Dubbo源码解析(二十三)远程调用——Proxy
目标:介绍远程调用代理的设计和实现,介绍dubbo-rpc-api中的各种proxy包的源码。
前言
首先声明叫做代理,代理在很多领域都存在,最形象的就是现在朋友圈的代理,厂家委托代理帮他们卖东西。这样做厂家对于消费者来说就是透明的,并且代理可以自己加上一些活动或者销售措施,但这并不影响到厂家。这里的厂家就是委托类,而代理就可以抽象为代理类。这样做有两个优点,第一是可以隐藏代理类的实现,第二就是委托类和调用方的解耦,并且能够在不修改委托类原本的逻辑情况下新增一些额外的处理。
代理分为两种,静态代理和动态代理。
- 静态代理:如果代理类在程序运行前就已经存在,那么这种代理就是静态代理。
- 动态代理:代理类在程序运行时创建的代理方式。动态代理关系由两组静态代理关系组成,这就是动态代理的原理。
上述稍微回顾了一下静态代理和动态代理,那么dubbo对于动态代理有两种方法实现,分别是javassist和jdk。Proxy 层封装了所有接口的透明化代理,而在其它层都以 Invoker 为中心,只有到了暴露给用户使用时,才用 Proxy 将 Invoker 转成接口,或将接口实现转成 Invoker,也就是去掉 Proxy 层 RPC 是可以 Run 的,只是不那么透明,不那么看起来像调本地服务一样调远程服务。我们来看看下面的图:
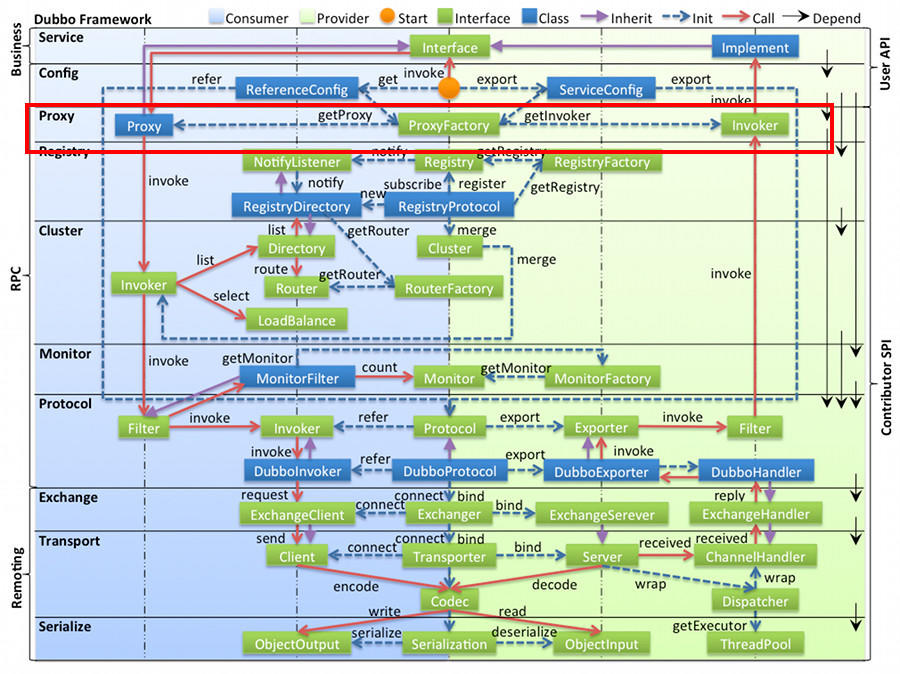
我们能看到左边是消费者的调用链,只有当消费者调用的时候,ProxyFactory才会通过Proxy把接口实现转化为invoker,并且在其他层的调用都使用的是invoker,同样的道理,在服务提供者暴露服务的时候,也只有在最后暴露给消费者的时候才会通过Proxy 将 Invoker 转成接口。
动态代理的底层原理就是字节码技术,dubbo提供了两种方式来实现代理:
- 第一种jdk,jdk动态代理比较简单,它内置在JDK中,因此不依赖第三方jar包,但是功能相对较弱,当调用Proxy 的静态方法创建动态代理类时,类名格式是“$ProxyN”,N代表第 N 次生成的动态代理类,如果重复创建动态代理类会直接返回原先创建的代理类。但是这个以“$ProxyN”命名的类是继承Proxy类的,并且实现了其所代理的一组接口,这里就出现了它的一个局限性,由于java的类只能单继承,所以JDK动态代理仅支持接口代理。
- 第二种是Javassist,Javassist是一款Java字节码引擎工具,能够在运行时编译生成class。该方法也是代理的默认方法。
源码分析
(一)AbstractProxyFactory
该类是代理工厂的抽象类,主要处理了一下需要代理的接口,然后把代理getProxy方法抽象出来。
public abstract class AbstractProxyFactory implements ProxyFactory {
@Override
public <T> T getProxy(Invoker<T> invoker) throws RpcException {
return getProxy(invoker, false);
}
@Override
public <T> T getProxy(Invoker<T> invoker, boolean generic) throws RpcException {
Class<?>[] interfaces = null;
// 获得需要代理的接口
String config = invoker.getUrl().getParameter("interfaces");
if (config != null && config.length() > 0) {
// 根据逗号把每个接口分割开
String[] types = Constants.COMMA_SPLIT_PATTERN.split(config);
if (types != null && types.length > 0) {
// 创建接口类型数组
interfaces = new Class<?>[types.length + 2];
// 第一个放invoker的服务接口
interfaces[0] = invoker.getInterface();
// 第二个位置放回声测试服务的接口类
interfaces[1] = EchoService.class;
// 其他接口循环放入
for (int i = 0; i < types.length; i++) {
interfaces[i + 1] = ReflectUtils.forName(types[i]);
}
}
}
// 如果接口为空,就是config为空,则是回声测试
if (interfaces == null) {
interfaces = new Class<?>[]{invoker.getInterface(), EchoService.class};
}
// 如果是泛化服务,那么在代理的接口集合中加入泛化服务类型
if (!invoker.getInterface().equals(GenericService.class) && generic) {
int len = interfaces.length;
Class<?>[] temp = interfaces;
interfaces = new Class<?>[len + 1];
System.arraycopy(temp, 0, interfaces, 0, len);
interfaces[len] = GenericService.class;
}
// 获得代理
return getProxy(invoker, interfaces);
}
public abstract <T> T getProxy(Invoker<T> invoker, Class<?>[] types);
}
复制代码
逻辑比较简单,就是处理了url中携带的interfaces的值。
(二)AbstractProxyInvoker
该类实现了Invoker接口,是代理invoker对象的抽象类。
@Override
