Mina实现Socket通信完整过程
title: Mina服务端客户端通信
date: 2018-09-30 09:00:30
tags:
- [mina] - [tcp]
categories:
- [编程]
permalink: zxh
[TOC]
前两章节已经完整的介绍了理论部分,今天我们就利用这些理论来实现tcp协议的c/s 通信。首先我们简单回顾下之前的介绍,
在mina中我们的客户端和服务端简直就是一模一样,只是我们用不同适配器。但是他的数据处理流程是一样的。今天我们就重点看看如何建立服务端、客户端
并且处理两者之间的消息通信处理
服务端
服务端和客户端不同的就是我们创建的监听对象不同而已,客户端发送消息到服务端,服务端需要经历过滤器的处理才能到达消息中心,但是在过滤器中我们就需要将消息进行解码,然后才会到消息接收的地方处理我们的业务。正常情况下我们处理完消息需要对客户端进行回应。回应的时候也会经历过滤器中的编码逻辑,进行数据编码然后发送。信息发送到客户端我们可以看成服务端的方向。也是需要进行编解码的。下面看看服务端的创建代码
//创建监听对象
IoAcceptor acceptor = new NioSocketAcceptor();
TextLineCodecFactory textLineCodecFactory =
new TextLineCodecFactory(Charset.forName("utf-8"), LineDelimiter.WINDOWS.getValue(),
LineDelimiter.WINDOWS.getValue());
//添加过滤器
acceptor.getFilterChain().addLast("logger",new LoggingFilter());
acceptor.getFilterChain().addLast("protocal",new ProtocolCodecFilter(
textLineCodecFactory
));
//设置时间处理的handler
acceptor.setHandler(new ServerMessageHandler());
//设置读取数据缓存区的大小
acceptor.getSessionConfig().setReadBufferSize(Constaint.READSIZE);
//设置多久没有消息就进入空闲状态
acceptor.getSessionConfig().setIdleTime(IdleStatus.BOTH_IDLE,Constaint.IDLETIME);
//绑定端口
try {
acceptor.bind(new InetSocketAddress(Constaint.REMOTE_PORT));
} catch (IOException e) {
logger.error(String.format("bind %s error",Constaint.REMOTE_PORT));
e.printStackTrace();
}
logger.info(String.format("bind %s success",Constaint.REMOTE_PORT));
客户端
//创建监听对象
IoConnector connector = new NioSocketConnector();
TextLineCodecFactory textLineCodecFactory =
new TextLineCodecFactory(Charset.forName("utf-8"), LineDelimiter.WINDOWS.getValue(),
LineDelimiter.WINDOWS.getValue());
//添加过滤器
//日志过滤器 。 sltf日志设置
connector.getFilterChain().addLast("logger",new LoggingFilter());
//在这个过滤器中提供了编解码,这里的编码是以信息中已/r/n结尾算是一条信息
connector.getFilterChain().addLast("protocal",new ProtocolCodecFilter(
new SocketFactory()
));
//设置时间处理的handler , 提供session生命周期的监听函数,消息接受,发送的函数
connector.setHandler(new ClientMessageHandler());
//设置读取数据缓存区的大小
connector.getSessionConfig().setReadBufferSize(Constaint.READSIZE);
//设置多久没有消息就进入空闲状态
connector.getSessionConfig().setIdleTime(IdleStatus.BOTH_IDLE,Constaint.IDLETIME);
ConnectFuture future = connector.connect(new InetSocketAddress(Constaint.REMOTE_IP,Constaint.REMOTE_PORT));
//是异步处理,这里不会造成阻塞
future.addListener(new IoFutureListener<IoFuture>() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(IoFuture ioFuture) {
logger.info("连接准备完成");
IoSession session = ioFuture.getSession();
}
});
通信
- 其实上面服务端,客户端两边创建好就应经在通信了,在上面创建的时候我们发现。创建的时候需要指定消息处理器(IoHandlerAdapter) , 这个在IoService中会排在IoFilter之后执行。在过滤器执行之后我们就会调用我们的消息处理器。
