Java多线程:线程状态
点击上方 IT牧场 ,选择 置顶或者星标
技术干货每日送达

# 面试题
-
Java中线程有哪几种状态,线程的生命周期。
-
每个状态的含义。
-
状态之间的转化过程以及触发条件,图示。
# 线程有哪几种状态
-
Java doc
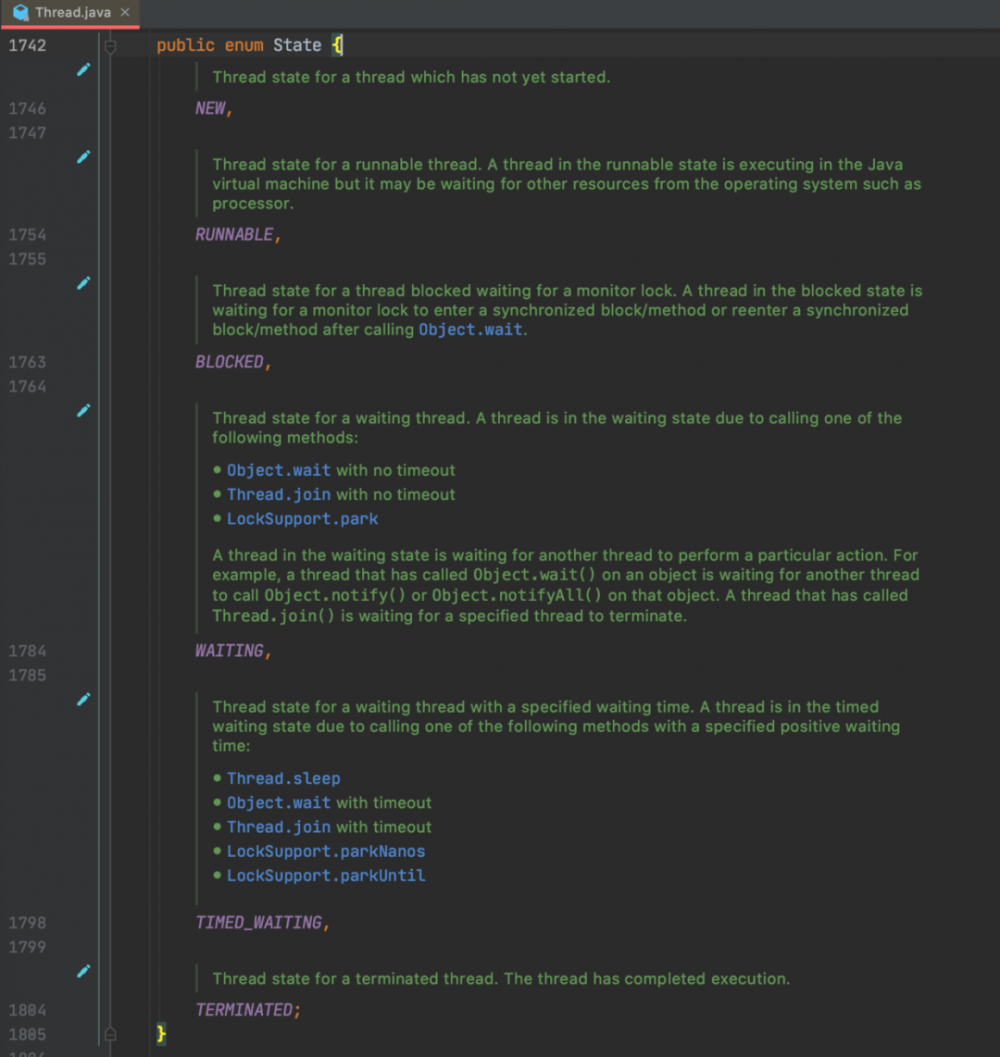
-
New ( 刚创建出线程实例 )
-
new Thread() -
Runnable ( 可运行/运行状态,等待CPU的调度 )(要注意:即使是正在运行的线程,状态也是Runnable,而不是Running)
-
调用了
thread.start()启动线程。 -
被
synchronized标记的代码,获取到同步监视器。 -
obj.notify()唤醒线程。 -
obj.notifyAll()唤醒线程。 -
obj.wait(time), thread.join(time)等待时间time耗尽。 -
Blocked ( 阻塞状态 )
-
运行被synchronized标记的代码且未获取到同步监视器。
-
Waiting ( 不超时等待状态 )
-
threadA中调用
threadB.join(),threadA将Waiting,直到threadB终止。 -
obj.wait()释放同步监视器obj,并进入阻塞状态。 -
TimedWaiting ( 等待指定时间time )。
-
threadA中调用
threadB.join(time)。 -
obj.wait(time) -
sleep(time)。 -
Terminated ( 线程终止 )
-
线程正常执行完毕。
-
发生了未捕获的异常。
# 注意
-
wait() wait(time) Waiting TimedWaiting notify() notifyAll() Blocked
