务。
3.2、work NioEventLoop循环任务
- 轮询Read、Write事件。
- 处理IO事件,在NioSocketChannel可读、可写事件发生时进行处理。
- 处理任务队列中的任务。
3.3、任务队列中的任务
- 用户程序自定义的普通任务
ctx.channel().eventLoop().execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
//...
}
});
- 非当前 Reactor 线程调用 Channel 的各种方法
例如在推送系统的业务线程里面,根据用户的标识,找到对应的 Channel 引用,然后调用 Write 类方法向该用户推送消息,就会进入到这种场景。最终的 Write 会提交到任务队列中后被异步消费。
- 用户自定义定时任务
ctx.channel().eventLoop().schedule(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
//...
}
}, 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
参考
这可能是目前最透彻的Netty原理架构解析
Netty 实战精髓篇
Netty入门教程
Essential Netty in Action 
正文到此结束
热门推荐
相关文章
Loading...











![[HBLOG]公众号](http://www.liuhaihua.cn/img/qrcode_gzh.jpg)