private static Logger logger = LogManager.getLogger(ServerMessageHandler.class);
public void sessionCreated(IoSession session) throws Exception {
super.sessionCreated(session);
logger.info("sessionCreated");
}
public void sessionOpened(IoSession session) throws Exception {
super.sessionOpened(session);
try {
IoBuffer buffer = IoBuffer.allocate(30);
buffer.clear();
buffer.putString("quit/r/n", Charset.forName("utf-8").newEncoder());
buffer.flip();
session.write(buffer);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error(e.toString());
}
logger.info("sessionOpened");
}
public void sessionClosed(IoSession session) throws Exception {
super.sessionClosed(session);
logger.info("sessionClosed");
}
public void sessionIdle(IoSession session, IdleStatus idleStatus) throws Exception {
super.sessionIdle(session,idleStatus);
try {
IoBuffer buffer = IoBuffer.allocate(30);
buffer.clear();
buffer.putString("quit/r/n", Charset.forName("utf-8").newEncoder());
buffer.flip();
session.write(buffer);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error(e.toString());
}
// logger.info("sessionIdle");
}
public void exceptionCaught(IoSession ioSession, Throwable throwable) throws Exception {
logger.info("exceptionCaught");
throwable.printStackTrace();
}
public void messageReceived(IoSession session, Object message) throws Exception {
super.messageReceived(session, message);
String info = message.toString();
Date date = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis());
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
String time = sdf.format(date);
session.write(time);
System.out.println("接收到的消息:"+info);
}
public void messageSent(IoSession session, Object message) throws Exception {
super.messageSent(session, message);
logger.info("messageSent");
}
- 这里消息处理器,提供了几个时刻可以控制,比如session创建、销毁的时候执行的地方。消息接收的地方,消息发送成功的地方。这些控制力度可以根据我们的需要进行适度的复写。
自定义工厂编解码
- 工厂是提供编解码的方法。这个工厂是加载在ProtocolCodecFilter这个过滤器中的。我们也可以自定义过滤器,在自定义的过滤器中我们也可以加载我们自定义的工厂,实现编解码。我们在编解码的地方,就可以加入我们的业务代码。比如解码通过约定的协议方式读取到内容后通过ProtocolDecoderOutput 将消息写出去就可以在我们的IoHandlerAdapter的messageReceived方法中获取到消息。然后业务书写。这样做到代码的解耦。
public class SocketFactory implements ProtocolCodecFactory {
private MessageDecoder decoder;
private MessageEncoder encoder;
public SocketFactory() {
decoder = new MessageDecoder();
encoder = new MessageEncoder();
}
public ProtocolDecoder getDecoder(IoSession session) throws Exception {
return this.decoder;
}
public ProtocolEncoder getEncoder(IoSession session) throws Exception {
return this.encoder;
}
}
解码器
