句柄数超限及大量CLOSE_WAIT连接问题排查
问题
一次框架升级之后,很多组件运行一段时间就会出现无法访问的现象,http请求一直pending
分析
1. 句柄数异常
出现问题后立刻查看日志,出现大量异常
Socket accept failed
java.io.IOException: Too many open files
经百度是进程打开的句柄数超出限制,这导致后续的连接无法创建,所以一直pending。
继续百度,用命令 lsof|awk '{print $2}'|sort|uniq -c|sort -nr|more 给所有进程按句柄数排序,注意这个命令统计的是所有的句柄(包括正常的和异常的连接,加了grep CLOSE_WAIT也不行,请大神指教),一看最高的有几十万!!!
2. 大量CLOSE_WAIT连接
用 lsof -p | wc -l 详细看看每个组件的句柄数,发现大量CLOSE_WAIT连接,对端是随机的端口。
上述命令加上grep CLOSE_WAIT再统计,终于正常了一点,但是最高的也有大几千- -!
回顾了一下tcp四次握手的知识,CLOSE_WAIT是服务端收到FIN报文并ACK之后没有回复FIN报文给客户端,导致服务端到客户端的单向连接一直挂起。
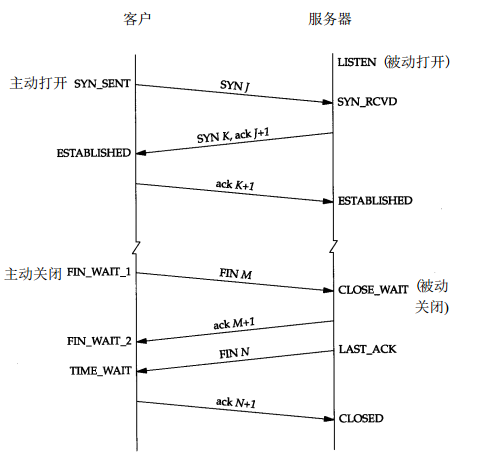
花了一下午重启环境,抓包分析,然而并没有什么卵用,只是证明了确实没有回复FIN报文而已;追踪有问题的请求也没有线索,因为发起端只会收到异常,而接收端压根收不到请求。。。
3. DB连接线程阻塞
cat /proc/pid/status 一看,thread有600,不正常!
经过同事的提醒,这种大量阻塞的情况,看线程状态最直观嘛(居然没想到)!
jstack走一波,发现大量死锁和WAITING状态的线程,都是自定义的数据源状态监控类(继承自spring-boot-actuator的AbstractHealthIndicator)获取数据库连接时产生的。
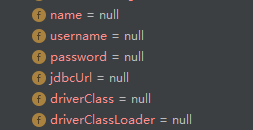
在配置类中注册此HealthIndicator的地方打断点,发现注入的数据源的连接属性全为空,而上一个版本中dataSource方法没有加上@Primary注解时是可以正常注入的
@Bean
@Primary
public DataSource dataSource(){
return DruidDataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
@Bean
public DataSourceHealthIndicator dataSourceHealthIndicator(){
return new DataSourceHealthIndicator(dataSource(),null);
}
往下分析发现是用这个dataSource获取连接时一直阻塞,也不报错,不想深究Druid的问题。
4. inter-bean references
inter-bean references(内部级联)是指同一个@Configuration注解的配置类内部,在一个@Bean注解的方法dataSourceHealthIndicator中调用另一个@Bean注解的方法dataSource时,会直接从容器中返回dataSource的实例,而不是重新创建。参见注释:
* <h3>{@code @Bean} Methods in {@code @Configuration} Classes</h3>
*
* <p>Typically, {@code @Bean} methods are declared within {@code @Configuration}
* classes. In this case, bean methods may reference other {@code @Bean} methods in the
* same class by calling them <i>directly</i>. This ensures that references between beans
* are strongly typed and navigable. Such so-called <em>'inter-bean references'</em> are
* guaranteed to respect scoping and AOP semantics, just like {@code getBean()} lookups
* would. These are the semantics known from the original 'Spring JavaConfig' project
* which require CGLIB subclassing of each such configuration class at runtime. As a
* consequence, {@code @Configuration} classes and their factory methods must not be
* marked as final or private in this mode. For example:
而在dataSource上使用了@Primary注解之后,该配置类虽然同样会在ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.enhanceConfigurationClasses方法中创建增强的代理子类,但实际调用dataSource方法时,却没有使用代理类。头晕,请大神指教先。
解决方案
使用@Qualifier注入dataSource
inter-bean references原理
-
spring容器启动后,调用配置类专用处理器ConfigurationClassPostProcessor,在其中遍历配置类,生成增加代理子类,并设置成BeanDefinition的beanClass
public void enhanceConfigurationClasses(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { Map<String, AbstractBeanDefinition> configBeanDefs = new LinkedHashMap<String, AbstractBeanDefinition>(); for (String beanName : beanFactory.getBeanDefinitionNames()) { // 遍历beanDefinition BeanDefinition beanDef = beanFactory.getBeanDefinition(beanName); if (ConfigurationClassUtils.isFullConfigurationClass(beanDef)) { // 是否@Configuration配置类 if (!(beanDef instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition)) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("Cannot enhance @Configuration bean definition '" + beanName + "' since it is not stored in an AbstractBeanDefinition subclass"); } else if (logger.isWarnEnabled() && beanFactory.containsSingleton(beanName)) { logger.warn("Cannot enhance @Configuration bean definition '" + beanName + "' since its singleton instance has been created too early. The typical cause " + "is a non-static @Bean method with a BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor " + "return type: Consider declaring such methods as 'static'."); } configBeanDefs.put(beanName, (AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDef); } } if (configBeanDefs.isEmpty()) { // nothing to enhance -> return immediately return; } ConfigurationClassEnhancer enhancer = new ConfigurationClassEnhancer(); for (Map.Entry<String, AbstractBeanDefinition> entry : configBeanDefs.entrySet()) { // 遍历配置类 AbstractBeanDefinition beanDef = entry.getValue(); // If a @Configuration class gets proxied, always proxy the target class beanDef.setAttribute(AutoProxyUtils.PRESERVE_TARGET_CLASS_ATTRIBUTE, Boolean.TRUE); try { // Set enhanced subclass of the user-specified bean class Class<?