Spring MVC--请求定位
承接上文,依照上文所说 DispatcherServlet 拿到请求后所作的第一件事情是定位到具体的 HandlerExecutionChain ,也就是该请求所需要执行的方法,包括拦截器方法与用户的业务方法,那么本篇来详细描述这个过程.
Spring MVC中的URL
在分析之前先理解Spring MVC中的URL,对于Spring MVC来说URL分为两类,一种是静态的,一种是动态的.
- 静态: 指的是一个方法所对应的URL自初始化就是不变的,比如
/api/v1/login/ - 动态: 指的是一个方法对应的URL有多种形式,比如
/api/v1/**,/api/{version}/login/这两种都属于动态的,是没法直接根绝URL定位到需要执行的方法.
HandlerMapping
HandlerMapping 是Spring MVC中定位到具体执行链所使用的类,其所提供的是对外的功能,根据请求拿到具体的执行链.
HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception;
在 DispatcherServlet 中根据请求得到对应的处理链(包括具体执行的方法与拦截器)调的是 getHandler 方法,该方法对 HandlerMappings 做了一个循环处理,直到找到第一个符合的 HandlerExecutionChain 为止, HandlerExecutionChain 是方法的执行链,其中包含着Spring MVC的 拦截器 以及用户定于的处理方法 HandlerMethod .
这里个人觉得可以做个优化,让每一个 HandlerMapping 持有一个 handlerCount 字段,每次选中的 HandlerMapping 处理成功后该 handlerCount 自增,然后对 this.handlerMappings 根据 handlerCount 排序,这样随着服务的运行,会使得这个循环的尽可能的用最少的次数找到最合适的处理器.
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
// 对所有的Handler循环,直到找到能够处理的Handler
for (HandlerMapping hm : this.handlerMappings) {
HandlerExecutionChain handler = hm.getHandler(request);
if (handler != null) {
return handler;
}
}
return null;
}
HandlerMappings 继承结构如下:
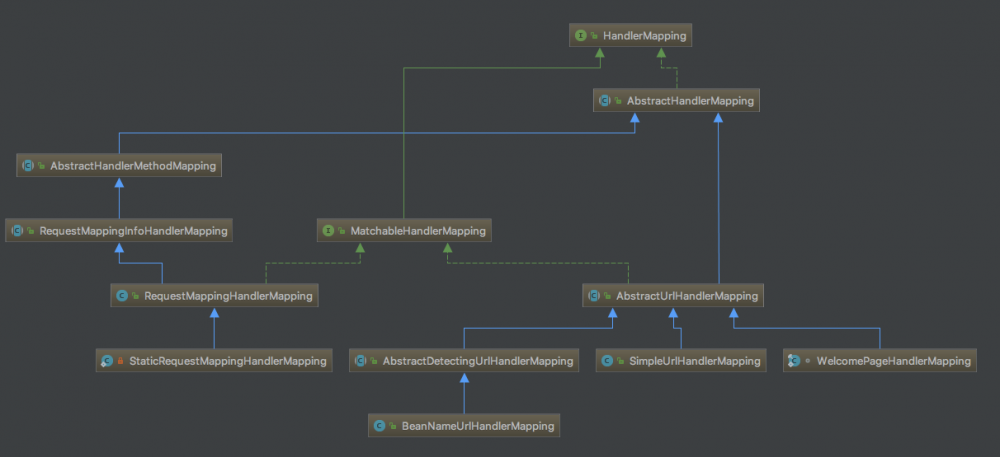
从关系图可以得到哪些信息?
- 这是一种模板方法设计模式,接口最上层提供对外的能力,抽象类在中间提供代码复用以及把功能拆分到具体的子类中实现,最后实现类则负责实现模板类所给自己提供的小任务的实现.
-
HandlerMapping分为两种类型,一种是url到方法AbstractHandlerMethodMapping,这种形式比较常用,也是业务开发中主要使用到的形式,一种是url到其他处理器比如Controller,Resource的AbstractUrlHandlerMapping,该类属于Spring3之前常用的类.
下面按照模板方法设计模式的思路来分析
模板类AbstractHandlerMapping
身为模板类的 AbstractHandlerMapping ,主要功能是实现 HandlerMapping 的方法,然后 拆解这个方法到更加细小的任务,传递到子类中 ,这个也是模板方法设计模式的本质.他的大概流程如下(省略了部分代码):
public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
// getHandlerInternal是有模板类延迟到子类的一个方法
Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request);
......
// handler是Spring的话则去获取到具体的Bean
if (handler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String) handler;
handler = getApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
// 构造执行链
HandlerExecutionChain executionChain = getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request);
....
// 返回
return executionChain;
}
// 延迟到子类的方法
protected abstract Object getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception;
其中 HandlerExecutionChain 是一个包含了拦截器与对应的业务方法的包装类,比较简单,就不做分析了.可以看到 AbstractHandlerMapping 细分了 getHandlerInternal() 方法交由子类实现,自己则负责整个流程的构建.
方法映射处理AbstractHandlerMethodMapping
AbstractHandlerMethodMapping 自然也是模板类,其承担的责任是根据URL找到具体的方法.
protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
// 取出具体的url信息
String lookupPath = getUrlPathHelper().getLookupPathForRequest(request);
// 获取读锁
this.mappingRegistry.acquireReadLock();
// 找到对应的方法
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = lookupHandlerMethod(lookupPath, request);
// 返回对应的处理方法
return (handlerMethod != null ? handlerMethod.createWithResolvedBean() : null);
// 释放读锁
this.mappingRegistry.releaseReadLock();
}
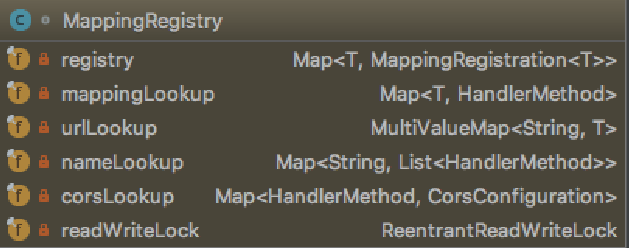
从上述流程可以看出,主要的寻找逻辑在 lookupHandlerMethod() 方法中,等下在分析该方法.在这个查找中有 MappingRegistry ,它是什么?为什么有需要读锁?
