Spring Security 实现 API Token 权限认证
常见的权限认证是通过提供“用户名密码”完成,业务中有一些 API,我们希望以 API Token 的形式验证。例如 URL 上加上 token /api?token=xxxx 就允许API 的访问。这种设计背后的逻辑是用户名密码拥有较高的权限,而 API token 可以只给出某个子系统的权限,类似于 Github 的 Personal API Tokens 。
本文会介绍如何用 Spring Security 来实现。Spring Security 虽然功能强大,但配置起来经常让人云里雾里,所以我们要试图了解一些 Spring Security 的工作原理,再具体实现 API Token 的权限认证。
Spring Security 基本原理
Java Servlet 和 Spring Security 都使用了设计模式中的 责任链模式 。简单地说,它们都定义了许多过滤器(Filter),每一个请求都会经过层层过滤器的处理,最终返回。如下图:
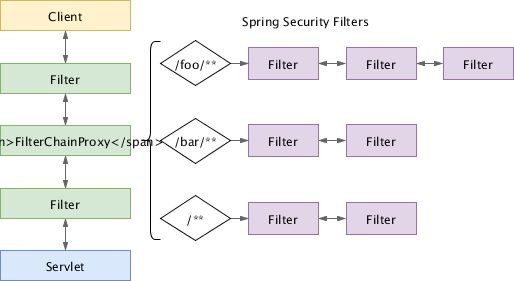
其中,Spring Security 在 Servlet 的过滤链(filter chain)中注册了一个过滤器 FilterChainProxy ,它会把请求代理到 Spring Security 自己维护的多个过滤链,每个过滤链会匹配一些 URL,如图中的 /foo/** ,如果匹配则执行对应的过滤器。过滤链是有顺序的,一个请求只会执行第一条匹配的过滤链。Spring Security 的配置本质上就是新增、删除、修改过滤器。下图是配置了 http.formLogin() 的过滤链:
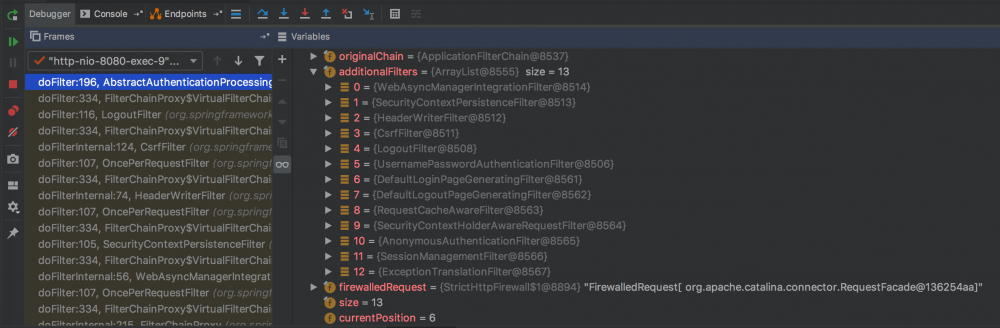
可以看到默认的过滤器里包含了许多内容,如 CsrfFilter 来生成和校验 CSRF Token , UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 来处理用户名密码的认证, SessionManagementFilter 来管理 Session 等等。而我们关心的“权限认证”,它其实分为两个部分:
- 认证(Authentication):即证明“你是你”,常见的如果用户名密码匹配,则认为操作者是该用户。
- 授权(Authorization):即判断“你有没有资格”,例如“删贴”功能只允许管理员使用。
认证(Authentication)
以用户名密码的方式为例,要认证一个用户是不是系统的用户,我们需要两个步骤:
Authentication
验证用户、密码的逻辑一般需要自定义且常常会比较复杂,Spring Security 中的 AuthenticationManager 定义了验证的接口:
public interface AuthenticationManager {
Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException;
}
AuthenticationException
Spring Security 内部使用最多的实现是 ProviderManager ,而它内部又使用了一个认证的链条,包含了多个 AuthenticationProvier , ProviderManager 会逐一调用它们直到有一个 provider成功返回。
public interface AuthenticationProvider {
Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException;
boolean supports(Class<?> authentication);
}
与 AuthenticationManager 不同的是它多了一个 supports 方法用来判断Provider 是否支持当前的认证信息。如一个 API Token 的认证器就不支持用户名密码的认证信息。
另外,ProviderManager 还定义了父子关系,如果当前 ProviderManager 中所有的 Provier 都无法认证某个信息,它就会让父 ProviderManager 来判断。如图:
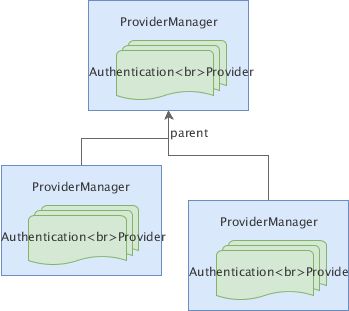
理论上我们不需要理解这些内容,完全可以自己编写一个过滤器来处理所有需求。只是如果使用了这套接口,就能享受 Spring Security 的一些“基础设施”,例如抛 AuthenticationException 时, ExceptionTranslationFilter 会调用配置好的 authenticationEntryPoint.commence() 方法进行处理,返回 401 等等。
授权(Authorization)
要判断“你有没有资格”,首先要知道关于“你”的信息,也就是前一小节中说的 Authentication 接口;其次需要知道要访问的资源及资源的配置,如要访问 URL,该 URL 能被什么角色访问。类似地,Spring Security 已经定义了相关的接口,授权会在 FilterSecurityInterceptor 中启动。
public interface AccessDecisionManager {
void decide(Authentication authentication,
Object object,
Collection<ConfigAttribute> configAttributes)
throws AccessDeniedException, InsufficientAuthenticationException;
boolean supports(ConfigAttribute attribute);
boolean supports(Class<?> clazz);
}
函数 decide 会决定授权是否成功,如果权限不足则抛 AccessDeniedException 异常。函数参数说明:
-
authentication代表了“认证信息”,从中可以获得诸如当前用户的角色等信息 -
object即要访问的资源,如某个 URL 或是某个函数 -
configAttributes代表该资源的配置,如该 URL 只能被“管理员”角色(ROLE_ADMIN)访问。
Spring Security 中,具体的授权策略是“投票机制”,每一个 AccessDecisionVoter 都能投票,而最后如何统计结果,由 AccessDecisionManager 的具体实现决定。如 AffirmativeBased 只需要有人赞成即可; ConsensusBased 需要多数人赞成; UnanimousBased 需要所有人赞成。默认使用 AffirmativeBased 。
