Java性能 -- 序列化
- Java RMI采用的是 Java序列化
- Spring Cloud采用的是 JSON序列化
- Dubbo虽然兼容Java序列化,但默认使用的是 Hessian序列化
Java序列化
原理

Serializable
- JDK提供了输入流对象 ObjectInputStream 和输出流对象 ObjectOutputStream
- 它们只能对实现了 Serializable 接口的类的对象进行序列化和反序列化
// 只能对实现了Serializable接口的类的对象进行序列化 // java.io.NotSerializableException: java.lang.Object ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(FILE_PATH)); oos.writeObject(new Object()); oos.close();
transient
- ObjectOutputStream的 默认 序列化方式,仅对对象的 非transient的实例变量 进行序列化
- 不会序列化对象的transient的实例变量,也不会序列化静态变量
@Getter
public class A implements Serializable {
private transient int f1 = 1;
private int f2 = 2;
@Getter
private static final int f3 = 3;
}
// 序列化
// 仅对对象的非transient的实例变量进行序列化
A a1 = new A();
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(FILE_PATH));
oos.writeObject(a1);
oos.close();
// 反序列化
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(FILE_PATH));
A a2 = (A) ois.readObject();
log.info("f1={}, f2={}, f3={}", a2.getF1(), a2.getF2(), a2.getF3()); // f1=0, f2=2, f3=3
ois.close();
serialVersionUID
- 在实现了Serializable接口的类的对象中,会生成一个 serialVersionUID 的版本号
- 在反序列化过程中用来验证序列化对象是否加载了反序列化的类
- 如果是具有 相同类名 的 不同版本号 的类,在反序列化中是 无法获取对象 的
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
public class B implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private int id;
}
@Test
public void test3() throws Exception {
// 序列化
B b1 = new B(1);
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(FILE_PATH));
oos.writeObject(b1);
oos.close();
}
@Test
public void test4() throws Exception {
// 如果先将B的serialVersionUID修改为1,直接反序列化磁盘上的文件,会报异常
// java.io.InvalidClassException: xxx.B; local class incompatible: stream classdesc serialVersionUID = 0, local class serialVersionUID = 1
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(FILE_PATH));
B b2 = (B) ois.readObject();
ois.close();
}
writeObject/readObject
具体实现序列化和反序列化的是 writeObject 和 readObject
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Student implements Serializable {
private long id;
private int age;
private String name;
// 只序列化部分字段
private void writeObject(ObjectOutputStream outputStream) throws IOException {
outputStream.writeLong(id);
outputStream.writeObject(name);
}
// 按序列化的顺序进行反序列化
private void readObject(ObjectInputStream inputStream) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
id = inputStream.readLong();
name = (String) inputStream.readObject();
}
}
Student s1 = new Student(1, 12, "Bob");
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(FILE_PATH));
oos.writeObject(s1);
oos.close();
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(FILE_PATH));
Student s2 = (Student) ois.readObject();
log.info("s2={}", s2); // s2=Student(id=1, age=0, name=Bob)
ois.close();
writeReplace/readResolve
- writeReplace :用在 序列化之前 替换序列化对象
- readResolve :用在 反序列化之后 对返回对象进行处理
// 反序列化会通过反射调用无参构造器返回一个新对象,破坏单例模式
// 可以通过readResolve()来解决
public class Singleton1 implements Serializable {
private static final Singleton1 SINGLETON_1 = new Singleton1();
private Singleton1() {
}
public static Singleton1 getInstance() {
return SINGLETON_1;
}
}
Singleton1 s1 = Singleton1.getInstance();
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(FILE_PATH));
oos.writeObject(s1);
oos.close();
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(FILE_PATH));
Singleton1 s2 = (Singleton1) ois.readObject();
log.info("{}", s1 == s2); // false
ois.close();
public class Singleton2 implements Serializable {
private static final Singleton2 SINGLETON_2 = new Singleton2();
private Singleton2() {
}
public static Singleton2 getInstance() {
return SINGLETON_2;
}
public Object writeRepalce() {
// 序列化之前,无需替换
return this;
}
private Object readResolve() {
// 反序列化之后,直接返回单例
return getInstance();
}
}
Singleton2 s1 = Singleton2.getInstance();
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(FILE_PATH));
oos.writeObject(s1);
oos.close();
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(FILE_PATH));
Singleton2 s2 = (Singleton2) ois.readObject();
log.info("{}", s1 == s2); // true
ois.close();
缺陷
无法跨语言
Java序列化 只适用 于基于Java语言实现的框架
易被攻击
-
Java序列化是 不安全
的
- Java官网:对 不信任数据的反序列化 ,本质上来说是 危险 的,应该予以回避
-
ObjectInputStream.readObject()
- 将类路径上几乎所有实现了Serializable接口的对象都实例化!!
