Java 基础 - 各项集合实现
- 集合类的基本接口是:Collection
public interface Collection<E>{
// 集合改变返回 true,否则返回 false
boolean add();
boolean addAll();
// 返回一个迭代器
Iterator<E> iterator();
int size();
boolean isEmpty();
// 集合中包含了和 obj 相等的对象,那么返回 true
boolean contains(Object obj);
// 如果集合中包含 other 集合中的所有元素,那么返回 true
boolean containsAll(Collect<?> other);
// 从这个集合中删除等于 obj 的对象,如果有匹配的对象,返回 true
boolean remove(Object obj);
// 从这个集合中删除 other 中存在的元素,如果这个调用改变了集合,那么返回 true
boolean removeAll(Collect<?> other);
void clear();
// 从这个集合中删除所有与 other 这个集合中的元素不同的元素,如果这个调用改变了集合,那么返回 true
boolean retainAll(Collection<?> other);
Object[] toArray();
<T> T[] toArray(T[] a);
}
复制代码
- 迭代器
public interface Iterator<E>{
// 反复调用,可以逐个访问集合中的每个元素(配合 hasNext() 这个方法)
E next();
boolean hasNext();
// 删除上次调用 next() 返回的元素,没有调用 next() 方法,调用 remove() 则会报 IllegalStateException 异常
void remove();
}
复制代码
- 迭代器的用法
- 用法 1
Collection<String> c = ....; Iterator<String> iterator = c.iterator(); while(iterator.hasNext()){ String element = iterator.next(); iterator.remove(); // todo something } 复制代码- 用法 2:java SE 5.0 之后的写法,for each 循环操作
Collection<String> c = ....; for(String element : c){ // todo something } 复制代码“for each” 循环可以与任何实现了 Iterable 接口的对象一起工作
集合概览图
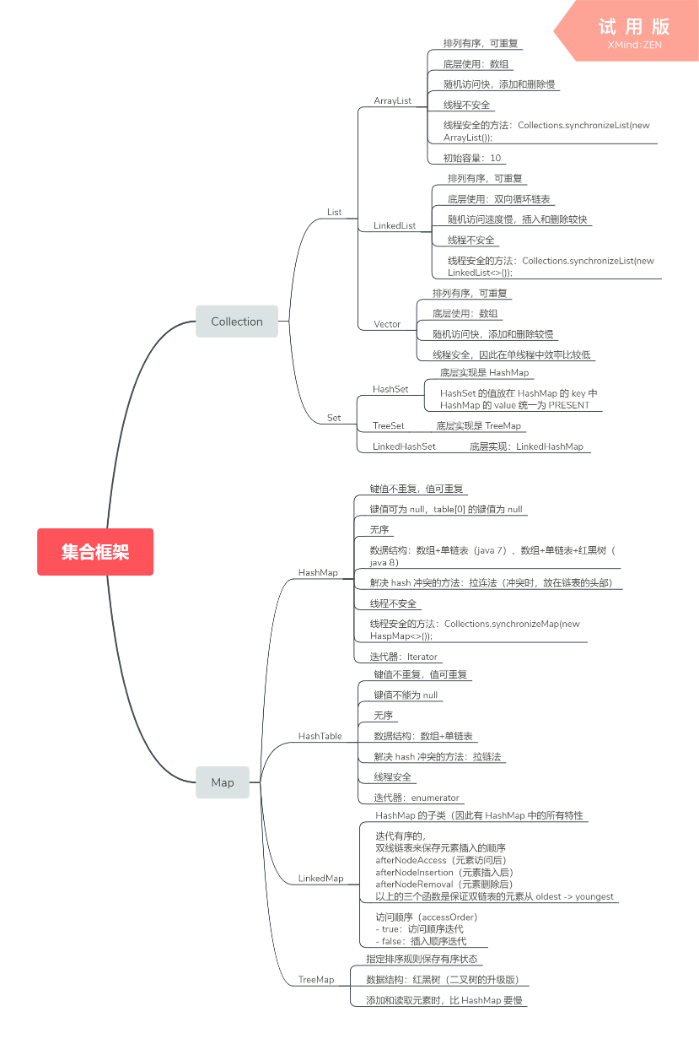
具体的集合实现
ArrayList
简介
- 继承于 AbstractList,实现了 List,是一个数组队列,提供添加、删除、修改、遍历的功能
- 实现了 RandomAccess 接口,提供随机访问的功能
- 实现了 Cloneable 接口,提供了克隆功能
- 实现了 java.io.Serializable 接口,提供序列化功能
定义
java.lang.Object
↳ java.util.AbstractCollection<E>
↳ java.util.AbstractList<E>
↳ java.util.ArrayList<E>
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable {}
复制代码
特性
- 关于 ArrayList 是线程不安全的,那么 ArrayList 只能在单线程中使用,如果需要多线程使用的话,那么可以使用 Vector 。或者是以下方式
// 将其包装成线程安全
List list = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList());
复制代码
- ArrayList 是一个动态数组队列,它能高效的随机访问元素和顺序遍历,但对于插入和删除效率会比较低,因为需要涉及到数组的移动。
扩容
- ArrayList 是一个动态的数组,那么一开始数组的大小是固定的(默认的话为 10),当向 ArrayList 中插入某个数组时,size 的值刚好为容量的大小,那么就会触发扩容的操作。扩容的方式是重新创建一个新的数组,拷贝原来的数据到新的数组中,并将新的元素插入到新的数组中,旧的数组则会被垃圾回收。
- 默认容量:10
- 扩容规则
-
JDK 1.6 及之前
int newCapacity = (oldCapacity * 3)/2 + 1; 复制代码
-
JDK 1.7 及之后
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1); 复制代码
-
JDK 1.8
private void grow(int minCapacity) { // overflow-conscious code int oldCapacity = elementData.length; int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1); if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) newCapacity = minCapacity; if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); // minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win: elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); } private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) { if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow throw new OutOfMemoryError(); return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : MAX_ARRAY_SIZE; } 复制代码