# 线程状态转换图示
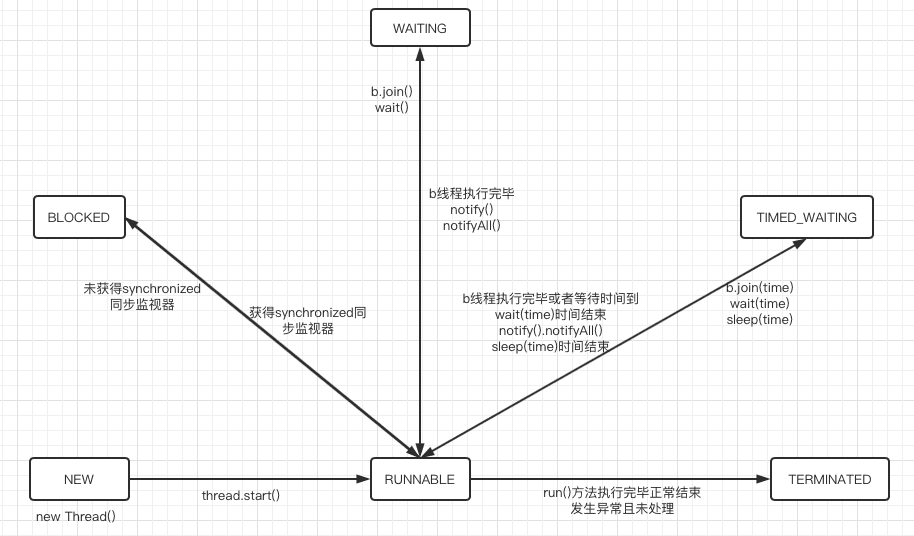
# 代码演示
-
New/Runnable/Terminated
/**
* 线程的状态演示:NEW,Runnable,Terminated
*
* @author futao
* @date 2020/6/7
*/
public class NewRunnableTerminated implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread thread = new Thread(new NewRunnableTerminated());
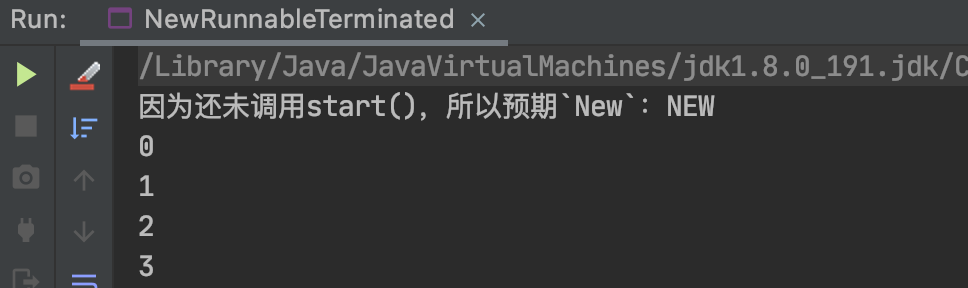
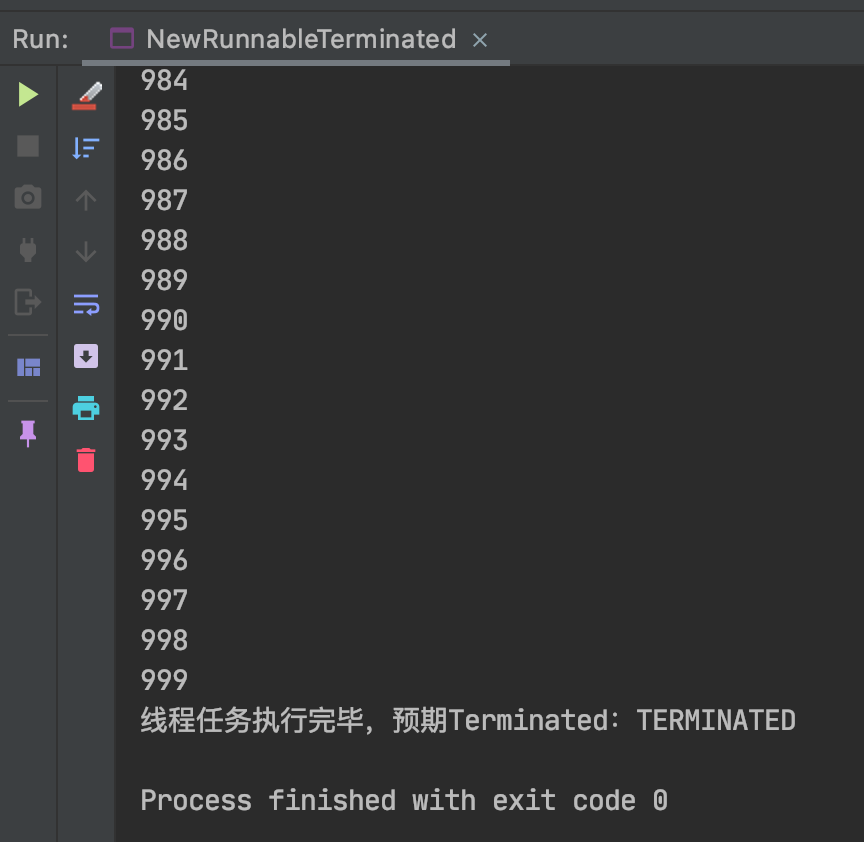
System.out.println("因为还未调用start(),所以预期`New`:" + thread.getState());
thread.start();
//等待子线程跑一会,看看运行中的状态是不是Runnable
Thread.sleep(10L);
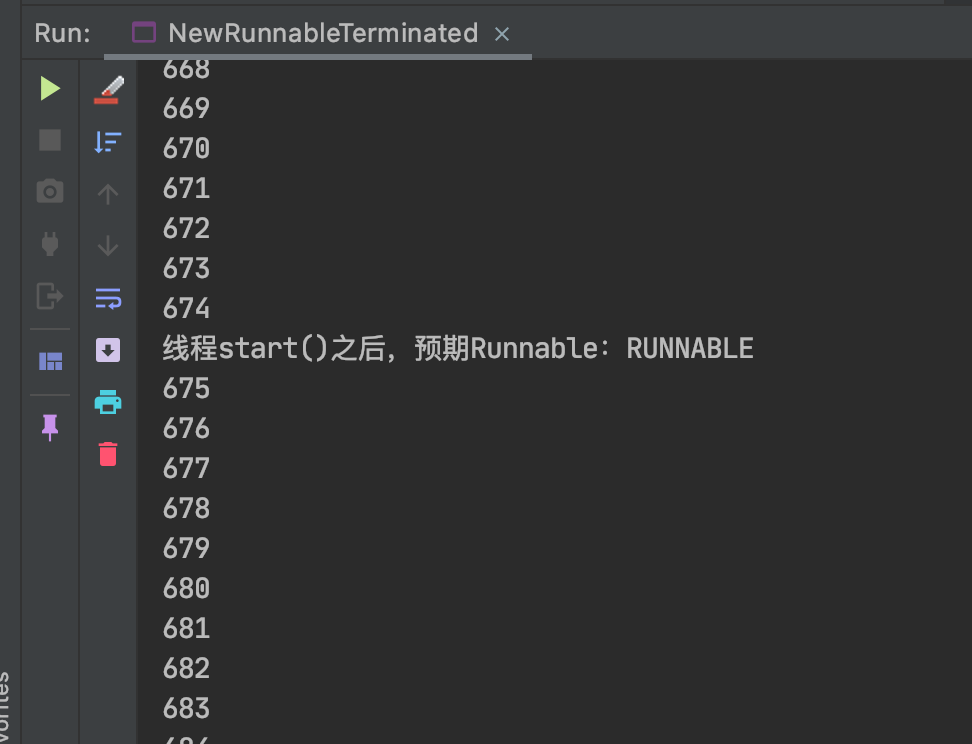
System.out.println("线程start()之后,预期Runnable:" + thread.getState());
//等待子线程执行完毕,再查看其状态
Thread.sleep(1000L);
System.out.println("线程任务执行完毕,预期Terminated:" + thread.getState());
}
}
-
结果
-
Blocked,Waiting,TimedWaiting