- 这意味着:在 反序列化字节流 的过程中,该方法 可以执行任意类型的代码 ,非常 危险
-
对于需要 长时间进行反序列化
的对象,不需要执行任何代码,也可以发起一次攻击
- 攻击者可以创建 循环对象链 ,然后将序列化后的对象传输到程序中进行反序列化
- 这会导致 haseCode 方法被调用的次数呈 次方爆发式增长 ,从而引发 栈溢出 异常
-
很多序列化协议都制定了 一套数据结构
来保存和获取对象,如JSON序列化、ProtocolBuf
- 它们只支持一些 基本类型 和 数组类型 ,可以避免反序列化创建一些 不确定 的实例
int itCount = 27;
Set root = new HashSet();
Set s1 = root;
Set s2 = new HashSet();
for (int i = 0; i < itCount; i++) {
Set t1 = new HashSet();
Set t2 = new HashSet();
t1.add("foo"); // 使t2不等于t1
s1.add(t1);
s1.add(t2);
s2.add(t1);
s2.add(t2);
s1 = t1;
s2 = t2;
}
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(FILE_PATH));
oos.writeObject(root);
oos.close();
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(FILE_PATH));
ois.readObject();
log.info("take : {}", System.currentTimeMillis() - start);
ois.close();
// itCount - take
// 25 - 3460
// 26 - 7346
// 27 - 11161
序列化后的流太大
- 序列化后的二进制流大小能体现序列化的能力
-
序列化后的二进制数组越大,占用的存储空间就越多,存储硬件的成本就越高
- 如果进行网络传输,则占用的 带宽 就越多,影响到系统的 吞吐量
- Java序列化使用ObjectOutputStream来实现对象转二进制编码,可以对比BIO中的ByteBuffer实现的二进制编码
@Data
class User implements Serializable {
private String userName;
private String password;
}
User user = new User();
user.setUserName("test");
user.setPassword("test");
// ObjectOutputStream
ByteArrayOutputStream os = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(os);
oos.writeObject(user);
log.info("{}", os.toByteArray().length); // 107
// NIO ByteBuffer
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(2048);
byte[] userName = user.getUserName().getBytes();
byte[] password = user.getPassword().getBytes();
byteBuffer.putInt(userName.length);
byteBuffer.put(userName);
byteBuffer.putInt(password.length);
byteBuffer.put(password);
byteBuffer.flip();
log.info("{}", byteBuffer.remaining()); // 16
序列化速度慢
- 序列化速度是体现序列化性能的重要指标
- 如果序列化的速度慢,就会影响 网络通信 的效率,从而增加系统的 响应时间
int count = 10_0000;
User user = new User();
user.setUserName("test");
user.setPassword("test");
// ObjectOutputStream
