Spring Cloud OAuth2 认证流程
Spring Cloud OAuth2 认证流程
本文基于官方提供的示例进行讲解,文中部分源码使用的 5.0 版本,基本上没太大差别。
建议配合本文提供的关键代码和官方示例结合查看,可以运行官方示例查看效果。
认证服务器: https://github.com/spring-cloud-samples/authserver
SSO客户端: https://github.com/spring-cloud-samples/sso
想要知道如何配置认证服务器和客户端,可以参考官方的这两个示例。
由于 Spring 封装的东西太多,所以看到 Spring 这么简单的配置时,你根本不知道他做了什么,在不了解整个流程的情况下,你很难对其中的过程进行定制,因此本文就是在上述两个示例上,对 Spring OAuth2 的部分配置和关键的认证流程做一个详细的介绍。
一、服务端配置
服务端最主要的一个配置就是使用 @EnableAuthorizationServer 注解,该注解的作用就是引入了一些 OAuth2 相关的端点,包含以下的端点:
-
AuthorizationEndpoint根据用户认证获得授权码,有下面两个方法:-
/oauth/authorize- GET -
/oauth/authorize- POST
-
-
TokenEndpoint客户端根据授权码获取 token
-
/oauth/token- GET -
/oauth/token- POST
-
-
CheckTokenEndpoint可以用于远程解码令牌
-
/oauth/check_token
-
-
WhitelabelApprovalEndpoint显示授权服务器的确认页。
-
/oauth/confirm_access
-
-
WhitelabelErrorEndpoint显示授权服务器的错误页
-
/oauth/error
-
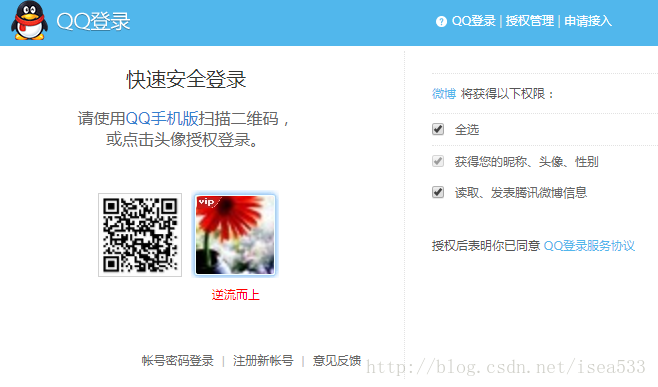
这些端点有个特点,如果你自己实现了上面的方法,他会优先使用你提供的方法,利用这个特点,通常都会根据自己的需要来设计自己的授权确认页面,例如使用 QQ 登录微博的认证页面:
在官方的示例中,通过下面代码直接指定了视图:
registry.addViewController("/oauth/confirm_access").setViewName("authorize");
如果想跳过这个认证确认的过程,可以看本文后面的 autoApprove 配置。
除了这么些端点外,还引入了主要的配置 AuthorizationServerSecurityConfiguration ,这个配置在这里并没有做太多的事,示例中提供的 OAuth2Config 真正干了有用的事,关于这个配置的详细信息可以参考 Spring Security 的文档。
示例中使用的 jwt,关于这个可以阅读下面的文章:
JSON Web Token - 在Web应用间安全地传递信息
http://blog.leapoahead.com/2015/09/06/understanding-jwt/
二、客户端配置
最简单的情况下,只需要 @EnableOAuth2Sso 注解和配置文件中配置的认证服务器信息,使用这个注解有两种情况,使用默认配置或者自定义配置:
第1种,通过 @EnableOAuth2Sso 注解开启,全部使用默认的配置。
第2种,使用 @EnableOAuth2Sso 注解标记一个 WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter 类,如下所示。
@Component
@EnableOAuth2Sso
public static class LoginConfigurer extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
想要自定义,必须按照上面的方式定义,这么定义的原因在于 @EnableOAuth2Sso 注解。
/**
* Enable OAuth2 Single Sign On (SSO). If there is an existing
* {@link WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter} provided by the user and annotated with
* {@code @EnableOAuth2Sso}, it is enhanced by adding an authentication filter and an
* authentication entry point. If the user only has {@code @EnableOAuth2Sso} but not on a
* WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter then one is added with all paths secured and with an order
* that puts it ahead of the default HTTP Basic security chain in Spring Boot.