public Result invoke(Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
try {
// 调用了抽象方法doInvoke
return new RpcResult(doInvoke(proxy, invocation.getMethodName(), invocation.getParameterTypes(), invocation.getArguments()));
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
return new RpcResult(e.getTargetException());
} catch (Throwable e) {
throw new RpcException("Failed to invoke remote proxy method " + invocation.getMethodName() + " to " + getUrl() + ", cause: " + e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
protected abstract Object doInvoke(T proxy, String methodName, Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Object[] arguments) throws Throwable;
复制代码
该类最关键的就是这两个方法,一个是invoke方法,调用了抽象方法doInvoke,另一个则是抽象方法。该方法被子类实现。
(三)InvokerInvocationHandler
该类实现了InvocationHandler接口,动态代理类都必须要实现InvocationHandler接口,而该类实现的是对于基础方法不适用rpc调用,其他方法使用rpc调用。
public class InvokerInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler {
private final Invoker<?> invoker;
public InvokerInvocationHandler(Invoker<?> handler) {
this.invoker = handler;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
// 获得方法名
String methodName = method.getName();
// 获得参数类型
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
// 如果方法参数类型是object类型,则直接反射调用
if (method.getDeclaringClass() == Object.class) {
return method.invoke(invoker, args);
}
// 基础方法,不使用 RPC 调用
if ("toString".equals(methodName) && parameterTypes.length == 0) {
return invoker.toString();
}
if ("hashCode".equals(methodName) && parameterTypes.length == 0) {
return invoker.hashCode();
}
if ("equals".equals(methodName) && parameterTypes.length == 1) {
return invoker.equals(args[0]);
}
// rpc调用
return invoker.invoke(new RpcInvocation(method, args)).recreate();
}
}
复制代码
(四)StubProxyFactoryWrapper
该类实现了本地存根的逻辑,关于本地存根的概念和使用在官方文档中都有详细说明。
地址: dubbo.apache.org/zh-cn/docs/…
public class StubProxyFactoryWrapper implements ProxyFactory {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(StubProxyFactoryWrapper.class);
/**
* 代理工厂
*/
private final ProxyFactory proxyFactory;
/**
* 协议
*/
private Protocol protocol;
public StubProxyFactoryWrapper(ProxyFactory proxyFactory) {
this.proxyFactory = proxyFactory;
}
public void setProtocol(Protocol protocol) {
this.protocol = protocol;
}
@Override
public <T> T getProxy(Invoker<T> invoker, boolean generic) throws RpcException {
return proxyFactory.getProxy(invoker, generic);
}
@Override
@SuppressWarnings({"unchecked", "rawtypes"})
public <T> T getProxy(Invoker<T> invoker) throws RpcException {
// 获得代理类对象
T proxy = proxyFactory.getProxy(invoker);
// 如果不是返回服务调用
if (GenericService.class != invoker.getInterface()) {
// 获得stub的配置
