BeanPostProcessor学习
BeanPostProcessor是什么?在看bean初始化时,看到了很多的BeanPostProcessor,具体作用还真搞不清楚。
前人说这是spring的扩展点,遵循“开-闭原则”的一个扩展。可以进行自定义的实例化、初始化、依赖装配、依赖检查等流程,即可以覆盖默认的实例化,也可以增强初始化、依赖注入、依赖检查等流程
但我还是一脸蒙逼,到底是什么鬼?
网上找几个实例来个大体认知一下
对所有bean做个代理: http://guoliangqi.iteye.com/blog/635826
对bean做一些改动: http://blog.csdn.net/partner4java/article/details/6973782
改变Bean的属性值: http://winneryj.iteye.com/blog/307736
做预加载: http://292528867.iteye.com/blog/2159499
感觉这个可以使用init-method来实现
这些实例都是对bean的属性和行为都可以修改
BeanPostProcessor定义
/**
* Factory hook that allows for custom modification of new bean instances,
* e.g. checking for marker interfaces or wrapping them with proxies.
* 大体意思是可以检查相应的标识接口完成一些自定义功能实现,如包装目标对象到代理对象。
*/
public interface BeanPostProcessor {
/**
* Apply this BeanPostProcessor to the given new bean instance <i>before</i> any bean
* initialization callbacks (like InitializingBean's {@code afterPropertiesSet}
* or a custom init-method). The bean will already be populated with property values.
* The returned bean instance may be a wrapper around the original.
* <p>The default implementation returns the given {@code bean} as-is.
* @param bean the new bean instance
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the bean instance to use, either the original or a wrapped one;
* if {@code null}, no subsequent BeanPostProcessors will be invoked
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet
*/
Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException;
/**
* Apply this BeanPostProcessor to the given new bean instance <i>after</i> any bean
* initialization callbacks (like InitializingBean's {@code afterPropertiesSet}
* or a custom init-method). The bean will already be populated with property values.
* The returned bean instance may be a wrapper around the original.
* <p>In case of a FactoryBean, this callback will be invoked for both the FactoryBean
* instance and the objects created by the FactoryBean (as of Spring 2.0). The
* post-processor can decide whether to apply to either the FactoryBean or created
* objects or both through corresponding {@code bean instanceof FactoryBean} checks.
* <p>This callback will also be invoked after a short-circuiting triggered by a
* {@link InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInstantiation} method,
* in contrast to all other BeanPostProcessor callbacks.
* <p>The default implementation returns the given {@code bean} as-is.
* @param bean the new bean instance
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the bean instance to use, either the original or a wrapped one;
* if {@code null}, no subsequent BeanPostProcessors will be invoked
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean
*/
Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException;
}
接口结构很简单,两个方法
- postProcessBeforeInitialization:在Spring调用任何bean的初始化钩子(例如InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet或者init方法)之前被调用。
- postProcessAfterInitialization:Spring在成功完成嵌入初始化以后调用他。
注册beanpostprocessor
这个还是在AbstractApplicationContext的refresh()中
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context. //注册beanfactorypostProcessor invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Register bean processors that intercept bean creation. //注册beanpostprocessor registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
具体的委托给PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate
/**
* Instantiate and invoke all registered BeanPostProcessor beans,
* respecting explicit order if given.
* <p>Must be called before any instantiation of application beans.
*/
protected void registerBeanPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, this);
}
注册前需要对Processor进行一下排序
/**
* 对所有beanpostprocessor进行排序后再注册
* @param beanFactory
* @param applicationContext
*/
public static void registerBeanPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, AbstractApplicationContext applicationContext) {
String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// Register BeanPostProcessorChecker that logs an info message when
// a bean is created during BeanPostProcessor instantiation, i.e. when
// a bean is not eligible for getting processed by all BeanPostProcessors.
int beanProcessorTargetCount = beanFactory.getBeanPostProcessorCount() + 1 + postProcessorNames.length;
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new BeanPostProcessorChecker(beanFactory, beanProcessorTargetCount));
// Separate between BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered,
// Ordered, and the rest.