同 Authentication 一样,遵循这套逻辑,Spring Security 的默认配置就能减少我们的工作量。例如上面提到的投票机制,还有抛 AccessDeniedException 异常时返回 403 等处理。
配置
Spring Security 的运行原理不难理解,但如何达到想要的配置一直是我学习时的痛点。这里也只是简要说明,具体的配置不是三言两语能说清的。下面举一个简单的示例,说明一些对应关系:
@Configuration
@Order(1)
public class TokenSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter { // ①
// ②
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.authenticationProvider(new TokenAuthenticationProvider(tokenService));
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.antMatcher("/api/v1/square/**") // ③
.addFilterAfter(new TokenAuthenticationFilter(), BasicAuthenticationFilter.class) // ④
.authorizeRequests()
.anyRequest().hasRole("API"); // ⑤
}
}
- 继承
WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter开始。之前提到 Spring Security 可以包含多条过滤链,每个WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter对应一条过滤链。③ 中指定要匹配的 URL 模式,顺序由@Order指定。 - 重载
configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth)方法来配置认证逻辑,一份WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter配置会生成一个ProviderManager,而这个configure方法可以提供多个AuthenticationProvier。 - 指定当前过滤链要匹配的 URL 模式。用
antMatcher指定一个模式,使用requestMatcher或requestMatchers来进行高级配置,如指定多个模式。 - 通过
addFilter相关方法可以在当前过滤链中添加过滤器,但似乎没有删除的方法。 -
hasRole等用来指定“授权”的逻辑,比如该行表示访问所有的 URL 都需要API角色。
API Token 实现
要实现开头说的 API Token 的权限认证,我们需要下面几样东西:
Authentication AuthenticationProvier
认证信息
由于 API token 只需要存放 token 本身即可,所以实现如下:
public class TokenAuthentication implements Authentication {
private String token;
private TokenAuthentication(String token) {
this.token = token;
}
@Override
public Object getCredentials() {
return token;
}
// ... 省略其它方法
}
抽取 token 的过滤器
因为 token 信息是在 URL 中指定的,所以这个过滤器会读取 URL 中的 parameter 并生成上节定义的 TokenAuthentication :
public class TokenAuthenticationFilter extends OncePerRequestFilter { // ①
@Override
protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse res, FilterChain fc)
throws ServletException, IOException {
SecurityContext context = SecurityContextHolder.getContext();
if (context.getAuthentication() != null && context.getAuthentication().isAuthenticated()) {
// do nothing
} else {
// ②
Map<String, String[]> params = req.getParameterMap();
if (!params.isEmpty() && params.containsKey("token")) {
String token = params.get("token")[0];
if (token != null) {
Authentication auth = new TokenAuthentication(token);
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(auth);
}
}
req.setAttribute("me.lotabout.springsecurityexample.security.TokenAuthenticationFilter.FILTERED", true); //③
}
fc.doFilter(req, res); //④
}
}
OncePerRequestFilter
校验逻辑
上面会 URL 中获得 Token,我们需要与数据库中的 token 比较看是否一致,这里就用内存中的比较代替:
public class TokenAuthenticationProvider implements AuthenticationProvider {
@Override
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
if (authentication.isAuthenticated()) {
return authentication;
}
// 从 TokenAuthentication 中获取 token