String stub = invoker.getUrl().getParameter(Constants.STUB_KEY, invoker.getUrl().getParameter(Constants.LOCAL_KEY));
// 如果配置不为空
if (ConfigUtils.isNotEmpty(stub)) {
Class<?> serviceType = invoker.getInterface();
if (ConfigUtils.isDefault(stub)) {
// 根据local和stub来生成stub
if (invoker.getUrl().hasParameter(Constants.STUB_KEY)) {
stub = serviceType.getName() + "Stub";
} else {
stub = serviceType.getName() + "Local";
}
}
try {
// 生成stub类
Class<?> stubClass = ReflectUtils.forName(stub);
if (!serviceType.isAssignableFrom(stubClass)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("The stub implementation class " + stubClass.getName() + " not implement interface " + serviceType.getName());
}
try {
// 获得构造方法,该构造方法必须是带有代理的对象的参数
Constructor<?> constructor = ReflectUtils.findConstructor(stubClass, serviceType);
// 使用指定的初始化参数创建和初始化构造函数声明类的新实例
proxy = (T) constructor.newInstance(new Object[]{proxy});
//export stub service
URL url = invoker.getUrl();
if (url.getParameter(Constants.STUB_EVENT_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_STUB_EVENT)) {
url = url.addParameter(Constants.STUB_EVENT_METHODS_KEY, StringUtils.join(Wrapper.getWrapper(proxy.getClass()).getDeclaredMethodNames(), ","));
url = url.addParameter(Constants.IS_SERVER_KEY, Boolean.FALSE.toString());
try {
// 暴露stub服务
export(proxy, (Class) invoker.getInterface(), url);
} catch (Exception e) {
LOGGER.error("export a stub service error.", e);
}
}
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No such constructor /"public " + stubClass.getSimpleName() + "(" + serviceType.getName() + ")/" in stub implementation class " + stubClass.getName(), e);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
LOGGER.error("Failed to create stub implementation class " + stub + " in consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost() + " use dubbo version " + Version.getVersion() + ", cause: " + t.getMessage(), t);
// ignore
}
}
}
return proxy;
}
@Override
public <T> Invoker<T> getInvoker(T proxy, Class<T> type, URL url) throws RpcException {
return proxyFactory.getInvoker(proxy, type, url);
}
private <T> Exporter<T> export(T instance, Class<T> type, URL url) {
return protocol.export(proxyFactory.getInvoker(instance, type, url));
}
复制代码
该类里面最重要的就是getProxy方法的实现,在该方法中先根据配置生成加载stub服务类,然后通过构造方法将代理的对象进行包装,最后暴露该服务,然后返回代理类对象。
(五)JdkProxyFactory
该类继承了AbstractProxyFactory,是jdk的代理工厂的主要逻辑。
public class JdkProxyFactory extends AbstractProxyFactory {
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T getProxy(Invoker<T> invoker, Class<?>[] interfaces) {
// 调用了 Proxy.newProxyInstance直接获得代理类
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader(), interfaces, new InvokerInvocationHandler(invoker));