*
* @author Dave Syer
* @since 1.3.0
*/
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@EnableOAuth2Client
@EnableConfigurationProperties(OAuth2SsoProperties.class)
@Import({ OAuth2SsoDefaultConfiguration.class, OAuth2SsoCustomConfiguration.class,
ResourceServerTokenServicesConfiguration.class })
public @interface EnableOAuth2Sso {
}
代码注释中说的就是上面说的这两种情况,分别对应 @Import 中的配置:
-
OAuth2SsoDefaultConfiguration默认配置,对所有路径进行保护 -
OAuth2SsoCustomConfiguration自定义配置,可以通过内部方法进行控制
这两个配置上的注解分别如下。
默认配置 OAuth2SsoDefaultConfiguration 。
@Configuration
@Conditional(NeedsWebSecurityCondition.class)
public class OAuth2SsoDefaultConfiguration extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter
implements Ordered {
自定义配置 OAuth2SsoCustomConfiguration 。
@Configuration
@Conditional(EnableOAuth2SsoCondition.class)
public class OAuth2SsoCustomConfiguration
implements ImportAware, BeanPostProcessor, ApplicationContextAware {
这两个配置上的条件分别如下。
protected static class NeedsWebSecurityCondition extends EnableOAuth2SsoCondition {
@Override
public ConditionOutcome getMatchOutcome(ConditionContext context,
AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
return ConditionOutcome.inverse(super.getMatchOutcome(context, metadata));
}
}
和
class EnableOAuth2SsoCondition extends SpringBootCondition {
@Override
public ConditionOutcome getMatchOutcome(ConditionContext context,
AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
String[] enablers = context.getBeanFactory()
.getBeanNamesForAnnotation(EnableOAuth2Sso.class);
ConditionMessage.Builder message = ConditionMessage
.forCondition("@EnableOAuth2Sso Condition");
for (String name : enablers) {
if (context.getBeanFactory().isTypeMatch(name,
WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter.class)) {
return ConditionOutcome.match(message
.found("@EnableOAuth2Sso annotation on WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter")
.items(name));
}
}
return ConditionOutcome.noMatch(message.didNotFind(
"@EnableOAuth2Sso annotation " + "on any WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter")
.atAll());
}
}
NeedsWebSecurityCondition 继承的 EnableOAuth2SsoCondition ,并且对结果取反了,所以这两者只会有一种情况生效。 EnableOAuth2SsoCondition 条件中对自定义的要求就是在一个继承 WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter 的类上添加 @EnableOAuth2Sso 注解。
一句话概括:只有继承 WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter 的类上带 @EnableOAuth2Sso 注解时,这个配置最后生成的过滤器链中才会有 oauth2 的过滤器 OAuth2ClientAuthenticationProcessingFilter 。
在 WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter 配置中的 http.antMatcher("xxx") 会决定某个请求能否被这些过滤器链进行处理。假设 oauth2 登录的请求 url 被别的配置拦截时,由于那个配置的拦截器链中没有 oauth2 的拦截器,因此就没法跳转到认证服务器。
上面这段逻辑可以看 FilterChainProxy 中:
private void doFilterInternal(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response,
FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
FirewalledRequest fwRequest = firewall
.getFirewalledRequest((HttpServletRequest) request);
HttpServletResponse fwResponse = firewall
.getFirewalledResponse((HttpServletResponse) response);
List<Filter> filters = getFilters(fwRequest);
if (filters == null || filters.size() == 0) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug(UrlUtils.buildRequestUrl(fwRequest)
+ (filters == null ? " has no matching filters"
: " has an empty filter list"));
}
fwRequest.reset();
chain.doFilter(fwRequest, fwResponse);
return;
}
VirtualFilterChain vfc = new VirtualFilterChain(fwRequest, chain, filters);
vfc.doFilter(fwRequest, fwResponse);
}
其中匹配过滤器链在:
List<Filter> filters = getFilters(fwRequest);
//getFilters 如下
private List<Filter> getFilters(HttpServletRequest request) {
for (SecurityFilterChain chain : filterChains) {
if (chain.matches(request)) {
return chain.getFilters();
}
}
return null;
}
其中 filterChains 的个数和项目中实现 WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter 的个数相同(除了自己创建的,系统默认也有),当不包含 oauth2 过滤器的 chain 匹配到认证请求时,就没法正常工作。
三、客户端关键配置
在 application.properties或 yml 配置文件中配置 oauth2 的登录地址:
security.oauth2.sso.login-path=/dashboard/login
和这个配置有关的内容如下,oauth2 配置属性:
配置 oauth2 登录地址。
/**
* Configuration properties for OAuth2 Single Sign On (SSO).