long t1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
ByteArrayOutputStream os = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(os);
oos.writeObject(user);
oos.flush();
oos.close();
byte[] bytes = os.toByteArray();
os.close();
}
long t2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("{}", t2 - t1); // 731
// NIO ByteBuffer
long t3 = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(2048);
byte[] userName = user.getUserName().getBytes();
byte[] password = user.getPassword().getBytes();
byteBuffer.putInt(userName.length);
byteBuffer.put(userName);
byteBuffer.putInt(password.length);
byteBuffer.put(password);
byteBuffer.flip();
byte[] bytes = new byte[byteBuffer.remaining()];
}
long t4 = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("{}", t4 - t3); // 182
ProtoBuf
-
ProtoBuf是由Google推出且支持多语言的序列化框架
- 在序列化框架性能测试报告中,ProtoBuf无论 编解码耗时 ,还是 二进制流压缩大小 ,都表现很好
- ProtoBuf以一个 .proto 后缀的文件为基础,该文件描述了字段以及字段类型,通过工具可以生成不同语言的数据结构文件
- 在序列化该数据对象的时候,ProtoBuf通过.proto文件描述来生成Protocol Buffers格式的编码
存储格式
- Protocol Buffers是一种轻便高效的 结构化 数据存储格式
-
Protocol Buffers使用 T-L-V
(标识-长度-字段值)的数据格式来存储数据
-
T代表字段的 正数序列
(tag)
- Protocol Buffers将对象中的 字段 与 正数序列 对应起来,对应关系的信息是由生成的代码来保证的
- 在 序列化的时候用整数值来代替字段名称 ,传输流量就可以 大幅缩减
- L代表Value的 字节长度 ,一般也只占用 一个字节
- V代表字段值经过 编码后 的值
-
T代表字段的 正数序列
(tag)
- 这种格式 不需要分隔符 ,也 不需要空格 ,同时 减少了冗余字段名
编码方式
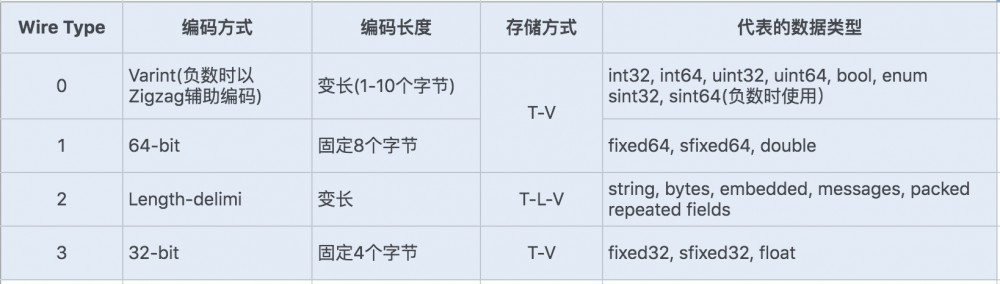
- ProtoBuf定义了一套自己的编码方式,几乎可以映射Java/Python等语言的 所有基础数据类型
- 不同的 编码方式 可以对应不同的 数据类型 ,还能采用不同的 存储格式
- 对于Varint编码的数据,由于数据占用的存储空间是 固定 的,因此不需要存储字节长度length,存储方式采用 T-V
-
Varint编码是一种 变长
的编码方式,每个数据类型 一个字节的最后一位
是 标志位
(msb)
- 0表示当前字节已经是 最后 一个字节
- 1表示后面还有一个字节
-
对于int32类型的数字,一般需要4个字节表示,如果采用Varint编码,对于很小的int类型数字,用1个字节就能表示
- 对于大部分整数类型数据来说,一般都是小于256,所以这样能起到很好的 数据压缩 效果
编解码
- ProtoBuf不仅 压缩 存储数据的效果好,而且 编解码 的性能也是很好的
-
ProtoBuf的编码和解码过程结合 .proto
文件格式,加上Protocol Buffers独特的编码格式
- 只需要 简单的数据运算 以及 位移 等操作就可以完成编码和解码
正文到此结束
热门推荐
相关文章
Loading...










![[HBLOG]公众号](https://www.liuhaihua.cn/img/qrcode_gzh.jpg)

