JVM 如何处理未捕获异常
继之前的文章详解JVM如何处理异常,今天再次发布一篇比较关联的文章,如题目可知,今天聊一聊在JVM中线程遇到未捕获异常的问题,其中涉及到线程如何处理未捕获异常和一些内容介绍。
什么是未捕获异常
未捕获异常指的是我们在方法体中没有使用try-catch捕获的异常,比如下面的例子
private static void testUncaughtException(String arg) {
try {
System.out.println(1 / arg.length());
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
上面的代码很有可能发生如下情况
- 如果方法参数arg传递null,会出现NullPointerException
- 如果参数arg传递内容为空的字符串(“”),会出现ArithmeticException
对于上面的问题,我们不难发现
- 上面可能出现的NullPointerException和ArithmeticException都属于Unchecked Exceptions
- 而ArithmeticException被我们人为try-catch捕获了,它不符合本文对于未捕获异常的定义
- NullPointerException 由于我们没有catch住,就变成了我们要聊的未捕获异常
- 另外,未捕获异常实际是Unchecked Exceptions的子集
UncaughtExceptionHandler 是什么
void uncaughtException(Thread t, Throwable e); Thread.setUncaughtExceptionHandler Thread.setDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler
ThreadGroup 是什么
- ThreadGroup 是线程的集合
- ThreadGroup 也可以包含子ThreadGroup
- 除了初始的ThreadGroup 之外,每个ThreadGroup都有一个父 ThreadGroup
- ThreadGroup 自身实现了Thread.UncaughtExceptionHandler,用来相应处理其内部的线程和ThreadGroup发生未捕获异常。
未捕获异常处理者 设置指南

线程发生了未捕获异常,JVM怎么处理
分发Throwable实例
当线程A中出现了未捕获异常时,JVM会调用线程A的 dispatchUncaughtException(Throwable)
方法
/**
* Dispatch an uncaught exception to the handler. This method is
* intended to be called only by the JVM.
*/
private void dispatchUncaughtException(Throwable e) {
getUncaughtExceptionHandler().uncaughtException(this, e);
}
获取未捕获异常处理者
- 每个线程会有一个变量(uncaughtExceptionHandler)来保存未捕获异常的处理者
- 在线程需要确定Throwable分发目标的处理者时,优先获取当前线程中uncaughtExceptionHandler变量
- 如果出问题线程的uncaughtExceptionHandler为null(即没有显式设置异常处理者),则使用自己所在的ThreadGroup来作为未捕获异常处理者。
/**
* Returns the handler invoked when this thread abruptly terminates
* due to an uncaught exception. If this thread has not had an
* uncaught exception handler explicitly set then this thread's
* <tt>ThreadGroup</tt> object is returned, unless this thread
* has terminated, in which case <tt>null</tt> is returned.
* @since 1.5
* @return the uncaught exception handler for this thread
*/
public UncaughtExceptionHandler getUncaughtExceptionHandler() {
return uncaughtExceptionHandler != null ?
uncaughtExceptionHandler : group;
}
如果Throwable分发给ThreadGroup
Thread.getDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler()
/**
* Called by the Java Virtual Machine when a thread in this
* thread group stops because of an uncaught exception, and the thread
* does not have a specific {@link Thread.UncaughtExceptionHandler}
* installed.
* <p>
* The <code>uncaughtException</code> method of
* <code>ThreadGroup</code> does the following:
* <ul>
* <li>If this thread group has a parent thread group, the
* <code>uncaughtException</code> method of that parent is called
* with the same two arguments.
* <li>Otherwise, this method checks to see if there is a
* {@linkplain Thread#getDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler default
* uncaught exception handler} installed, and if so, its
* <code>uncaughtException</code> method is called with the same
* two arguments.
* <li>Otherwise, this method determines if the <code>Throwable</code>
* argument is an instance of {@link ThreadDeath}. If so, nothing
* special is done. Otherwise, a message containing the
* thread's name, as returned from the thread's {@link
* Thread#getName getName} method, and a stack backtrace,
* using the <code>Throwable</code>'s {@link
* Throwable#printStackTrace printStackTrace} method, is
* printed to the {@linkplain System#err standard error stream}.
* </ul>
* <p>
* Applications can override this method in subclasses of
* <code>ThreadGroup</code> to provide alternative handling of
* uncaught exceptions.
*
* @param t the thread that is about to exit.
* @param e the uncaught exception.
* @since JDK1.0
*/
public void uncaughtException(Thread t, Throwable e) {
if (parent != null) {
parent.uncaughtException(t, e);
} else {
Thread.UncaughtExceptionHandler ueh =
Thread.getDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler();
if (ueh != null) {
ueh.uncaughtException(t, e);
} else if (!(e instanceof ThreadDeath)) {
System.err.print("Exception in thread /""
+ t.getName() + "/" ");
e.printStackTrace(System.err);
}
}
}
将上面的处理流程做成图的形式,就是下图所示
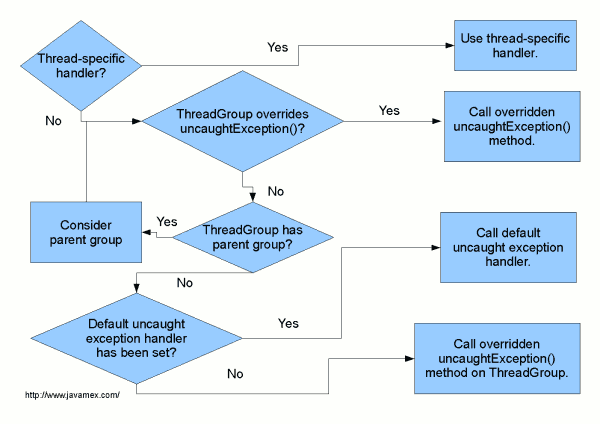
注:上述图片来自 https://www.javamex.com/tutorials/exceptions/exceptions_uncaught_handler.shtml
Questions
初始的ThreadGroup是什么
上面提到了初始的ThreadGroup没有父ThreadGroup,是主线程所在的ThreadGroup么?
这个问题,我们可以通过这样一段代码验证
private static void dumpThreadGroups() {
ThreadGroup threadGroup = Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup();
while(threadGroup != null) {
System.out.println("dumpThreadGroups threadGroup=" + threadGroup.getName());
threadGroup = threadGroup.getParent();
}
}
执行该方法对应的输出是
dumpThreadGroups threadGroup=main dumpThreadGroups threadGroup=system
因此我们可以发现,初始的ThreadGroup是一个叫做system的ThreadGroup,而不是main ThreadGroup
setDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler 设置的一定会被调用到么
这其实是一个很好的问题,答案是不一定会被调用,因为可能存在以下的情况
- 出问题的线程设置了对应的UncaughtExcpetionHandler,优先响应分发到这个Handler
- 出问题的线程所在的ThreadGroup包括其祖先ThreadGroup 重写了uncaughtException 也可能造成线程默认的Handler无法被调用
- 出问题的线程重写了dispatchUncaughtException 可能性较小
- 出问题的线程重写了getUncaughtExceptionHandler 可能性较小
参考声明
- How uncaught exceptions are handled
正文到此结束
热门推荐
相关文章
Loading...










![[HBLOG]公众号](https://www.liuhaihua.cn/img/qrcode_gzh.jpg)