-
toArray()
- 2 种实现
Object[] toArray()
<T> T[] toArray(T[] contents)
复制代码
- 关于 “java.lang.ClassCastException”异常 toArray() 会抛出异常是因为 toArray() 返回的是 Object[] 数组,将 Object[] 转换为其它类型(如如,将Object[]转换为的Integer[])则会抛出“java.lang.ClassCastException”异常,因为Java不支持向下转型。
- 关于转换为数组的方式
// toArray(T[] contents)调用方式一
public static Integer[] vectorToArray1(ArrayList<Integer> v) {
Integer[] newText = new Integer[v.size()];
v.toArray(newText);
return newText;
}
// toArray(T[] contents)调用方式二。最常用!
public static Integer[] vectorToArray2(ArrayList<Integer> v) {
Integer[] newText = (Integer[])v.toArray(new Integer[0]);
return newText;
}
// toArray(T[] contents)调用方式三
public static Integer[] vectorToArray3(ArrayList<Integer> v) {
Integer[] newText = new Integer[v.size()];
Integer[] newStrings = (Integer[])v.toArray(newText);
return newStrings;
}
复制代码
注意点
- 多线程的话不使用 ArrayList,而是使用 Vector。
LinkedList
一种可以在任意位置进行高效插入及删除的操作的有序序列
简介
- 继承了 AbstractSequentialList 的双向链表,因此 LinkedList 是可以被当做堆栈、列表和双端列表进行操作
- 实现 List 接口,进行队列的操作
- 实现 Cloneable 接口,可以进行克隆操作
- 实现 Deque 接口,可以进行双端队列操作
- 实现 java.io.Serializable 接口,可以实现序列化
- 非同步的
定义
java.lang.Object
↳ java.util.AbstractCollection<E>
↳ java.util.AbstractList<E>
↳ java.util.AbstractSequentialList<E>
↳ java.util.LinkedList<E>
public class LinkedList<E>
extends AbstractSequentialList<E>
implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
复制代码
特性
- 顺序访问的效率高,但是随机访问的效率比较低
- 删除及添加的操作效率高
- 不同步(线程不安全)
将LinkedList当作 LIFO(后进先出)的堆栈示例
public static void useLinkedListAsLIFO() {
System.out.println("/nuseLinkedListAsLIFO");
// 新建一个LinkedList
LinkedList stack = new LinkedList();
// 将1,2,3,4添加到堆栈中
stack.push("1");
stack.push("2");
stack.push("3");
stack.push("4");
// 打印“栈”
System.out.println("stack:"+stack);
// 删除“栈顶元素”
System.out.println("stack.pop():"+stack.pop());
// 取出“栈顶元素”
System.out.println("stack.peek():"+stack.peek());
// 打印“栈”
System.out.println("stack:"+stack);
}
复制代码
将LinkedList当作 FIFO(先进先出)的队列
public static void useLinkedListAsFIFO() {
System.out.println("/nuseLinkedListAsFIFO");
// 新建一个LinkedList
LinkedList queue = new LinkedList();
// 将10,20,30,40添加到队列。每次都是插入到末尾
queue.add("10");
queue.add("20");
queue.add("30");
queue.add("40");
// 打印“队列”
System.out.println("queue:"+queue);
// 删除(队列的第一个元素)
System.out.println("queue.remove():"+queue.remove());
// 读取(队列的第一个元素)
System.out.println("queue.element():"+queue.element());
// 打印“队列”
System.out.println("queue:"+queue);
}
复制代码
HashMap(JDK 1.7 及之前)
简介
HashMap 它是基于 hash 表的 Map 接口实现,以 key-value 的形式存在的,HashMap 总是以 key-value 的形式存在的,系统会通过计算 key 的 hash 值来定位 key-value 的存储位置的,我们可以快速的通过 key 来存取 value;
定义
public class HashMap<K,V>
extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable
复制代码
数据结构
关于 HashMap 的数据结构,底层的话还是数组的,只不过数组的每一项就是一个链表
构造函数的源码
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
//初始容量不能<0
