从0开始造一个轮子(方的)

俗话说「不要重复造轮子」,但是我觉得通过研究大神造的轮子,然后自己去尝试造一个简陋版的,对于提升自己的软件构思是很有帮助的。
回归正题,最近在做一个作业,和计算机网络相关的,笔者选择了用Java开发一个简陋版的HTTP客户端,于是笔者去拜读了 Square 公司开源的 OkHttp ,参照了Okhttp的设计思想,开发了 Yohttp 。
这里给出 Github 地址: YoHttp ,欢迎大家一起学习探讨。
软件架构
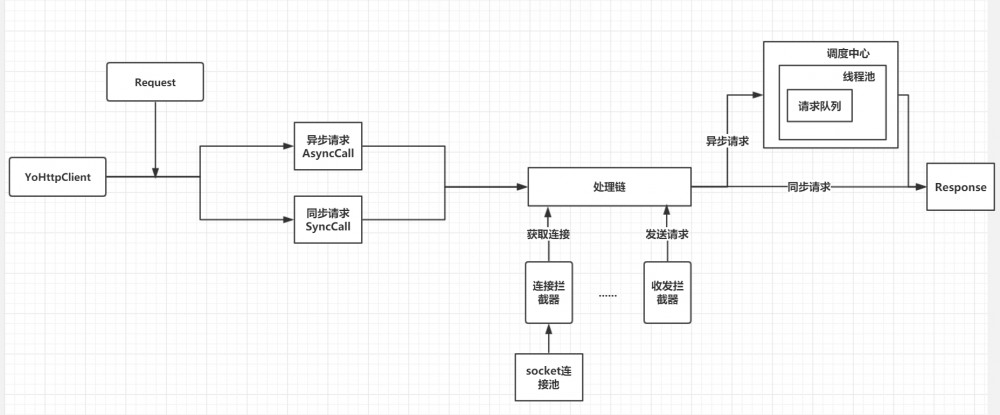
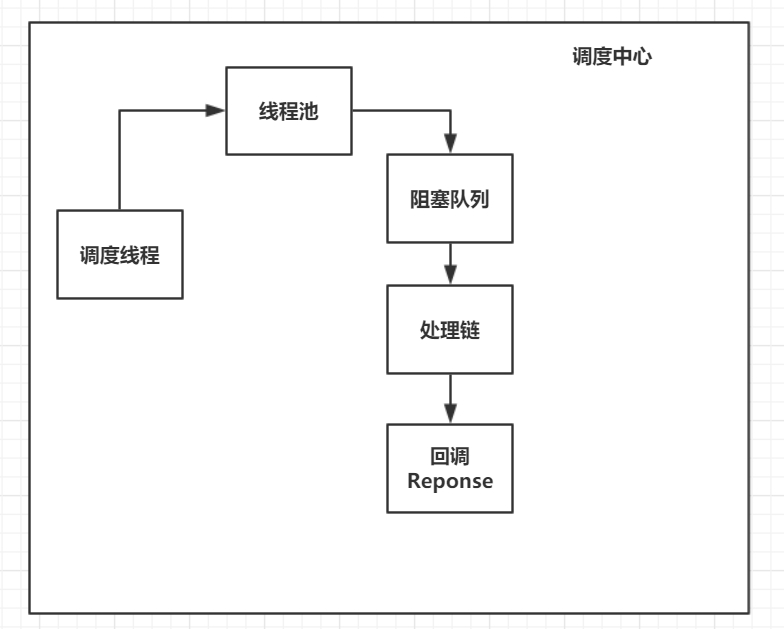
笔者将软件大概设计成五大模块:
- 请求信息
这部分即对应上图的Request,用于用户构建请求信息,如URL、method、请求头等。这部分是用户可以操作的。 - Yohttp客户端
用户创建一个YoHttp,然后将请求信息注入到Yohttp即可以开始使用请求功能,请求包括同步请求和异步请求,其中一个YoHttp包含一个调度中心、一个连接池,所以对于一个项目来说,维护着一个YoHttp客户端就足以。 - 处理链
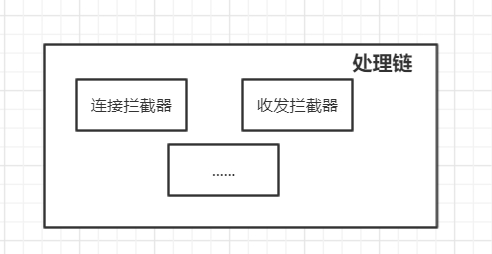
这里是请求的具体实现操作,笔者将一个一个操作封装成一个拦截器,如把获取Socket连接的操作封装成连接拦截器、把Socket流的读写封装成收发拦截器,然后我们请求需要用到哪些操作,即可把这些拦截器一个一个拼接起来组合成一个处理链(Chain), 一个处理链对应着一个请求 。执行处理链中的一个个拦截器,直到执行完所有的拦截器,也对应着一个请求的完成。这也是为什么我们需要将收发拦截器放在最后,因为一个请求的最后一个操作肯定是进行Socket流的写和读。
笔者认为这样将一个一个操作封装成拦截器,然后组合拦截器拼凑成处理链,最后执行处理链即可达到执行操作,极大的解耦了请求过程,同时也提高了扩展性。
-
调度中心
调度中心在使用异步请求的时候用到,调度中心维护着一个请求队列和一个线程池,请求队列里面存储的是处理链
Chain。线程池负责执行队列中的处理链。笔者认为这里使用线程池能提高队列的处理效率,毕竟现在PC都是多核心的,充分利用CPU提高效率还是不错的。
-
连接池
每个请求都是去连接池获取
Socket连接,如果连接池中存在IP、PORT相同的连接则直接返回,否则创建一个Socket连接存储到连接池然后返回,而连接池中的连接 闲置时间超过最大允许闲置的时间后就会被关闭 。笔者认为通过使用连接池能减少连接创建销毁的开销,在请求较多、请求频率较高的场景下能提高效率。
介绍完了架构,我们看看怎么使用我们的HTTP客户端:
- 同步请求
Request request = new Request.Builder() .url("www.baidu.com") .get() .build(); YoHttpClient httpClient = new YoHttpClient(); Response response = httpClient.SyncCall(request).executor(); System.out.println(response.getBody());
第一步新建个请求信息 Request ,填写请求的 URL 、请求方法、请求头等信息。
第二步新建个 YoHttp 客户端, 选择同步于请求 并将请求信息注入,执行请求。
- 异步请求
Request request = new Request.Builder() .url("www.baidu.com") .get() .build(); YoHttpClient httpClient = new YoHttpClient(); httpClient.AsyncCall(request).executor(new CallBack() { @Override public void onResponse(Response response) { System.out.println(response.getBody()); } });