}
@Override
public <T> Invoker<T> getInvoker(T proxy, Class<T> type, URL url) {
// 创建AbstractProxyInvoker对象
return new AbstractProxyInvoker<T>(proxy, type, url) {
@Override
protected Object doInvoke(T proxy, String methodName,
Class<?>[] parameterTypes,
Object[] arguments) throws Throwable {
// 反射获得方法
Method method = proxy.getClass().getMethod(methodName, parameterTypes);
// 执行方法
return method.invoke(proxy, arguments);
}
};
}
}
复制代码
不过逻辑实现比较简单,因为jdk中都封装好了,直接调用Proxy.newProxyInstance方法就可以获得代理类。
(六)JavassistProxyFactory
该类是基于Javassist实现的动态代理工厂类。
public class JavassistProxyFactory extends AbstractProxyFactory {
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T getProxy(Invoker<T> invoker, Class<?>[] interfaces) {
// 创建代理
return (T) Proxy.getProxy(interfaces).newInstance(new InvokerInvocationHandler(invoker));
}
@Override
public <T> Invoker<T> getInvoker(T proxy, Class<T> type, URL url) {
// TODO Wrapper cannot handle this scenario correctly: the classname contains '$'
// 创建Wrapper对象
final Wrapper wrapper = Wrapper.getWrapper(proxy.getClass().getName().indexOf('$') < 0 ? proxy.getClass() : type);
return new AbstractProxyInvoker<T>(proxy, type, url) {
@Override
protected Object doInvoke(T proxy, String methodName,
Class<?>[] parameterTypes,
Object[] arguments) throws Throwable {
// 调用方法
return wrapper.invokeMethod(proxy, methodName, parameterTypes, arguments);
}
};
}
}
复制代码
在这里看不出什么具体的实现,感觉看起来跟JdkProxyFactory差不多,下面我将讲解com.alibaba.dubbo.common.bytecode.Proxy类的getProxy方法和com.alibaba.dubbo.common.bytecode.Wrapper类的getWrapper方法。
(七)Proxy#getProxy()
public static Proxy getProxy(Class<?>... ics) {
// 获得代理类
return getProxy(ClassHelper.getClassLoader(Proxy.class), ics);
}
/**
* Get proxy.
*
* @param cl class loader.
* @param ics interface class array.
* @return Proxy instance.
*/
public static Proxy getProxy(ClassLoader cl, Class<?>... ics) {
// 最大的代理接口数限制是65535
if (ics.length > 65535)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("interface limit exceeded");
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
// 遍历代理接口,获取接口的全限定名并以分号分隔连接成字符串
for (int i = 0; i < ics.length; i++) {
// 获得类名
String itf = ics[i].getName();
// 判断是否为接口
if (!ics[i].isInterface())
throw new RuntimeException(itf + " is not a interface.");
Class<?> tmp = null;
try {
// 获得与itf对应的Class对象
tmp = Class.forName(itf, false, cl);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
}
// 如果通过类名获得的类型跟ics中的类型不一样,则抛出异常
if (tmp != ics[i])
throw new IllegalArgumentException(ics[i] + " is not visible from class loader");
// 拼接类
sb.append(itf).append(';');
}
// use interface class name list as key.
String key = sb.toString();
// get cache by class loader.