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: "
+ initialCapacity);
//初始容量不能 > 最大容量值,HashMap的最大容量值为2^30
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
//负载因子不能 < 0
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: "
+ loadFactor);
// 计算出大于 initialCapacity 的最小的 2 的 n 次方值。
int capacity = 1;
while (capacity < initialCapacity)
capacity <<= 1;
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
//设置HashMap的容量极限,当HashMap的容量达到该极限时就会进行扩容操作
threshold = (int) (capacity * loadFactor);
//初始化table数组
table = new Entry[capacity];
init();
}
复制代码
Entry 的源码
static class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final K key;
V value;
Entry<K,V> next;
final int hash;
/**
* Creates new entry.
*/
Entry(int h, K k, V v, Entry<K,V> n) {
value = v;
next = n;
key = k;
hash = h;
}
.......
}
复制代码
Entry 是 HashMap 的内部类,其中包含了 key,value 和 下一个 Entry,以及 hash 值,正因为有这下才构成了数组的项为一个列表。
容量、加载因子、临界值及哈希冲突
- 容量 :table 数组的大小,一般默认为 16
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // aka 16 复制代码
- 加载因子 :表示 table 数组的饱和程度
- 加载因子越大,填满的元素越多,空间利用率越高,但冲突的机会加大了。 反之;
- 加载因子越小,填满的元素越少,冲突的机会减小,但空间浪费多了。
- 临界值 :
- 为了避免造成哈希冲突率,那么当 HashMap 的数组长度达到一个临界值的时候就会触发扩容,把所有的元素重新计算 hash 值,再放到扩容后的容器中,这是一个比较耗时的操作。
- 临界值由加载因子及当前的容量来决定,默认情况下 16*0.75=12 就会触发扩容
DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY*DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR 复制代码
- 为了避免造成哈希冲突率,那么当 HashMap 的数组长度达到一个临界值的时候就会触发扩容,把所有的元素重新计算 hash 值,再放到扩容后的容器中,这是一个比较耗时的操作。
哈希冲突
在关键字的 hash 地址上已经有了记录,那么这就是哈希冲突 复制代码
- 解决冲突的方法
- 开放定址法
- 再哈希法
- 建立一个公共溢出区
- 链地址法(拉链法)
存储实现:put(key,value)
public V put(K key, V value) {
//当key为null,调用putForNullKey方法,保存null与table第一个位置中,这是HashMap允许为null的原因
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
//计算key的hash值
int hash = hash(key.hashCode()); ------(1)
//计算key hash 值在 table 数组中的位置
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length); ------(2)
//从i出开始迭代 e,找到 key 保存的位置
for (Entry<K, V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
//判断该条链上是否有hash值相同的(key相同)
//若存在相同,则直接覆盖value,返回旧value
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value; //旧值 = 新值
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue; //返回旧值
}
}
//修改次数增加1
modCount++;
//将 key、value 添加至i位置处
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}
复制代码
(1)处代码实现:技术 hash 值
static int hash(int h) {
h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12);
return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4);
}
复制代码
(2)处代码实现:根据 hash 值计算出 key 在 table 数组中所对应的位置
static int indexFor(int h, int length) {
return h & (length-1);
}
复制代码
(3)将节点插入表头
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
//获取bucketIndex处的Entry
Entry<K, V> e = table[bucketIndex];
//将新创建的 Entry 放入 bucketIndex 索引处,并让新的 Entry 指向原来的 Entry
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<K, V>(hash, key, value, e);
//若HashMap中元素的个数超过极限了,则容量扩大两倍