第一步新建个请求信息 Request ,填写请求的 URL 、请求方法、请求头等信息。
第二步新建个 YoHttp 客户端, 选择异步于请求 并将请求信息注入,执行请求,当请求有响应的时候,会通过回调异步请求的 onResponse 方法来反馈响应内容。
说完了架构还有使用方法,接下来笔者介绍各个模块的具体实现。
请求信息
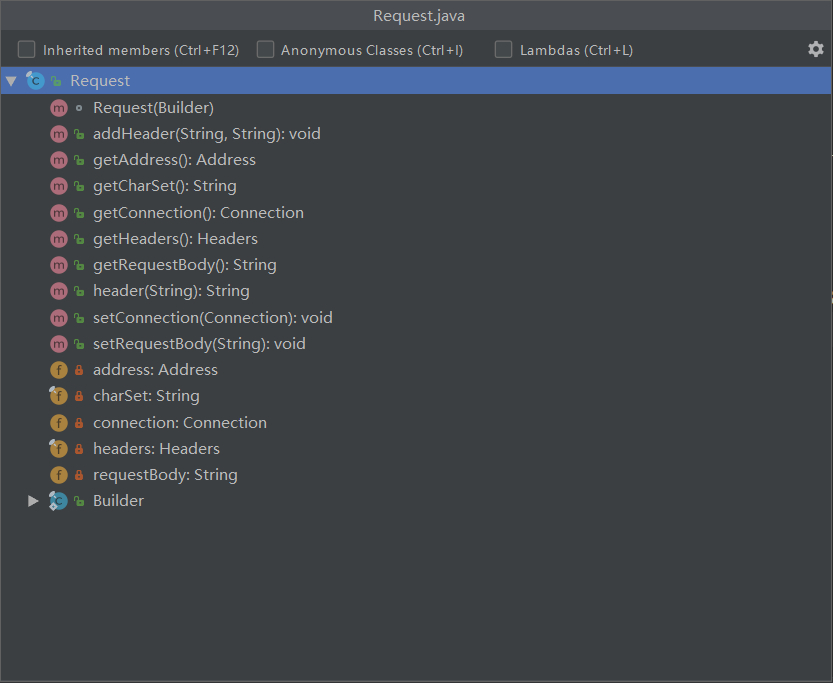
在实现 Request 的时候,笔者使用的是 Builder 模式,即构造者模式,在 Request 中添加个 静态内部类Builder ,用于构造Request。
YoHttpClient
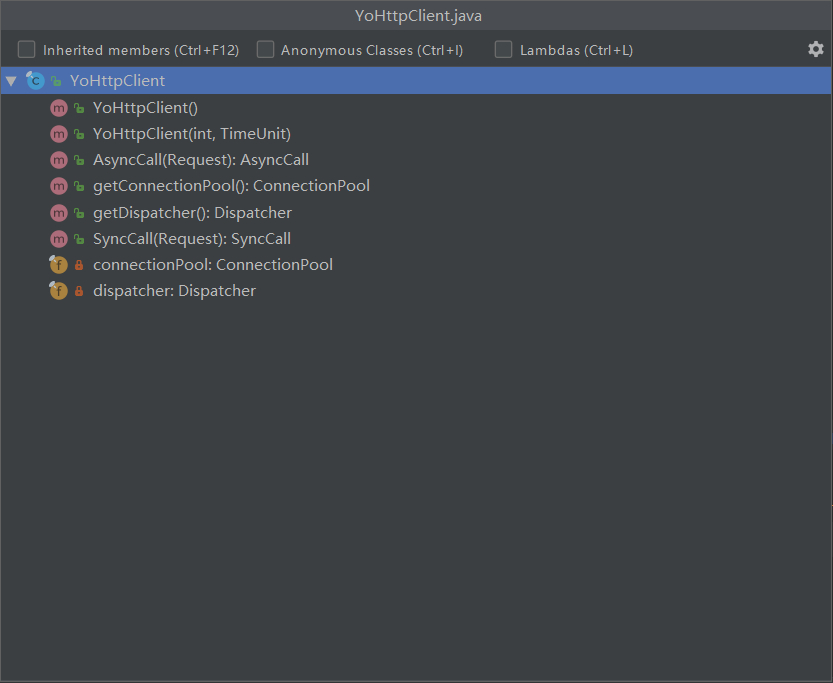
在YoHttp客户端中有一个调度中心和一个连接池,调度中心是使用异步请求的时候用上的,连接池则是在请求获取 Socket 连接的时候使用。
-
构造方法
笔者设置了两个构造方法:
public YoHttpClient() { this(5, TimeUnit.MINUTES); } public YoHttpClient(int keepAliveTime, TimeUnit timeUnit) { this.dispatcher = new Dispatcher(); this.connectionPool = new ConnectionPool(keepAliveTime, timeUnit); }
一个是无参构造方法,一个是指定连接池中连接最大闲置时间的构造方法,如果用户使用了无参构造方法,默认设置连接池中的连接最大闲置时间是 5 分钟。
- 同步请求方法SynchCall
public SyncCall SyncCall(Request request) { return new SyncCall(this, request); } // SyncCall.java @Override public Response executor() { synchronized (this) { if (this.executed) throw new IllegalStateException("Call Already Executed"); this.executed = true; } List<Interceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<>(); interceptors.add(new ConnectionInterceptor(yoHttpClient, request)); interceptors.add(new CallServerInterceptor(request)); Chain chain = new Chain(interceptors, null); Response response = chain.proceed(); chain = null; return response; } //Chain.java public Response proceed() { Response response = new Response(); for (int i = 0; i < interceptors.size(); i++) { response = interceptors.get(i).proceed(response); } return response; }
创建一个 SynchCall 同步请求,SynchCall里面有个 executor 方法,这个方法创建一个存储拦截器 Interceptor 的List,我们把请求中需要用到的操作(拦截器)存入到List中,例如我们用到了连接拦截器(ConnectionInterceptor)、收发拦截器(CallServerInterceptor),然后将List封装成一个 处理链(Chain) ,最后调用处理链的 proceed 方法遍历List中的拦截器并执行,这样即可达到执行一个请求的所有操作,这里是同步请求,所以阻塞到处理链执行完成返回response之后才return。