/**
* 演示Blocked,Waiting,TimedWaiting
*
* @author futao
* @date 2020/6/7
*/
public class BlockedWaitingTimedWaiting implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 同步方法
*
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
public synchronized void sync() throws InterruptedException {
Thread.sleep(1000L);
wait();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
BlockedWaitingTimedWaiting blockedWaitingTimedWaiting = new BlockedWaitingTimedWaiting();
Thread thread1 = new Thread(blockedWaitingTimedWaiting);
Thread thread2 = new Thread(blockedWaitingTimedWaiting);
thread1.start();
//为了尽可能让thread1先执行,获取到同步方法的锁
Thread.sleep(10L);
thread2.start();
Thread.sleep(500L);
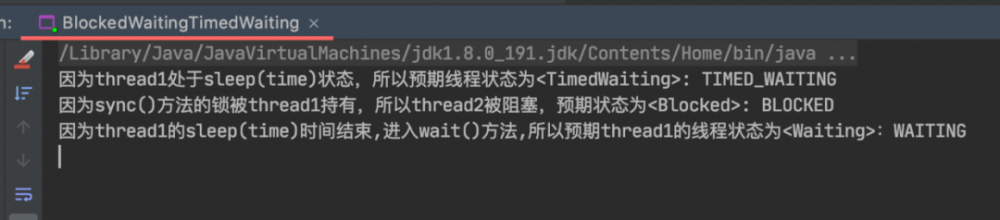
System.out.println("因为thread1处于sleep(time)状态,所以预期线程状态为<TimedWaiting>: " + thread1.getState());