*
* @author Dave Syer
* @since 1.3.0
*/
@ConfigurationProperties("security.oauth2.sso")
public class OAuth2SsoProperties {
public static final String DEFAULT_LOGIN_PATH = "/login";
/**
* Path to the login page, i.e. the one that triggers the redirect to the OAuth2
* Authorization Server.
*/
private String loginPath = DEFAULT_LOGIN_PATH;
默认的 /login ,这个值会在创建 OAuth2ClientAuthenticationProcessingFilter 过滤器时用到。
private OAuth2ClientAuthenticationProcessingFilter oauth2SsoFilter(
OAuth2SsoProperties sso) {
OAuth2RestOperations restTemplate = this.beanFactory
.getBean(OAuth2RestOperations.class);
ResourceServerTokenServices tokenServices = this.beanFactory
.getBean(ResourceServerTokenServices.class);
OAuth2ClientAuthenticationProcessingFilter filter = new
OAuth2ClientAuthenticationProcessingFilter(
sso.getLoginPath());//这里
filter.setRestTemplate(restTemplate);
filter.setTokenServices(tokenServices);
return filter;
}
所以后续在 Spring Security 过滤器链中,当匹配到这个地址时,就会根据当前是否认证过,来跳转到认证服务器。
四、认证流程
这里开始完整的认证流程。
(一) 初始阶段,客户端的权限校验和登录页面的跳转
除了直接访问客户端的 /dashboard/login 地址外,如果访问了一个受限的资源,也会跳转到这个登录页面,然后又会根据 oauth2 的过滤器跳转到认证服务器。
从受限资源跳转到 /dashboard/login 的处理过程如下。
看下面这个方法,上面的 oauth2SsoFilter 也是在下面方法中调用的,在这个方法后面还有一个添加 entrypoint 的方法。
public void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
OAuth2SsoProperties sso = this.beanFactory.getBean(OAuth2SsoProperties.class);
// Delay the processing of the filter until we know the
// SessionAuthenticationStrategy is available:
http.apply(new OAuth2ClientAuthenticationConfigurer(oauth2SsoFilter(sso)));
addAuthenticationEntryPoint(http, sso);
}
addAuthenticationEntryPoint 方法。
private void addAuthenticationEntryPoint(HttpSecurity http, OAuth2SsoProperties sso)
throws Exception {
ExceptionHandlingConfigurer<HttpSecurity> exceptions = http.exceptionHandling();
ContentNegotiationStrategy contentNegotiationStrategy = http
.getSharedObject(ContentNegotiationStrategy.class);
if (contentNegotiationStrategy == null) {
contentNegotiationStrategy = new HeaderContentNegotiationStrategy();
}
MediaTypeRequestMatcher preferredMatcher = new MediaTypeRequestMatcher(
contentNegotiationStrategy, MediaType.APPLICATION_XHTML_XML,
new MediaType("image", "*"), MediaType.TEXT_HTML, MediaType.TEXT_PLAIN);
preferredMatcher.setIgnoredMediaTypes(Collections.singleton(MediaType.ALL));
exceptions.defaultAuthenticationEntryPointFor(
new LoginUrlAuthenticationEntryPoint(sso.getLoginPath()),
preferredMatcher);
// When multiple entry points are provided the default is the first one
exceptions.defaultAuthenticationEntryPointFor(
new HttpStatusEntryPoint(HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED),
new RequestHeaderRequestMatcher("X-Requested-With", "XMLHttpRequest"));
}
看着两行。
exceptions.defaultAuthenticationEntryPointFor(
new LoginUrlAuthenticationEntryPoint(sso.getLoginPath()),
preferredMatcher);
这里设置了 ExceptionTranslationFilter 过滤器的几个属性。