- 异步请求AsyncCall
public AsyncCall AsyncCall(Request request) { return new AsyncCall(this, request); } //AsyncCall.java public void executor(CallBack callBack) { synchronized (this) { if (this.executed) throw new IllegalStateException("Call Already Executed"); this.executed = true; } List<Interceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<>(); interceptors.add(new ConnectionInterceptor(yoHttpClient, request)); interceptors.add(new CallServerInterceptor(request)); Chain chain = new Chain(interceptors, callBack); yoHttpClient.getDispatcher().addChain(chain); }
异步请求中,同样是在 executor 方法构造好所需的拦截器,将拦截器封装成处理链, 区别的地方在这里并不是马上调用处理链的 proceed 方法,而是将处理链添加到调度中心的请求队列中,然后马上返回了 ,调度中心的具体实现在后文介绍。
处理链
处理链在上文的YoHttpClient介绍的差不多了,这里补充一下拦截器的设计。
所有的拦截器都实现 Interceptor 这个接口,这个接口很简单,只有一个方法 proceed ,只需要将具体的操作写到这个方法即可。例如连接拦截器 ConnectionInterceptor 的实现如下。
@Override
public Response proceed(Response response) {
Address address = request.getAddress();
Connection connection = yoHttpClient.getConnectionPool().getConnection(address);
request.setConnection(connection);
return response;
}
第一步是获取请求信息中的 IP 、 PORT (笔者将这两者封装成了Address)
第二步是使用这个address去连接池中获取连接。
这个proceed方法是提供给处理链中执行的。
调度中心
调度中心在异步请求中使用到,调度中心维护着一个请求队列和一个线程池。笔者采用的是阻塞队列(考虑到并发问题)和可缓存线程池,这个线程池的特点:核心线程数是0,线程数最大是 Integer.MAX_VALUE ,线程闲置时间最大允许为60秒。
调度中心有2个内部类,一个是 CallRunnable ,这个内部类的作用是将处理链Chain封装成 Runnable 公线程执行。另一个是 ChainQueue ,这个内部类维护着一个阻塞队列,控制着请求的入队和出队。
private void executor() {
Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
while (chainQueue.size() > 0) {
executorService.submit(new CallRunnable(chainQueue.pollChain()));
}
}
}
});
thread.start();
}
//CallRunnable内部类
private final class CallRunnable implements Runnable {
private Chain chain;
CallRunnable(Chain chain) {
this.chain = chain;
}