Map<String, Object> cache;
synchronized (ProxyCacheMap) {
// 通过类加载器获得缓存
cache = ProxyCacheMap.get(cl);
if (cache == null) {
cache = new HashMap<String, Object>();
ProxyCacheMap.put(cl, cache);
}
}
Proxy proxy = null;
synchronized (cache) {
do {
Object value = cache.get(key);
// 如果缓存中存在,则直接返回代理对象
if (value instanceof Reference<?>) {
proxy = (Proxy) ((Reference<?>) value).get();
if (proxy != null)
return proxy;
}
// 是等待生成的类型,则等待
if (value == PendingGenerationMarker) {
try {
cache.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
} else {
// 否则放入缓存中
cache.put(key, PendingGenerationMarker);
break;
}
}
while (true);
}
// AtomicLong自增生成代理类类名后缀id,防止冲突
long id = PROXY_CLASS_COUNTER.getAndIncrement();
String pkg = null;
ClassGenerator ccp = null, ccm = null;
try {
ccp = ClassGenerator.newInstance(cl);
Set<String> worked = new HashSet<String>();
List<Method> methods = new ArrayList<Method>();
for (int i = 0; i < ics.length; i++) {
// 判断是否为public
if (!Modifier.isPublic(ics[i].getModifiers())) {
// 获得该类的包名
String npkg = ics[i].getPackage().getName();
if (pkg == null) {
pkg = npkg;
} else {
if (!pkg.equals(npkg))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("non-public interfaces from different packages");
}
}
// 把接口加入到ccp的mInterfaces中
ccp.addInterface(ics[i]);
// 遍历每个类的方法
for (Method method : ics[i].getMethods()) {
// 获得方法描述 这个方法描述是自定义:
// 例如:int do(int arg1) => "do(I)I"
// 例如:void do(String arg1,boolean arg2) => "do(Ljava/lang/String;Z)V"
String desc = ReflectUtils.getDesc(method);
if (worked.contains(desc))
continue;
// 如果集合中不存在,则加入该描述
worked.add(desc);
int ix = methods.size();
// 获得方法返回类型
Class<?> rt = method.getReturnType();
// 获得方法参数类型
Class<?>[] pts = method.getParameterTypes();
// 新建一句代码
// 例如Object[] args = new Object[参数数量】
StringBuilder code = new StringBuilder("Object[] args = new Object[").append(pts.length).append("];");
// 每一个参数都生成一句代码
// 例如args[0] = ($w)$1;
// 例如 Object ret = handler.invoke(this, methods[3], args);
for (int j = 0; j < pts.length; j++)
code.append(" args[").append(j).append("] = ($w)$").append(j + 1).append(";");
code.append(" Object ret = handler.invoke(this, methods[" + ix + "], args);");
// 如果方法不是void类型
// 则拼接 return ret;
if (!Void.TYPE.equals(rt))
code.append(" return ").append(asArgument(rt, "ret")).append(";");
methods.add(method);
ccp.addMethod(method.getName(), method.getModifiers(), rt, pts, method.getExceptionTypes(), code.toString());
}
}
if (pkg == null)
pkg = PACKAGE_NAME;
// create ProxyInstance class.
String pcn = pkg + ".proxy" + id;
ccp.setClassName(pcn);
// 添加静态字段Method[] methods
ccp.addField("public static java.lang.reflect.Method[] methods;");
ccp.addField("private " + InvocationHandler.class.getName() + " handler;");
// 添加实例对象InvokerInvocationHandler hanler,添加参数为InvokerInvocationHandler的构造器
ccp.addConstructor(Modifier.PUBLIC, new Class<?>[]{InvocationHandler.class}, new Class<?>[0], "handler=$1;");
// 添加默认无参构造器
ccp.addDefaultConstructor();
// 使用toClass方法生成对应的字节码
Class<?> clazz = ccp.toClass();
clazz.getField("methods").set(null, methods.toArray(new Method[0]));
// create Proxy class.