最终在 ExceptionHandlingConfigurer 执行 config 方法时,使用了这里添加的两个端点。
@Override
public void configure(H http) throws Exception {
AuthenticationEntryPoint entryPoint = getAuthenticationEntryPoint(http);
ExceptionTranslationFilter exceptionTranslationFilter = new ExceptionTranslationFilter(
entryPoint, getRequestCache(http));
if (accessDeniedHandler != null) {
exceptionTranslationFilter.setAccessDeniedHandler(accessDeniedHandler);
}
exceptionTranslationFilter = postProcess(exceptionTranslationFilter);
http.addFilter(exceptionTranslationFilter);
}
getAuthenticationEntryPoint(http) 如下。
AuthenticationEntryPoint getAuthenticationEntryPoint(H http) {
AuthenticationEntryPoint entryPoint = this.authenticationEntryPoint;
if (entryPoint == null) {
entryPoint = createDefaultEntryPoint(http);
}
return entryPoint;
}
private AuthenticationEntryPoint createDefaultEntryPoint(H http) {
if (defaultEntryPointMappings.isEmpty()) {
return new Http403ForbiddenEntryPoint();
}
if (defaultEntryPointMappings.size() == 1) {
return defaultEntryPointMappings.values().iterator().next();
}
DelegatingAuthenticationEntryPoint entryPoint = new DelegatingAuthenticationEntryPoint(
defaultEntryPointMappings);
//这里的 values 就是前面添加的两个端点
entryPoint.setDefaultEntryPoint(defaultEntryPointMappings.values().iterator()
.next());
return entryPoint;
}
所以在出现访问异常时,能够获取要跳转到当前登录地址的信息。
ExceptionTranslationFilter 中的关键代码如下:
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res;
try {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
logger.debug("Chain processed normally");
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Exception ex) {
// Try to extract a SpringSecurityException from the stacktrace
Throwable[] causeChain = throwableAnalyzer.determineCauseChain(ex);
RuntimeException ase = (AuthenticationException) throwableAnalyzer
.getFirstThrowableOfType(AuthenticationException.class, causeChain);
if (ase == null) {
ase = (AccessDeniedException) throwableAnalyzer.getFirstThrowableOfType(
AccessDeniedException.class, causeChain);
}
if (ase != null) {
handleSpringSecurityException(request, response, chain, ase);
}
else {
//省略
}
}
}
在这个过滤器的 try 部分中会继续执行过滤器链中剩余的过滤器,正常情况下,后面会执行的一个过滤器是 FilterSecurityInterceptor ,这个过滤器是用来处理授权的,就是验证用户是否有权访问某个资源,如果没有权限,就会抛出 AccessDeniedException ,此时就会进入 handleSpringSecurityException 方法执行。这个方法就会发送 302跳转到认证页面。
跳转地址,仍然在客户端上:
Location:http://localhost:9999/dashboard/login
此时的地址就会匹配客户端的 OAuth2ClientAuthenticationProcessingFilter 过滤器。
然后尝试获取认证信息。
accessToken = restTemplate.getAccessToken();
获取token。因为获取不到 token 而抛出异常( UserRedirectRequiredException ):
throw getRedirectForAuthorization(resource, request);
异常会一直抛到 OAuth2ClientContextFilter (这个过滤器来自 @EnableOAuth2Sso 上的 @EnableOAuth2Client 中导入的 OAuth2ClientConfiguration )中。
try {
chain.doFilter(servletRequest, servletResponse);
} catch (IOException ex) {
throw ex;
} catch (Exception ex) {