@Override
public void run() {
Response response = chain.proceed();
chain.getCallBack().onResponse(response);
chain = null;
}
}
在调度中心开启了一个线程,通过遍历阻塞队列,如果阻塞队列中有请求,则交给线程池去处理,线程通过调用处理链的proceed方法来遍历处理链中的拦截器,这个和同步请求中的一样的,当执行完后才能通过回调将响应返回给客户端。
连接池
笔者将 Socket 连接封装成一个 Connection ,而连接池维护的则是一个存储 Connection 的HashMap。
- 获取连接
public Connection getConnection(Address address) { return tryAcquire(address); } private Connection tryAcquire(Address address) { if (connections.containsKey(address)) { connections.get(address).setTime(System.currentTimeMillis()); return connections.get(address); } synchronized (address) { cleanUpConnection(); if (!connections.containsKey(address)) { Connection connection = new Connection(address); connection.setTime(System.currentTimeMillis()); connections.put(address, connection); return connection; } else { connections.get(address).setTime(System.currentTimeMillis()); return connections.get(address); } } }
通过调用 getConnection 方法即可获取到一个连接,而getConnection的实现是通过调用私有方法 tryAcquire ,获取的流程如下:
第一步先判断连接池中是否存在address相同的连接,有则则更新线程的活跃时间然后直接返回,没有则执行第二步。
第二步锁住address,目的是防止多个线程同时创建同一个连接,锁住之后再次判断连接池是否存在连接了,没有则进行创建然后返回。
- 清理超过闲置时间的连接
private void cleanUpConnection() { for (Map.Entry<Address, Connection> entry: connections.entrySet()) { if (System.currentTimeMillis() - entry.getValue().getTime() <= keepAliveTime) { try { connections.get(entry.getKey()).getSocket().close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } connections.remove(entry.getKey()); } } }
这个cleanUpConnection方法在每次获取连接的时候都会执行一次,遍历连接池中的连接,如果连接池中的连接超过允许的闲置时间则关闭这个连接然后将连接移除Map。
总结
这个项目仅是学习使用,请勿用于生产环境。
目前仅实现了 GET 、 POST 、 DELETE 、 PUT 方法,希望后面会完善更多功能还有把IO改成NIO提高性能。
希望各位前辈看完之后能给点意见或者留下个赞~
最后再附上 Github 地址: YoHttp ,欢迎大家一起学习探讨。










![[HBLOG]公众号](https://www.liuhaihua.cn/img/qrcode_gzh.jpg)