// 生成的字节码对象为服务接口的代理对象
String fcn = Proxy.class.getName() + id;
ccm = ClassGenerator.newInstance(cl);
ccm.setClassName(fcn);
ccm.addDefaultConstructor();
ccm.setSuperClass(Proxy.class);
ccm.addMethod("public Object newInstance(" + InvocationHandler.class.getName() + " h){ return new " + pcn + "($1); }");
Class<?> pc = ccm.toClass();
proxy = (Proxy) pc.newInstance();
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e.getMessage(), e);
} finally {
// release ClassGenerator
// 重置类构造器
if (ccp != null)
ccp.release();
if (ccm != null)
ccm.release();
synchronized (cache) {
if (proxy == null)
cache.remove(key);
else
cache.put(key, new WeakReference<Proxy>(proxy));
cache.notifyAll();
}
}
return proxy;
}
复制代码
Proxy是是生成代理对象的工具类,跟JdkProxyFactory中用到的Proxy不是同一个,JdkProxyFactory中的是jdk自带的java.lang.reflect.Proxy。而该Proxy是dubbo基于javassit实现的com.alibaba.dubbo.common.bytecode.Proxy。该方法比较长,可以分开五个步骤来看:
- 遍历代理接口,获取接口的全限定名,并以分号分隔连接成字符串,以此字符串为key,查找缓存map,如果缓存存在,则获取代理对象直接返回。
- 由一个AtomicLong自增生成代理类类名后缀id,防止冲突
- 遍历接口中的方法,获取返回类型和参数类型,构建的方法体见注释
- 创建工具类ClassGenerator实例,添加静态字段Method[] methods,添加实例对象InvokerInvocationHandler hanler,添加参数为InvokerInvocationHandler的构造器,添加无参构造器,然后使用toClass方法生成对应的字节码。
- 4中生成的字节码对象为服务接口的代理对象,而Proxy类本身是抽象类,需要实现newInstance(InvocationHandler handler)方法,生成Proxy的实现类,其中proxy0即上面生成的服务接口的代理对象。
(八)Wrapper#getWrapper
public static Wrapper getWrapper(Class<?> c) {
// 判断c是否继承 ClassGenerator.DC.class ,如果是,则拿到父类,避免重复包装
while (ClassGenerator.isDynamicClass(c)) // can not wrapper on dynamic class.
c = c.getSuperclass();
// 如果类为object类型
if (c == Object.class)
return OBJECT_WRAPPER;
// 如果缓存里面没有该对象,则新建一个wrapper
Wrapper ret = WRAPPER_MAP.get(c);
if (ret == null) {
ret = makeWrapper(c);
WRAPPER_MAP.put(c, ret);
}
return ret;
}
private static Wrapper makeWrapper(Class<?> c) {
// 如果c不是似有类,则抛出异常
if (c.isPrimitive())
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Can not create wrapper for primitive type: " + c);
// 获得类名
String name = c.getName();
// 获得类加载器
ClassLoader cl = ClassHelper.getClassLoader(c);
// 设置属性的方法第一行public void setPropertyValue(Object o, String n, Object v){
StringBuilder c1 = new StringBuilder("public void setPropertyValue(Object o, String n, Object v){ ");
// 获得属性的方法第一行 public Object getPropertyValue(Object o, String n){
StringBuilder c2 = new StringBuilder("public Object getPropertyValue(Object o, String n){ ");
// 执行方法的第一行
StringBuilder c3 = new StringBuilder("public Object invokeMethod(Object o, String n, Class[] p, Object[] v) throws " + InvocationTargetException.class.getName() + "{ ");
// 添加每个方法中被调用对象的类型转换的代码
c1.append(name).append(" w; try{ w = ((").append(name).append(")$1); }catch(Throwable e){ throw new IllegalArgumentException(e); }");
c2.append(name).append(" w; try{ w = ((").append(name).append(")$1); }catch(Throwable e){ throw new IllegalArgumentException(e); }");
c3.append(name).append(" w; try{ w = ((").append(name).append(")$1); }catch(Throwable e){ throw new IllegalArgumentException(e); }");
Map<String, Class<?>> pts = new HashMap<String, Class<?>>(); // <property name, property types>
Map<String, Method> ms = new LinkedHashMap<String, Method>(); // <method desc, Method instance>
List<String> mns = new ArrayList<String>(); // method names.