// Try to extract a SpringSecurityException from the stacktrace
Throwable[] causeChain = throwableAnalyzer.determineCauseChain(ex);
UserRedirectRequiredException redirect = (UserRedirectRequiredException) throwableAnalyzer
.getFirstThrowableOfType(
UserRedirectRequiredException.class, causeChain);
if (redirect != null) {
redirectUser(redirect, request, response);
} else {
if (ex instanceof ServletException) {
throw (ServletException) ex;
}
if (ex instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) ex;
}
throw new NestedServletException("Unhandled exception", ex);
}
}
redirectUser(redirect, request, response); 跳转到下面地址。
http://localhost:8080/uaa/oauth/authorize?client_id=acme&redirect_uri=http://localhost:9999/dashboard/login&response_type=code&state=O53UrS
此时oauth2客户端的操作已经结束,除资源文件外,产生的请求如下。
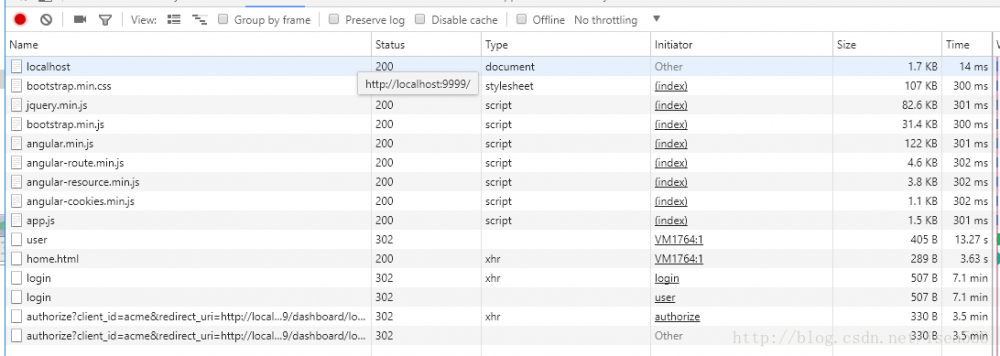
由于这里使用的 ajax 方式,因此页面不会真正跳转。
并且这些个请求是因为请求了受限的 /dashboard/user 引发的。
(二) OAuth2 认证开始
经过前面的内容,我们应该知道访问登录页面或者需要授权的页面时会跳转到认证服务器。
下面是 authorization code 方式的认证流程。
详细内容参考:
http://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2014/05/oauth_2_0.html
http://www.rfcreader.com/#rfc6749_line1027
+----------+
| Resource |
| Owner |
| |
+----------+
^
|
(B)
+----|-----+ Client Identifier +---------------+
| -+----(A)-- & Redirection URI ---->| |
| User- | | Authorization |
| Agent -+----(B)-- User authenticates --->| Server |
| | | |
| -+----(C)-- Authorization Code ---<| |
+-|----|---+ +---------------+
| | ^ v
(A) (C) | |
| | | |
^ v | |
+---------+ | |
| |>---(D)-- Authorization Code ---------' |
| Client | & Redirection URI |
| | |
| |<---(E)----- Access Token -------------------'
+---------+ (w/ Optional Refresh Token)
A. 导向认证服务器
首先,在前一步中,我们知道了,客户端会根据 oauth2 配置下面的信息去获取授权:
security:
oauth2:
client:
accessTokenUri: http://localhost:8080/uaa/oauth/token
userAuthorizationUri: http://localhost:8080/uaa/oauth/authorize
当用户已经在认证服务器登录时,能够直接认证,如果用户没有登录,根据认证服务端的配置,也会把用户导向到登录页面。
初始状态时,用户没有登录,由于请求地址 /oauth/authorize (完整地址如下)没有访问权限,因此 uaa 服务端又会跳转到登录页面(和上面客户端跳转到 /login 一样)。
请求地址: http://localhost:8080/uaa/oauth/authorize?client_id=acme&redirect_uri=http://localhost:9999/dashboard/login&response_type=code&state=O53UrS
跳转。
登录地址: http://localhost:8080/uaa
当通过非 ajax 方式请求受限地址时,会真正跳转到这个地址。
B. 登录授权
在授权服务器中,默认是存在 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 过滤器,还有默认的登录页面过滤器。
在该登录页面输入帐号密码后,会进入 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 过滤器。
在登录页面输入用户名密码认证成功后,在 SavedRequestAwareAuthenticationSuccessHandler 过滤器中会获取到跳转到登录页面前的请求信息。
SavedRequest savedRequest = requestCache.getRequest(request, response);
从该请求获取跳转地址然后跳转过去:
String targetUrl = savedRequest.getRedirectUrl(); getRedirectStrategy().sendRedirect(request, response, targetUrl);
此时跳转地址可能是下面这样的:
http://localhost:8080/uaa/oauth/authorize?client_id=acme&redirect_uri=http://localhost:9999/dashboard/login&response_type=code&state=vEFlOH