String token = authentication.getCredentials().toString();
if (Strings.isNullOrEmpty(token)) {
return authentication;
}
if (!token.equals("abcdefg")) {
throw ResultException.of(MyError.TOKEN_NOT_FOUND).errorData(token);
}
User user = User.builder()
.username("api")
.password("")
.authorities(Role.API)
.build();
// 返回新的认证信息,带上 token 和反查出的用户信息
Authentication auth = new PreAuthenticatedAuthenticationToken(user, token, user.getAuthorities());
auth.setAuthenticated(true);
return auth;
}
@Override
public boolean supports(Class<?> aClass) {
return (TokenAuthenticationFilter.TokenAuthentication.class.isAssignableFrom(aClass));
}
}
错误处理
我们希望在错误时,返回 200 状态码,同时 body 中包含 "success": false 及具体的错误信息。
public class ResultExceptionTranslationFilter extends GenericFilterBean {
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain fc) throws IOException, ServletException {
try {
fc.doFilter(request, response);
} catch (ResultException ex) {
response.setContentType("application/json; charset=UTF-8");
response.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
response.getWriter().println(JsonUtil.toJson(Response.of(ex)));
response.getWriter().flush();
}
}
}
组装配置
具体的配置和上面提到的差不多,注意到我们还关闭了 CSRF 和 Session。
@Configuration
@Order(1)
public class PredictorSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.authenticationProvider(new TokenAuthenticationProvider(tokenService));
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.antMatcher(PATTERN_SQUARE)
.addFilterAfter(new TokenAuthenticationFilter(), BasicAuthenticationFilter.class)
.addFilterAfter(new ResultExceptionTranslationFilter(), ExceptionTranslationFilter.class)
.authorizeRequests()
.anyRequest().hasRole("API")
.and()
.csrf()
.disable()
.sessionManagement()
.sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS);
}
}
完整的代码可以在 Spring Security Example 找到。
小结
每次用 Spring Security 都是现搜现用,如果示例不工作时往往不知道如何处理,所以这些更深入地学习了原理并做了笔记,希望各位看官用得上。
- Spring Security 会注册 FilterChainProxy,自身包含多个 Filter Chain
- 认证 Authentication 与授权 Authorization 是分开的两套逻辑
-
AuthenticationManager包含多个AuthenticationProvider且可以有父节点 - 授权的入口是
AccessDecisionManager,它的几个实现类代表着不同的投票方法。 - 每个继承
WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter的类定义一条新的 Filter Chain
最后我们用了上面的知识实现了基于 API token 的认证,授权仍旧用的 Spring Security 默认的机制。
参考
- https://spring.io/guides/topicals/spring-security-architecture/ Spring Security 官方架构文档,本文的知识很多来源于此
- Spring Security源码分析一:Spring Security认证过程 详细认证过程分析,对于理解认证链路很有帮助。
- Spring Security源码分析二:Spring Security授权过程
- 本文标签: 删除 authenticate IO map 需求 equals example spring Authorization git id IDE json http 认证 ORM cat 代码 session Uber 云 Architect servlet 希望 数据 App 统计 源码 bean 数据库 GitHub token provider ACE 工作原理 UI CTO 2019 src web Service js API 本质 参数 Word tab Collection 配置 设计模式 Proxy build java Security https 管理 Spring Security key
- 版权声明: 本文为互联网转载文章,出处已在文章中说明(部分除外)。如果侵权,请联系本站长删除,谢谢。
- 本文海报: 生成海报一 生成海报二










![[HBLOG]公众号](https://www.liuhaihua.cn/img/qrcode_gzh.jpg)

