Java中的转换器设计模式
在这篇文章中,我们将讨论 Java / J2EE项目中最常用的 Converter Design Pattern。由于Java8 功能不仅提供了相应类型之间的通用双向转换方式,而且还提供了转换相同类型对象集合的常用方法,从而将样板代码减少到绝对最小值。我们使用Java8 功能编写了此模式的源代码。
目的
转换器设计模式的目的是为相应类型之间的双向转换提供一种通用的方式,允许类型无需彼此了解的简洁的实现。此外,转换器设计模式引入了双向收集映射,将样板代码减少到最小。
源代码
转换器设计模式是一种行为设计模式,允许在相应类型(如DTO和逻辑同构类型的域表示)之间进行双向转换。此外,该模式还引入了一种在类型之间转换对象集合的通用方法。
类图
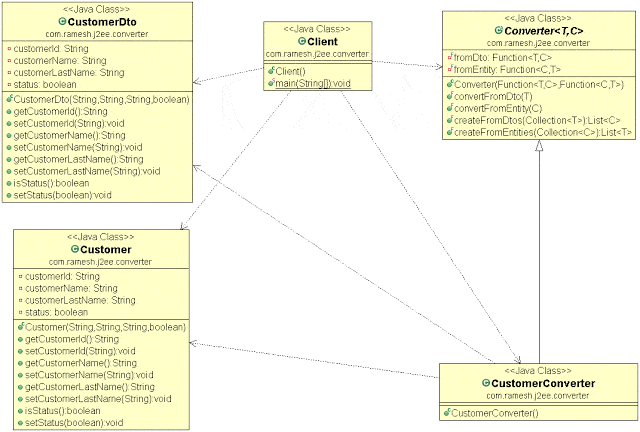
让我们根据上面的类图编写源代码。
在本例中,我们将把customerd转换为customer实体,反之亦然,我们还将在类型之间转换对象集合。
步骤1:让我们创建一个通用转换器。
<b>public</b> <b>abstract</b> <b>class</b> Converter < T, C > {
<b>private</b> <b>final</b> Function < T,
C > fromDto;
<b>private</b> <b>final</b> Function < C,
T > fromEntity;
<font><i>/**
* @param fromDto
* Function that converts given dto entity into the domain
* entity.
* @param fromEntity
* Function that converts given domain entity into the dto
* entity.
*/</i></font><font>
<b>public</b> Converter(<b>final</b> Function < T, C > fromDto, <b>final</b> Function < C, T > fromEntity) {
<b>this</b>.fromDto = fromDto;
<b>this</b>.fromEntity = fromEntity;
}
</font><font><i>/**
* @param customerDto
* DTO entity
* @return The domain representation - the result of the converting function
* application on dto entity.
*/</i></font><font>
<b>public</b> <b>final</b> C convertFromDto(<b>final</b> T customerDto) {
<b>return</b> fromDto.apply(customerDto);
}
</font><font><i>/**
* @param customer
* domain entity
* @return The DTO representation - the result of the converting function
* application on domain entity.
*/</i></font><font>
<b>public</b> <b>final</b> T convertFromEntity(<b>final</b> C customer) {
<b>return</b> fromEntity.apply(customer);
}
</font><font><i>/**
* @param dtoCustomers
* collection of DTO entities
* @return List of domain representation of provided entities retrieved by
* mapping each of them with the conversion function
*/</i></font><font>
<b>public</b> <b>final</b> List < C > createFromDtos(<b>final</b> Collection < T > dtoCustomers) {
<b>return</b> dtoCustomers.stream().map(<b>this</b>::convertFromDto).collect(Collectors.toList());
}
</font><font><i>/**
* @param customers
* collection of domain entities
* @return List of domain representation of provided entities retrieved by
* mapping each of them with the conversion function
*/</i></font><font>
<b>public</b> <b>final</b> List < T > createFromEntities(<b>final</b> Collection < C > customers) {
<b>return</b> customers.stream().map(<b>this</b>::convertFromEntity).collect(Collectors.toList());
}
}
</font>
步骤2:让我们创建一个简单客户转换器的实现。
<b>public</b> <b>class</b> CustomerConverter <b>extends</b> Converter<CustomerDto, Customer> {
<b>public</b> CustomerConverter() {
<b>super</b>(customerDto -> <b>new</b> Customer(customerDto.getCustomerId(), customerDto.getCustomerName(),
customerDto.getCustomerLastName(), customerDto.isStatus()),
customer -> <b>new</b> CustomerDto(customer.getCustomerId(), customer.getCustomerName(),
customer.getCustomerLastName(), customer.isStatus()));
}
}
步骤3: 创建customerdto类。
<b>public</b> <b>class</b> CustomerDto {
<b>private</b> String customerId;
<b>private</b> String customerName;
<b>private</b> String customerLastName;
<b>private</b> <b>boolean</b> status;
<b>public</b> CustomerDto(String customerId, String customerName, String customerLastName, <b>boolean</b> status) {
<b>super</b>();
<b>this</b>.customerId = customerId;
<b>this</b>.customerName = customerName;
<b>this</b>.customerLastName = customerLastName;
<b>this</b>.status = status;
}
<b>public</b> String getCustomerId() {
<b>return</b> customerId;
}
<b>public</b> <b>void</b> setCustomerId(String customerId) {
<b>this</b>.customerId = customerId;
}
<b>public</b> String getCustomerName() {
<b>return</b> customerName;
}
<b>public</b> <b>void</b> setCustomerName(String customerName) {
<b>this</b>.customerName = customerName;