if (size++ >= threshold)
resize(2 * table.length);
}
复制代码
存储步骤:
- step 1:判断 key 是否为 null,若为 null,那么直接调用 putForNullKey 方法(table[0] 的数组项),否则进入 step2;
- step 2:计算 key 的 hash 值
- step 3:计算 key 的 hash 值在 table 数组中的位置 index
- step 4:在 table[index] 项中迭代,找出 key 的存储位置,如果存在则替换就的值,并将旧的值返回,如果不存在对应的 key 的存储位置,则进入 step5;
- step 5:将 key-value 放在 table[index] 的链表头
扩容问题
随着 HashMap 中的元素越来越多,发生 hash 冲突的概率越来越大,链表的长度越来越长,查找的效率就越来越低;这样我们就必须在 HashMap 的某个临界值进行扩容处理。扩容的方式:重新创建一个新的 table 数组,重新计算 key 的 hash 值,并放入新的 table 数组中,这样的操作是比较耗时的,如果我们能够预知 HashMap 中的大小时,我们可以指定 HashMap 中的元素个数。
- 读取实现:get(key) 通过 key 的 hash 值找到在 table 数组中的索引处的 Entry,然后返回该 key 对应的 value 即可。
public V get(Object key) {
// 若为null,调用getForNullKey方法返回相对应的value
if (key == null)
return getForNullKey();
// 根据该 key 的 hashCode 值计算它的 hash 码
int hash = hash(key.hashCode());
// 取出 table 数组中指定索引处的值
for (Entry<K, V> e = table[indexFor(hash, table.length)]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
//若搜索的key与查找的key相同,则返回相对应的value
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k)))
return e.value;
}
return null;
}
复制代码
HashMap 非同步
HashMap 是线程不安全的,我们可以通过 Collections 的静态方法 SynchronizedMap 来获取线程安全的 HashMap
Map map = Collections.SynchronizedMap(new HashMap<>(); 复制代码
LinkedHashMap
介绍
- LinkedHashMap 是 HashMap 的子类,因此 LinkedHashMap 拥有 HashMap 中的所有特性,但是 HashMap 的迭代是没有顺序的。LinkedHashMap 通过维护一个双链表来保证迭代的顺序( 插入顺序或者访问顺序 ),但是同时也增加了时间和空间的开销。
数据结构
- HashMap(数组+链表)+双链表
双链表
``
/**
* HashMap.Node subclass for normal LinkedHashMap entries.
*/
static class LinkedHashMapEntry<K,V> extends HashMap.Node<K,V> {
LinkedHashMapEntry<K,V> before, after;
LinkedHashMapEntry(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
super(hash, key, value, next);
}
}
```
复制代码
重要变量
- head:双链表头部,保存最早插入的元素。
- tail:双链表的尾部,保存最近插入的元素。
- accessOrder:访问顺序(true:访问顺序迭代;false:插入顺序迭代)
重要函数
// Callbacks to allow LinkedHashMap post-actions
// 访问元素之后
void afterNodeAccess(Node<K,V> p) { }
// 插入节点之后
void afterNodeInsertion(boolean evict) { }
// 删除节点之后
void afterNodeRemoval(Node<K,V> p) { }
复制代码
HashMap 和 HashTable 的区别
HashTable 和 HashMap 都实现了 Map 接口,他们的主要区别在于线程安全、速度。
- HashMap 可以接受 key 为 null,HashTable 不可以接受 key 为 null
- HashMap 是线程不安全(非 synchronize),HashTable 是线程安全的(synchronize)。synchronize 代表着每一次在一个线程中修改 HashTable 中的数据时,都需要获得同步锁,其他的线程要修改 HashTable 中的数据时,需要等待同步锁被释放才能进行。
- HashMap 的迭代器是 Iterator,HashTable 的迭代器是 enumerator。
- 在单线程的操作中,HashMap 的操作速度要比 HashTable 快,因为 HashTable 是 synchronize 的,所以会有同步锁的获取和释放过程。
- 本文标签: 安全 HashTable CTO 同步 tab Collection NSA equals key ACE 线程 HashMap rand 空间 final 源码 IO 数据 ArrayList Collections 删除 集合类 zab 时间 锁 java ORM UI LinkedList DOM http https id 代码 synchronized list Action map 索引 遍历 src node 垃圾回收 多线程 静态方法 value queue
- 版权声明: 本文为互联网转载文章,出处已在文章中说明(部分除外)。如果侵权,请联系本站长删除,谢谢。
- 本文海报: 生成海报一 生成海报二










![[HBLOG]公众号](https://www.liuhaihua.cn/img/qrcode_gzh.jpg)