按照该类的注释所说,该类是一个路由表,其包含着Spring MVC所管理的所有映射关系,并且运用读写锁提供并发访问能力,之所以需要并发因为 MappingRegistry 并不是一个线程安全的类,其提供了写入与获取方法,并且共享了一些线程不安全的类,比如 HashMap ,并且其属于读写比非常大的场景,因此使用读写锁实现高性能访问与并发安全在合适不过了.
有了所有的映射关系接下来是匹配流程,也就是 lookupHandlerMethod 的方法执行逻辑(代码比较长,参考注释观看):
protected HandlerMethod lookupHandlerMethod(String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
List<Match> matches = new ArrayList<Match>();
// 从urlLookup中取出匹配结果,这里是直接匹配
List<T> directPathMatches = this.mappingRegistry.getMappingsByUrl(lookupPath);
if (directPathMatches != null) {
addMatchingMappings(directPathMatches, matches, request);
}
// 上述直接匹配不到则全部匹配(这里是坑)
if (matches.isEmpty()) {
addMatchingMappings(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), matches, request);
}
// 匹配后进行筛选
if (!matches.isEmpty()) {
Comparator<Match> comparator = new MatchComparator(getMappingComparator(request));
Collections.sort(matches, comparator);
...
// 默认排序后第一个为最佳匹配
Match bestMatch = matches.get(0);
if (matches.size() > 1) {
if (CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) {
return PREFLIGHT_AMBIGUOUS_MATCH;
}
// 不允许有两个一样的处理器
Match secondBestMatch = matches.get(1);
if (comparator.compare(bestMatch, secondBestMatch) == 0) {
Method m1 = bestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod();
Method m2 = secondBestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod();
throw new IllegalStateException("Ambiguous handler methods mapped for HTTP path '" +
request.getRequestURL() + "': {" + m1 + ", " + m2 + "}");
}
}
// 处理匹配结果
handleMatch(bestMatch.mapping, lookupPath, request);
return bestMatch.handlerMethod;
}
else {
// 匹配不到的处理一般是找出原因,抛出相应的异常
return handleNoMatch(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), lookupPath, request);
}
}
有何问题?
当 directPathMatches 匹配不到时,会造成 全量的遍历 ,笔者公司一个20w行代码的项目全量匹配是要循环300次,每一个URL方法都要试试匹配,然后再排序,再筛选,并且随着请求量的增加循环次数也在增加,系统负载能力是下降趋势的.那么哪些操作造成全量匹配?
分析 directPathMatches 的来源,其是根据URL查找出对应的处理链,然后再逐一判断,换句话说 动态的URL就找不到对应的处理器链,从而造成全量匹配 ,对于Spring MVC来说是 @PathVariable 或者是 login/** 通配符形式会导致全量匹配.因为这两种情况下链接本身不是固定的,因此无法精确匹配,只能全量搜索查找.
如果项目大量使用了类似的写法,解决办法就是定制解析流程,可以参考达达的定制过程 SpringMVC RESTful 性能优化
模板类AbstractUrlHandlerMapping
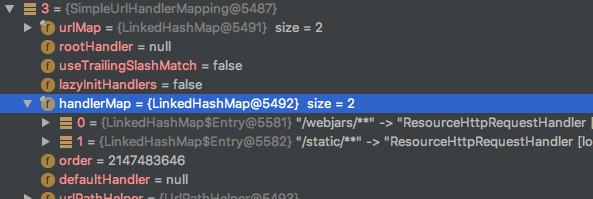
该类属于Spring3之前所提供的类,由于笔者对Spring3之前的开发方式不是很清楚,因此不会过多的讨论该类,只从现在角度来分析该类的用处.该类的实现比较简单,其内部拥有一个Map保存了所有的映射关系,可以映射到对应的Controller,也可以映射到其他的Handler.
private final Map<String, Object> handlerMap = new LinkedHashMap<String, Object>();
有何问题?
-
LinkedHashMap是一个线程不安全的类,因此对于这种类要求必须再启动时把所有的信息都注入,从而保证再运行时没有put写入的请求,以及扩容的需求,从而达到线程安全. - 该类直接匹配不到同样进行全遍历
笔者用Spring Boot写个了Demo后发现该类承担的角色一般是静态资源匹配.也就是以下参数spring.mvc.static-path-pattern=/static/**
 由于使用不多,这里就不多研究了.
由于使用不多,这里就不多研究了.
总结
Spring MVC请求定位的实现原理就是先获取所有的映射关系,然后拿到请求后的url进行匹配,在匹配结果中筛选最合适的一个进行处理的过程.
- 版权声明: 感谢您的阅读,本文由屈定's Blog版权所有。如若转载,请注明出处。
- 文章标题:Spring MVC--请求定位
- 文章链接: https://mrdear.cn/2018/04/16/framework/spring/springmvc--find_request/
Spring MVC--所存在的疑惑










![[HBLOG]公众号](https://www.liuhaihua.cn/img/qrcode_gzh.jpg)