//排序分类,前面的是PriorityOrder,再是Order,最后是没有实现排序接口的
List<BeanPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<BeanPostProcessor> internalPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
else {
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
}
// First, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
sortPostProcessors(beanFactory, priorityOrderedPostProcessors);
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, priorityOrderedPostProcessors);
// Next, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
List<BeanPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
for (String ppName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
orderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(beanFactory, orderedPostProcessors);
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, orderedPostProcessors);
// Now, register all regular BeanPostProcessors.
List<BeanPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
for (String ppName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, nonOrderedPostProcessors);
// Finally, re-register all internal BeanPostProcessors.
sortPostProcessors(beanFactory, internalPostProcessors);
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, internalPostProcessors);
// Re-register post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners,
// moving it to the end of the processor chain (for picking up proxies etc).
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(applicationContext));
}
/**
* Register the given BeanPostProcessor beans.
* 具体注册行为,放到beanfactory的proocessor集合中
*/
private static void registerBeanPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List<BeanPostProcessor> postProcessors) {
for (BeanPostProcessor postProcessor : postProcessors) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(postProcessor);
}
}
BeanPostProcessor调用
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory的doCreateBean()方法里
// Initialize the bean instance.
//bean实例化完成
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
//属性赋值
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
if (exposedObject != null) {
//这里面处理aware,init methods and bean post processors
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
}
protected Object initializeBean(final String beanName, final Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
//aware方法
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Object>() {
@Override
public Object run() {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
return null;
}
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
}
Object wrappedBean = bean;
//postProcessBeforeInitialization方法
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
try {
//调用init-method
invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
(mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null),
beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex);
}
//postProcessAfterInitialization
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
return wrappedBean;
}
private void invokeAwareMethods(final String beanName, final Object bean) {
if (bean instanceof Aware) {
if (bean instanceof BeanNameAware) {
((BeanNameAware) bean).setBeanName(beanName);
}
if (bean instanceof BeanClassLoaderAware) {
((BeanClassLoaderAware) bean).setBeanClassLoader(getBeanClassLoader());
}
if (bean instanceof BeanFactoryAware) {
((BeanFactoryAware) bean).setBeanFactory(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.this);
}
}
}
通过代码,可以看出bean的顺序
bean实例化 –> bean属性注入 –> aware接口 –> postProcessBeforeInitialization方法 –> init-method –> postProcessAfterInitialization
AOP
如果要实现代理类有对应的接口,Spring AOP 默认使用 JDK 自带的 InvocationHandler 来实现代理类。
如果没有对应的接口,Spring 使用 CGLib 来实现代理类
那AOP跟这儿的BeanPostProcessor有什么关系呢? 其实还有一个aspectj
Spring AOP也是对目标类增强,生成代理类。但是与AspectJ的最大区别在于—Spring AOP的运行时增强,而AspectJ是编译时增强。
曾经以为AspectJ是Spring AOP一部分,是因为Spring AOP使用了AspectJ的Annotation。使用了Aspect来定义切面,使用Pointcut来定义切入点,使用Advice来定义增强处理。
虽然使用了Aspect的Annotation,但是并没有使用它的编译器和织入器。其实现原理是JDK 动态代理,在运行时生成代理类。
spring在处理aspectj时,其实使用的是BeanPostProcessor机制
主要处理类是AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator
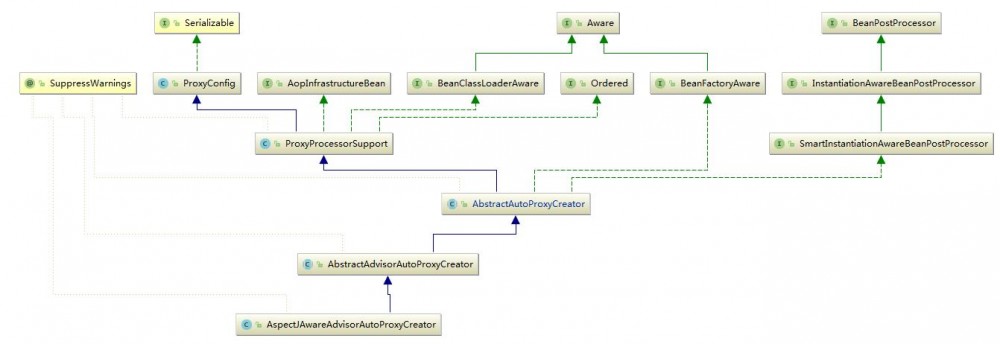
此类实现了BeanPostProcessor接口,在创建完bean后,postProcessAfterInitialization
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (bean != null) {
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName);
if (!this.earlyProxyReferences.contains(cacheKey)) {
return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
}
}
return bean;
}
/**
* Wrap the given bean if necessary, i.e. if it is eligible for being proxied.