> configClass = beanDef.resolveBeanClass(this.beanClassLoader); // 生成增强代理子类 Class<?> enhancedClass = enhancer.enhance(configClass, this.beanClassLoader); if (configClass != enhancedClass) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug(String.format("Replacing bean definition '%s' existing class '%s' with " + "enhanced class '%s'", entry.getKey(), configClass.getName(), enhancedClass.getName())); } // 设置成beanClass beanDef.setBeanClass(enhancedClass); } } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot load configuration class: " + beanDef.getBeanClassName(), ex); } } } -
生成的增强代理子类实际是ConfigurationClassEnhancer,注册有两个过滤器,其中BeanMethodInterceptor会在调用带有@Bean注解的方法时切入(具体在哪配置的切入没找到,求指教ORZ),在intercept方法中判断当前执行的方法和切面方法是不是同一个,不是的话就去容器中拿切面方法对应的bean,没有就创建
@Override public Object intercept(Object enhancedConfigInstance, Method beanMethod, Object[] beanMethodArgs, MethodProxy cglibMethodProxy) throws Throwable { ConfigurableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory(enhancedConfigInstance); String beanName = BeanAnnotationHelper.determineBeanNameFor(beanMethod); // Determine whether this bean is a scoped-proxy Scope scope = AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(beanMethod, Scope.class); if (scope != null && scope.proxyMode() != ScopedProxyMode.NO) { String scopedBeanName = ScopedProxyCreator.getTargetBeanName(beanName); if (beanFactory.isCurrentlyInCreation(scopedBeanName)) { beanName = scopedBeanName; } } // To handle the case of an inter-bean method reference, we must explicitly check the // container for already cached instances. // First, check to see if the requested bean is a FactoryBean. If so, create a subclass // proxy that intercepts calls to getObject() and returns any cached bean instance. // This ensures that the semantics of calling a FactoryBean from within @Bean methods // is the same as that of referring to a FactoryBean within XML. See SPR-6602. if (factoryContainsBean(beanFactory, BeanFactory.FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName) && factoryContainsBean(beanFactory, beanName)) { Object factoryBean = beanFactory.getBean(BeanFactory.FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName); if (factoryBean instanceof ScopedProxyFactoryBean) { // Scoped proxy factory beans are a special case and should not be further proxied } else { // It is a candidate FactoryBean - go ahead with enhancement return enhanceFactoryBean(factoryBean, beanMethod.getReturnType(), beanFactory, beanName); } } // 判断当前执行的方法是不是切面方法 if (isCurrentlyInvokedFactoryMethod(beanMethod)) { // The factory is calling the bean method in order to instantiate and register the bean // (i.e. via a getBean() call) -> invoke the super implementation of the method to actually // create the bean instance. if (logger.isWarnEnabled() && BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class.isAssignableFrom(beanMethod.getReturnType())) { logger.warn(String.format("@Bean method %s.%s is non-static and returns an object " + "assignable to Spring's BeanFactoryPostProcessor interface. This will " + "result in a failure to process annotations such as @Autowired, " + "@Resource and @PostConstruct within the method's declaring " + "@Configuration class. Add the 'static' modifier to this method to avoid " + "these container lifecycle issues; see @Bean javadoc for complete details.", beanMethod.getDeclaringClass().getSimpleName(), beanMethod.getName())); } // 是的话创建当前方法的bean return cglibMethodProxy.invokeSuper(enhancedConfigInstance, beanMethodArgs); } // 不是的话从容器中获取切面方法的bean return obtainBeanInstanceFromFactory(beanMethod, beanMethodArgs, beanFactory, beanName); }
- 本文标签: db dataSource 数据库 处理器 时间 bug java value js src map cache CTO Qualifier 端口 百度 grep ACE IDE id spring key https lib cat ORM CEO cglib IBM final find jstack 数据 服务端 rmi XML awk build 进程 bean TCP Proxy tab 锁 tar http UI AOP 实例 tk struct example 线程 BeanDefinition 注释 HashMap ssl list 统计 配置 IO 遍历 druid
- 版权声明: 本文为互联网转载文章,出处已在文章中说明(部分除外)。如果侵权,请联系本站长删除,谢谢。
- 本文海报: 生成海报一 生成海报二










![[HBLOG]公众号](https://www.liuhaihua.cn/img/qrcode_gzh.jpg)

