Java并发 -- Semaphore
- 信号量是由计算机科学家Dijkstra在1965年提出,在之后的15年,信号量一直都是并发编程领域的终结者
- 直到1980年管程被提出来,才有了第二选择,目前所有支持并发编程的语言都支持信号量机制
信号量模型
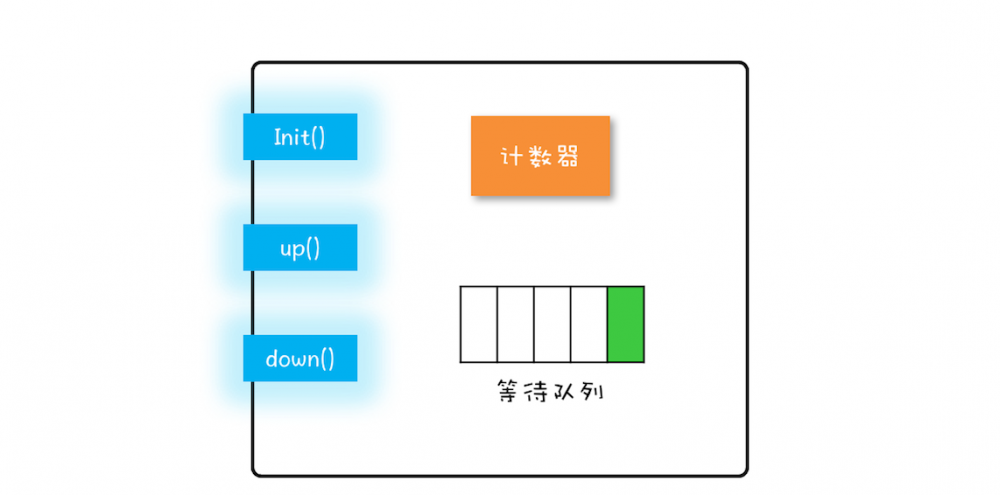
- 在信号量模型里,计数器和等待队列对外都是 透明 的,只能通过信号量模型提供的三个方法来访问它们,即init/down/up
- init():设置计数器的初始值
- down():计数器的值 减1 ,如果此时计数器的值 小于0 ,则当前线程将 阻塞 ,否则当前线程可以继续执行
- up():计数器 加1 ,如果此时计数器的值 大于或等于0 ,则 唤醒 等待队列中的一个线程,并将其从等待队列中移除
- init/down/up都是 原子性 的,这个原子性由信号量模型的实现方保证
- 在JUC中,信号量模型由java.util.concurrent.Semaphore实现,Semaphore能够保证这三个方法的原子性操作
- 在信号量模型里,down/up这两个操作最早被称为P操作和V操作,因此信号量模型也被称为 PV原语
- 在JUC中,down和up对应的是acquire和release
使用信号量
互斥
public class Counter {
private static final Semaphore SEMAPHORE = new Semaphore(1);
private static int count;
// 用信号量保证互斥
public static void addOne() throws InterruptedException {
// 原子操作
SEMAPHORE.acquire();
try {
count += 1;
} finally {
// 原子操作
SEMAPHORE.release();
}
}
}
- 假设两个线程T1和T2同时访问addOne,当两个线程同时调用acquire的时候,由于acquire是一个原子操作
- 只能一个线程(T1)把信号量的计数器减为0,另一个线程(T2)把信号量的计数器减为-1
- 对于T1,信号量里计数器值为0,大于等于0,T1会继续执行,对于T2,信号量里计数器值为-1,小于0,T2将被阻塞
- 因此此时只有T1能够进入临界区执行count += 1
- 当T1执行release,此时信号量里计数器的值为-1,加1之后的值为0,大于等于0,唤醒信号量里等待队列中的线程(T2)
- 于是T2在T1执行完临界区代码后才有机会进入临界区执行代码,从而保证了 互斥性
限流器
- Semaphore对比Lock:Semaphore 允许多个线程访问同一个临界区
- 常见场景为各种 池化资源 ,例如 连接池、对象池和线程池
- 对象池需求:一次性创建N个对象,之后所有的线程都重用这N个对象,在对象被释放前,不允许其他线程使用
public class ObjPool<T, R> {
private final List<T> pool;
// 用信号量实现限流器
private final Semaphore semaphore;
public ObjPool(int size, T t) {
// 信号量允许多个线程进入临界区,因此采用并发安全的Vector
pool = new Vector<T>();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
pool.add(t);
}
semaphore = new Semaphore(size);
}
// 利用对象池中的对象,调用func
public R exec(Function<T, R> func) throws InterruptedException {
T t = null;
semaphore.acquire();
try {
// 分配对象
t = pool.remove(0);
return func.apply(t);
} finally {
// 释放对象
pool.add(t);
semaphore.release();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
// 创建对象池
ObjPool<Long, String> objPool = new ObjPool<>(10, 2L);
// 通过对象池获取t后执行
objPool.exec(t -> {
System.out.println(t);
return t.toString();
});
}
}
小结
- 信号量在Java中的名气并不算大,在其他语言中有很高的知名度
- Java在并发领域 重点支持 的还是 管程模型
- 管程模型理论上解决了信号量模型的一些不足,主要体现在 易用性 和 工程化 方面
转载请注明出处:http://zhongmingmao.me/2019/05/08/java-concurrent-semaphore/
访问原文「 Java并发 -- Semaphore 」获取最佳阅读体验并参与讨论
正文到此结束
热门推荐
相关文章
Loading...










![[HBLOG]公众号](https://www.liuhaihua.cn/img/qrcode_gzh.jpg)