List<String> dmns = new ArrayList<String>(); // declaring method names.
// get all public field.
// 遍历每个public的属性,放入setPropertyValue和getPropertyValue方法中
for (Field f : c.getFields()) {
String fn = f.getName();
Class<?> ft = f.getType();
// // 排除有static 和 transient修饰的属性
if (Modifier.isStatic(f.getModifiers()) || Modifier.isTransient(f.getModifiers()))
continue;
c1.append(" if( $2.equals(/"").append(fn).append("/") ){ w.").append(fn).append("=").append(arg(ft, "$3")).append("; return; }");
c2.append(" if( $2.equals(/"").append(fn).append("/") ){ return ($w)w.").append(fn).append("; }");
pts.put(fn, ft);
}
Method[] methods = c.getMethods();
// get all public method.
boolean hasMethod = hasMethods(methods);
// 在invokeMethod方法中添加try的代码
if (hasMethod) {
c3.append(" try{");
}
// 遍历方法
for (Method m : methods) {
// 忽律Object的方法
if (m.getDeclaringClass() == Object.class) //ignore Object's method.
continue;
// 判断方法名和方法参数长度
String mn = m.getName();
c3.append(" if( /"").append(mn).append("/".equals( $2 ) ");
// 方法参数长度
int len = m.getParameterTypes().length;
// 判断方法参数长度代码
c3.append(" && ").append(" $3.length == ").append(len);
// 若相同方法名存在多个,增加参数类型数组的比较判断
boolean override = false;
for (Method m2 : methods) {
if (m != m2 && m.getName().equals(m2.getName())) {
override = true;
break;
}
}
if (override) {
if (len > 0) {
for (int l = 0; l < len; l++) {
c3.append(" && ").append(" $3[").append(l).append("].getName().equals(/"")
.append(m.getParameterTypes()[l].getName()).append("/")");
}
}
}
c3.append(" ) { ");
// 如果返回类型是void,则return null,如果不是,则返回对应参数类型
if (m.getReturnType() == Void.TYPE)
c3.append(" w.").append(mn).append('(').append(args(m.getParameterTypes(), "$4")).append(");").append(" return null;");
else
c3.append(" return ($w)w.").append(mn).append('(').append(args(m.getParameterTypes(), "$4")).append(");");
c3.append(" }");
mns.add(mn);
if (m.getDeclaringClass() == c)
dmns.add(mn);
ms.put(ReflectUtils.getDesc(m), m);
}
if (hasMethod) {
c3.append(" } catch(Throwable e) { ");
c3.append(" throw new java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException(e); ");
c3.append(" }");
}
c3.append(" throw new " + NoSuchMethodException.class.getName() + "(/"Not found method ///"/"+$2+/"///" in class " + c.getName() + "./"); }");
// 处理get set方法
// deal with get/set method.