- 上面的工厂就是提供编解码的。和我们生活中一样工厂提供功能,但是实际并不是工厂做的,工厂可能只代理功能,仅仅是个加工厂而已。mina通信也是如此。真正编解码的并不是工厂执行的,本节将揭露解码者CumulativeProtocolDecoder
-
解码器写好之后只需要在上面自定义工厂中创建就好了。至于自定义编码器只需要继承CumulativeProtocolDecoder这个类就好了。而且复写doDecode方法就好了。这个方法的返回值是boolean类型。返回值不同代表意义不一。这里需要重点理清楚
- true: 返回true表示你已经从CumulativeProtocolDecoder的消息中消费了信息,在编码器中返回true之前也应该调用ProtocolDecoderOutput 的wirte将消息发布到IoHandAdaptor中进行业务处理。但是这里会出现其他情况,应为我们服务端客户端是长连接所以在我们消息中消息是不断发过来的,我们缓存中的消息可能是完整一条消息,也可能不够一整条消息,也可能是一整条多了一点,
1、如果不是一条完整(半包)的那么我们返回falsed等待客户端继续发送
2、如果正好是一整条,那么我们接受到之后返回true的时候我们缓存中就没有数据了,在CumulativeProtocolDecoder会停止对解码中doDecode的调用了,这种情况不会出现意外
3、数据比一条完整信息(粘包)多,那么我们处理到一条信息后也需要返回true,但是CumulativeProtocolDecoder会将剩余的缓存继续拼装,剩余消息就相当于内部进行了第二次解码。如果不过那么相当于上面第一种情况
记住三种情况 半包 、 正常 、 粘包
- false: 返回false就是缓存中的数据不够我们一整条消息,需要继续等待客户端的消息。CumulativeProtocolDecoder中的缓存机制会不断的将客户端发过来的数据拼接到缓存中
- true: 返回true表示你已经从CumulativeProtocolDecoder的消息中消费了信息,在编码器中返回true之前也应该调用ProtocolDecoderOutput 的wirte将消息发布到IoHandAdaptor中进行业务处理。但是这里会出现其他情况,应为我们服务端客户端是长连接所以在我们消息中消息是不断发过来的,我们缓存中的消息可能是完整一条消息,也可能不够一整条消息,也可能是一整条多了一点,
public class MessageDecoder extends CumulativeProtocolDecoder {
/**
* 此方法return true : 表示父类中CumulativeProtocolDecoder会不断的调用此方法进行消息的消费
* return false: 表示消息已经消费完全了,缓存中就算有数据也不会再消费了。等待再次客户端
* 发送消息时会触发消息发送接口,此时会将新旧消息拼接再一起进行处理
* @param ioSession
* @param ioBuffer
* @param protocolDecoderOutput
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
protected boolean doDecode(IoSession ioSession, IoBuffer ioBuffer, ProtocolDecoderOutput protocolDecoderOutput) throws Exception {
IoBuffer buffer = IoBuffer.allocate(10);
while (ioBuffer.hasRemaining()) {
if (ioBuffer.remaining()<3) {
//继续接受
return false;
}
//获取三个字节
int oldLimit = ioBuffer.limit();
ioBuffer.limit(ioBuffer.position()+3);
String text = ioBuffer.getString(Charset.forName("UTF-8").newDecoder());
protocolDecoderOutput.write(text);
ioBuffer.limit(oldLimit);
if (ioBuffer.hasRemaining()) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
编码器
- 编码器相对解码器简单很多,编码器就是加入我们的协议,正常情况就是我们业务代码中消息是一个Java实体,我们需要做的是将Java实体按照协议转换成IoBuffer进行发送。但是我们mina中发送消息是通过IoSession中write方法发送的。我们查看源码发现在IoSession.write(Object o),发送的如果是IoBuffer那么就不经过我们的编码器,否则会经过我们编码器进行编码最终将转换后的IoBuffer发送出去。
public class MessageEncoder extends ProtocolEncoderAdapter {
@Override
public void encode(IoSession ioSession, Object o, ProtocolEncoderOutput protocolEncoderOutput) throws Exception {
//TODO 根据协议编码
//组装好之后 ioSession.write(IoBuffer)写出
System.out.println(o);
}
}
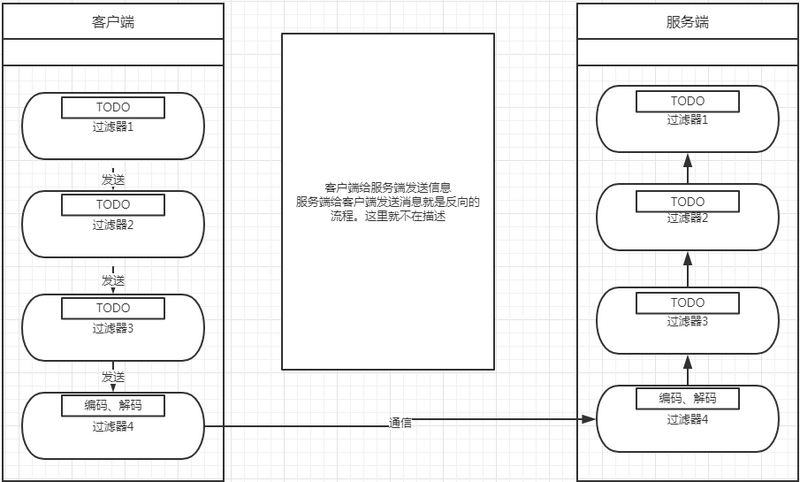
总结
<span id="addMe">加入战队</span>
微信公众号

正文到此结束
热门推荐
相关文章
Loading...










![[HBLOG]公众号](https://www.liuhaihua.cn/img/qrcode_gzh.jpg)