* @param bean the raw bean instance
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param cacheKey the cache key for metadata access
* @return a proxy wrapping the bean, or the raw bean instance as-is
*/
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {
if (beanName != null && this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) {
return bean;
}
if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this.advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) {
return bean;
}
if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) || shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
// Create proxy if we have advice.
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null);
if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE);
//创建proxy
Object proxy = createProxy(
bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));
this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
return proxy;
}
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
protected Object createProxy(
Class<?> beanClass, String beanName, Object[] specificInterceptors, TargetSource targetSource) {
if (this.beanFactory instanceof ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) {
AutoProxyUtils.exposeTargetClass((ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) this.beanFactory, beanName, beanClass);
}
//通过proxyFactory去创建proxy
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory();
proxyFactory.copyFrom(this);
if (!proxyFactory.isProxyTargetClass()) {
if (shouldProxyTargetClass(beanClass, beanName)) {
proxyFactory.setProxyTargetClass(true);
}
else {
evaluateProxyInterfaces(beanClass, proxyFactory);
}
}
Advisor[] advisors = buildAdvisors(beanName, specificInterceptors);
for (Advisor advisor : advisors) {
proxyFactory.addAdvisor(advisor);
}
proxyFactory.setTargetSource(targetSource);
customizeProxyFactory(proxyFactory);
proxyFactory.setFrozen(this.freezeProxy);
if (advisorsPreFiltered()) {
proxyFactory.setPreFiltered(true);
}
return proxyFactory.getProxy(getProxyClassLoader());
}
进入到ProxyFactory里面
public Object getProxy(ClassLoader classLoader) {
return createAopProxy().getProxy(classLoader);
}
protected final synchronized AopProxy createAopProxy() {
if (!this.active) {
activate();
}
//这儿又来一个factory
return getAopProxyFactory().createAopProxy(this);
}
/** 其实是个默认的实现,没有多态
* Create a new ProxyCreatorSupport instance.
*/
public ProxyCreatorSupport() {
this.aopProxyFactory = new DefaultAopProxyFactory();
}
在这个DefaultAopProxyFactory里面
@Override
public AopProxy createAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException {
if (config.isOptimize() || config.isProxyTargetClass() || hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(config)) {
Class<?> targetClass = config.getTargetClass();
if (targetClass == null) {
throw new AopConfigException("TargetSource cannot determine target class: " +
"Either an interface or a target is required for proxy creation.");
}
//targetClass如果是接口,或者是实现了Proxy接口,就使用JDK动态代理了
if (targetClass.isInterface() || Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass)) {
return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);
}
//不然使用cglib方式
return new ObjenesisCglibAopProxy(config);
}
else {
return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);
}
}
再深入就是aop自身的知识点了,后面再写文章
总结
通过一系列的实现,其实还是开篇的一句话
BeanPostProcessor是spring的扩展点,遵循“开-闭原则”的一个扩展。
可以进行自定义的实例化、初始化、依赖装配、依赖检查等流程,即可以覆盖默认的实例化,也可以增强初始化、依赖注入、依赖检查等流程
- 本文标签: https Property GitHub REST db trigger cat IO App java lib git BeanDefinition SDN list tab 文章 description cache CTO spring build struct Security API value 编译 ACE tar bean CEO rmi 总结 ip message IDE id key ssl http Action 代码 final Listeners UI AOP 实例 root src
- 版权声明: 本文为互联网转载文章,出处已在文章中说明(部分除外)。如果侵权,请联系本站长删除,谢谢。
- 本文海报: 生成海报一 生成海报二










![[HBLOG]公众号](https://www.liuhaihua.cn/img/qrcode_gzh.jpg)