Matcher matcher;
for (Map.Entry<String, Method> entry : ms.entrySet()) {
String md = entry.getKey();
Method method = (Method) entry.getValue();
if ((matcher = ReflectUtils.GETTER_METHOD_DESC_PATTERN.matcher(md)).matches()) {
String pn = propertyName(matcher.group(1));
c2.append(" if( $2.equals(/"").append(pn).append("/") ){ return ($w)w.").append(method.getName()).append("(); }");
pts.put(pn, method.getReturnType());
} else if ((matcher = ReflectUtils.IS_HAS_CAN_METHOD_DESC_PATTERN.matcher(md)).matches()) {
String pn = propertyName(matcher.group(1));
c2.append(" if( $2.equals(/"").append(pn).append("/") ){ return ($w)w.").append(method.getName()).append("(); }");
pts.put(pn, method.getReturnType());
} else if ((matcher = ReflectUtils.SETTER_METHOD_DESC_PATTERN.matcher(md)).matches()) {
Class<?> pt = method.getParameterTypes()[0];
String pn = propertyName(matcher.group(1));
c1.append(" if( $2.equals(/"").append(pn).append("/") ){ w.").append(method.getName()).append("(").append(arg(pt, "$3")).append("); return; }");
pts.put(pn, pt);
}
}
c1.append(" throw new " + NoSuchPropertyException.class.getName() + "(/"Not found property ///"/"+$2+/"///" filed or setter method in class " + c.getName() + "./"); }");
c2.append(" throw new " + NoSuchPropertyException.class.getName() + "(/"Not found property ///"/"+$2+/"///" filed or setter method in class " + c.getName() + "./"); }");
// make class
long id = WRAPPER_CLASS_COUNTER.getAndIncrement();
ClassGenerator cc = ClassGenerator.newInstance(cl);
cc.setClassName((Modifier.isPublic(c.getModifiers()) ? Wrapper.class.getName() : c.getName() + "$sw") + id);
cc.setSuperClass(Wrapper.class);
// 增加无参构造器
cc.addDefaultConstructor();
// 添加属性
cc.addField("public static String[] pns;"); // property name array.
cc.addField("public static " + Map.class.getName() + " pts;"); // property type map.
cc.addField("public static String[] mns;"); // all method name array.
cc.addField("public static String[] dmns;"); // declared method name array.
for (int i = 0, len = ms.size(); i < len; i++)
cc.addField("public static Class[] mts" + i + ";");
// 添加属性相关的方法
cc.addMethod("public String[] getPropertyNames(){ return pns; }");
cc.addMethod("public boolean hasProperty(String n){ return pts.containsKey($1); }");
cc.addMethod("public Class getPropertyType(String n){ return (Class)pts.get($1); }");
cc.addMethod("public String[] getMethodNames(){ return mns; }");
cc.addMethod("public String[] getDeclaredMethodNames(){ return dmns; }");
cc.addMethod(c1.toString());
cc.addMethod(c2.toString());
cc.addMethod(c3.toString());
try {
// 生成字节码
Class<?> wc = cc.toClass();
// setup static field.
// 反射,设置静态变量的值
wc.getField("pts").set(null, pts);
wc.getField("pns").set(null, pts.keySet().toArray(new String[0]));
wc.getField("mns").set(null, mns.toArray(new String[0]));
wc.getField("dmns").set(null, dmns.toArray(new String[0]));
int ix = 0;
for (Method m : ms.values())
wc.getField("mts" + ix++).set(null, m.getParameterTypes());
// // 创建对象并且返回
return (Wrapper) wc.newInstance();
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Throwable e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e.getMessage(), e);
} finally {
cc.release();
ms.clear();
mns.clear();
dmns.clear();
}
}
复制代码
Wrapper是用于创建某个对象的方法调用的包装器,利用字节码技术在调用方法时进行编译相关方法。其中getWrapper就是获得Wrapper 对象,其中关键的是makeWrapper方法,所以我在上面加上了makeWrapper方法的解释,其中就是相关方法的字节码生成过程。
- 本文标签: HashMap 配置 Proxy 解析 ssl consumer Service 静态方法 代码 value 源码 http id map newProxyInstance App apache dubbo Property https 字节码 API tk key 测试 src IO cat 类加载器 CTO ssh final Atom struct equals IDE HashSet 实例 协议 lib cache find synchronized CEO java 参数 message db ArrayList UI 缓存 遍历 编译 build constant tar 构造方法 注释 list remote ACE
- 版权声明: 本文为互联网转载文章,出处已在文章中说明(部分除外)。如果侵权,请联系本站长删除,谢谢。
- 本文海报: 生成海报一 生成海报二










![[HBLOG]公众号](https://www.liuhaihua.cn/img/qrcode_gzh.jpg)

