java并发编程学习之线程的生命周期-interrupt(七)
resume、suspend、stop
- resume和suspend是配套使用的,suspend方法容易导致死锁。
- stop方法不会保证线程的资源正常释放
interrupt
- interrupt()方法:给线程打个停止标记,将线程的中断状态设置为true,并没有马上强制中断线程,线程是否中断由线程自己决定。
- isInterrupted()方法:判断当前线程是否中断,不清除中断标志。
- interrupted()方法:判断当前线程是否中断,清除中断标志。
如果跑出异常,中断状态设置为false。
示例
例子1
public class InterruptThread extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
InterruptThread thread = new InterruptThread();
thread.start();
System.out.println(thread.getState());
sleep(1000);
thread.interrupt();
System.out.println(thread.getState());
System.out.println(thread.isInterrupted());
}
}
运行结果如下

可以看出,虽然中断状态是true了,但是程序依然在运行,所以interrupt并没有强制中断线程。
例子2
public class InterruptThread2 extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
while (!isInterrupted()) {
}
System.out.println("已中断");
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
InterruptThread2 thread = new InterruptThread2();
thread.start();
System.out.println(thread.getState());
sleep(1000);
thread.interrupt();
System.out.println(thread.getState());
System.out.println(thread.isInterrupted());
}
}
运行结果如下:
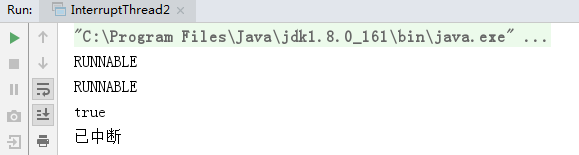
跟例子1的区别是,通过判断中断状态,来处理我们自己的业务逻辑,这样的设计,给程序带来了极大的利灵活性。
例子3
public class InterruptWait extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
waitFun();
}
public synchronized void waitFun(){
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("打扰我等待了");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
InterruptWait thread = new InterruptWait();
thread.start();
System.out.println(thread.getState());
sleep(1000);
thread.interrupt();
sleep(1000);
System.out.println(thread.getState());
System.out.println(thread.isInterrupted());
sleep(1000);
System.out.println(thread.getState());
}
}
运行结果如下:
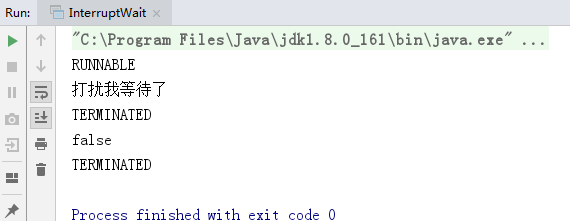
中断wait方法,这里需要注意的是,抛出异常后,中断状态变成false。
例子4
public class InterruptWait extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
waitFun();
}
public synchronized void waitFun(){
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("打扰我等待了");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
InterruptWait thread = new InterruptWait();
thread.start();
System.out.println(thread.getState());
sleep(1000);
thread.interrupt();
sleep(1000);
System.out.println(thread.getState());
System.out.println(thread.isInterrupted());
sleep(1000);
System.out.println(thread.getState());
}
}
运行结果如下:
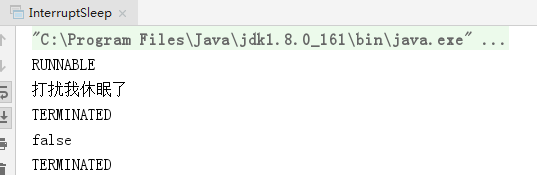
结果同上,抛出异常后,中断状态变成false。
例子5
public class InterruptSync extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
syncFun();
}
public static synchronized void syncFun() {
while (true) {
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
InterruptSync thread = new InterruptSync();
InterruptSync thread2 = new InterruptSync();
thread.start();
sleep(1000);
thread2.start();
sleep(1000);
System.out.println(thread.getState());
System.out.println(thread2.getState());
thread2.interrupt();
sleep(1000);
System.out.println(thread2.getState());
System.out.println(thread2.isInterrupted());
}
}
运行结果如下:
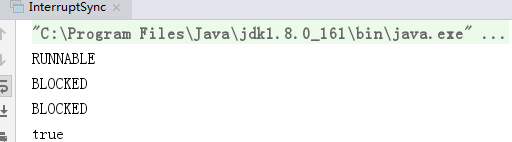
没有抛异常,结果同例子1。
正文到此结束
热门推荐
相关文章
Loading...










![[HBLOG]公众号](https://www.liuhaihua.cn/img/qrcode_gzh.jpg)