System.out.println("因为sync()方法的锁被thread1持有,所以thread2被阻塞,预期状态为<Blocked>: " + thread2.getState());
//等待thread1的sleep(time)时间结束,进入wait()方法
Thread.sleep(1000L);
System.out.println("因为thread1的sleep(time)时间结束,进入wait()方法,所以预期thread1的线程状态为<Waiting>:" + thread1.getState());
}
}
欢迎在评论区留下你看文章时的思考,及时说出,有助于加深记忆和理解,还能和像你一样也喜欢这个话题的读者相遇~
# 本文源代码
-
https://github.com/FutaoSmile/learn-thread/tree/master/src/main/java/com/futao/learn/threads/d_线程的生命周期
干货分享
最近将个人学习笔记整理成册,使用PDF分享。关注我,回复如下代码,即可获得百度盘地址,无套路领取!
• 001:《Java并发与高并发解决方案》学习笔记; • 002:《深入JVM内核——原理、诊断与优化》学习笔记; • 003:《Java面试宝典》 • 004:《Docker开源书》 • 005:《Kubernetes开源书》 • 006:《DDD速成(领域驱动设计速成)》 • 007: 全部 • 008: 加技术群讨论
近期热文
关注我

喜欢就点个"在看"呗^_^










![[HBLOG]公众号](https://www.liuhaihua.cn/img/qrcode_gzh.jpg)