这个地址仍然是认证服务的, AuthorizationEndpoint 会处理 /oauth/authorize 请求。
根据上面 url 中的信息对客户端进行验证,处理 redirect_uri 请求中的参数。
下面有段关键的代码。
boolean approved = userApprovalHandler.isApproved(authorizationRequest, (Authentication) principal);
authorizationRequest.setApproved(approved);
if (authorizationRequest.isApproved()) {
if (responseTypes.contains("token")) {
return getImplicitGrantResponse(authorizationRequest);
}
if (responseTypes.contains("code")) {
return new ModelAndView(getAuthorizationCodeResponse(authorizationRequest,
(Authentication) principal));
}
}
model.put("authorizationRequest", authorizationRequest);
return getUserApprovalPageResponse(model, authorizationRequest, (Authentication) principal);
如果 approved = true ,那么就直接跳转到客户端页面,如果不是,就会跳转到用户确认授权页面。 apporved 默认值可以通过下面的方式设置:
@Override
public void configure(ClientDetailsServiceConfigurer clients) throws Exception {
clients.inMemory()
.withClient("acme")
.secret("acmesecret").autoApprove(true)
...;
}
C. 获取授权码
当用户同意授权时,会转发到客户端:
http://localhost:9999/dashboard/login?code=8FbLWt&state=7Fw78E
此时客户端得到了授权码 code=8FbLWt 。
D, E. 使用授权码获取 token
客户端通过这个授权码,使用 AuthorizationCodeAccessTokenProvider ,通过 RestTemplate 向认证服务器发送请求获取 token。
服务端的 TokenEndpoint 会处理这个请求。
根据请求信息生成 token 后返回给客户端。
使用 jwt 的情况下,生成的 token 类似下面这样:
eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJleHAiOjE1MDYyNzQ0NzEsInVzZXJfbmFtZSI6InVzZXIiLCJhdXRob3JpdGllcyI6WyJST0xFX0FETUlOIiwiUk9MRV9VU0VSIl0sImp0aSI6IjUyZDM4Y2U2LTMxNjMtNDZjOC1iYjg0LTJhNjNjNjc5OWY2ZCIsImNsaWVudF9pZCI6ImFjbWUiLCJzY29wZSI6WyJvcGVuaWQiXX0.mEWQ2V3NAHDjxsSrFin1_ooNo8F4GKrtIIlOrGlBWr-HTcVDQJ-0OERAET5JyyBtxxtP1OEYgRT5uoyX4RKulwnmV83hLk5o_rSWV5uZQ67lqRvG5M_HL8ATRALpQaaz93o2j1ottpjmDNNw2Jxuk6IrKhRnSvdw5Ss9m_pZvcwva2FXTzEjmBFaNs6MHncNkMXorrLtljWp6b55pm5IUIAVmwj8EIbJPKlzTBGUBJff1c1urrtlhUHU-_ezoG-5Te15sneCcM48I-UuQFugfBnj1ij4EicGW_4UPu3HAZxfVLBpZvYd4aZqN9QQc5pMHn9G_q8xIdiC3hByL1L8OA
客户端通过 DefaultTokenServices 的 loadAuthentication 方法对上面的 token 进行处理,使用 JwtTokenStore 解析上面的 token 值,结果如下:
{“alg”:”RS256”,”typ”:”JWT”} {“exp”:1506274471,”user_name”:”user”,”authorities”:[“ROLE_ADMIN”,”ROLE_USER”],”jti”:”52d38ce6-3163-46c8-bb84-2a63c6799f6d”,”client_id”:”acme”,”scope”:[“openid”]} [256 crypto bytes]
客户端解析后就得到了用户的认证和授权信息,此后就能根据这些信息来做各种校验了。
最后
如果看到这里有些蒙也不要紧,如果你在使用 Spring OAuth2 的时候没有遇到问题,也不必如此关注这些问题,如果你总会遇到莫名其妙的问题,你可能需要看看这篇博客,同时深入去看源码去解决了。
- 本文标签: Word map bean CEO XML springboot 源码 build trigger NSA 代码注释 Collection spring 参数 servlet 博客 安全 Service 注释 Collections Spring Security 定制 Ajax js 2015 IDE HTML IO rmi REST http cat Security 代码 json Spring Boot 服务器 微博 https 文章 UI cache App list authenticate src find Authorization GitHub Document id web provider git ACE 配置 ORM CTO value bug 认证 client tar message SDN 解析 服务端 ssh final ip
- 版权声明: 本文为互联网转载文章,出处已在文章中说明(部分除外)。如果侵权,请联系本站长删除,谢谢。
- 本文海报: 生成海报一 生成海报二










![[HBLOG]公众号](https://www.liuhaihua.cn/img/qrcode_gzh.jpg)