}
<b>public</b> String getCustomerLastName() {
<b>return</b> customerLastName;
}
<b>public</b> <b>void</b> setCustomerLastName(String customerLastName) {
<b>this</b>.customerLastName = customerLastName;
}
<b>public</b> <b>boolean</b> isStatus() {
<b>return</b> status;
}
<b>public</b> <b>void</b> setStatus(<b>boolean</b> status) {
<b>this</b>.status = status;
}
}
步骤4: 创建Customer实体类。
<b>public</b> <b>class</b> Customer {
<b>private</b> String customerId;
<b>private</b> String customerName;
<b>private</b> String customerLastName;
<b>private</b> <b>boolean</b> status;
<b>public</b> Customer(String customerId, String customerName, String customerLastName, <b>boolean</b> status) {
<b>super</b>();
<b>this</b>.customerId = customerId;
<b>this</b>.customerName = customerName;
<b>this</b>.customerLastName = customerLastName;
<b>this</b>.status = status;
}
<b>public</b> String getCustomerId() {
<b>return</b> customerId;
}
<b>public</b> <b>void</b> setCustomerId(String customerId) {
<b>this</b>.customerId = customerId;
}
<b>public</b> String getCustomerName() {
<b>return</b> customerName;
}
<b>public</b> <b>void</b> setCustomerName(String customerName) {
<b>this</b>.customerName = customerName;
}
<b>public</b> String getCustomerLastName() {
<b>return</b> customerLastName;
}
<b>public</b> <b>void</b> setCustomerLastName(String customerLastName) {
<b>this</b>.customerLastName = customerLastName;
}
<b>public</b> <b>boolean</b> isStatus() {
<b>return</b> status;
}
<b>public</b> <b>void</b> setStatus(<b>boolean</b> status) {
<b>this</b>.status = status;
}
}
步骤5: 现在,让我们通过创建Client类来测试这个模式。
<b>public</b> <b>class</b> Client {
<font><i>/**
* Program entry point
*
* @param args command line args
*/</i></font><font>
<b>public</b> <b>static</b> <b>void</b> main(String[] args) {
Converter < CustomerDto, Customer > CustomerConverter = <b>new</b> CustomerConverter();
CustomerDto dtoCustomer = <b>new</b> CustomerDto(</font><font>"100"</font><font>, </font><font>"Ramesh"</font><font>, </font><font>"Fadatare"</font><font>, <b>true</b>);
Customer Customer = CustomerConverter.convertFromDto(dtoCustomer);
System.out.println(</font><font>"Entity converted from DTO:"</font><font> + Customer);
List < Customer > customers = <b>new</b> ArrayList < > ();
customers.add(<b>new</b> Customer(</font><font>"100"</font><font>, </font><font>"Ramesh1"</font><font>, </font><font>"Fadatare"</font><font>, <b>true</b>));
customers.add(<b>new</b> Customer(</font><font>"200"</font><font>, </font><font>"Ramesh2"</font><font>, </font><font>"Fadatare"</font><font>, <b>true</b>));
customers.add(<b>new</b> Customer(</font><font>"300"</font><font>, </font><font>"Ramesh3"</font><font>, </font><font>"Fadatare"</font><font>, <b>true</b>));
customers.forEach(System.out::println);
customers.forEach((customer) - > System.out.println(customer.getCustomerId()));
System.out.println(</font><font>"DTO entities converted from domain:"</font><font>);
List < CustomerDto > dtoEntities = CustomerConverter.createFromEntities(customers);
dtoEntities.forEach(System.out::println);
dtoEntities.forEach((customer) - > System.out.println(customer.getCustomerId()));
}
}
</font>
输出:
Entity converted from DTO:com.ramesh.j2ee.converter.Customer@87aac27 com.ramesh.j2ee.converter.Customer@1b28cdfa com.ramesh.j2ee.converter.Customer@eed1f14 com.ramesh.j2ee.converter.Customer@7229724f 100 200 300 DTO entities converted from domain: com.ramesh.j2ee.converter.CustomerDto@4dd8dc3 com.ramesh.j2ee.converter.CustomerDto@6d03e736 com.ramesh.j2ee.converter.CustomerDto@568db2f2 100 200 300
适用性
在以下情况下 使用 转换器模式 :
- 当您拥有逻辑上与其他类型相对应的类型时,您需要在它们之间转换实体
- 如果要根据上下文提供不同类型的转换方式
- 每当您引入DTO(数据传输对象)时,您可能需要将其转换为域等效。
正文到此结束
热门推荐
相关文章
Loading...










![[HBLOG]公众号](https://www.liuhaihua.cn/img/qrcode_gzh.jpg)

