Spring系列五:Bean 的生命周期
换我心,为你心,始知相忆深。

概述
在本章中,我们学习 Spring bean 的生命周期。掌握 bean 生命周期的各个阶段,初始化和销毁回调方法。我们将学习使用 XML 配置和注释配置来控制 bean 生命周期事件。
Bean的声明周期
当容器启动时–-需要基于 Java 或 XML bean 定义实例化 Spring bean 。还需要执行一些初始化后的步骤,以使其进入可用状态。 Spring Boot 启动应用程序也具有相同的 bean 生命周期。
之后,当不再需要该 bean 时,它将被从 IoC 容器中删除。
Spring bean factory 负责管理通过 Spring 容器创建的 bean 的生命周期。
生命周期回调
Spring bean factory 控制 bean 的创建和销毁。为了执行一些自定义操作,它提供了回调方法,这些方法可以大致分为两类:
Post-initialization Pre-destruction
生命周期图解
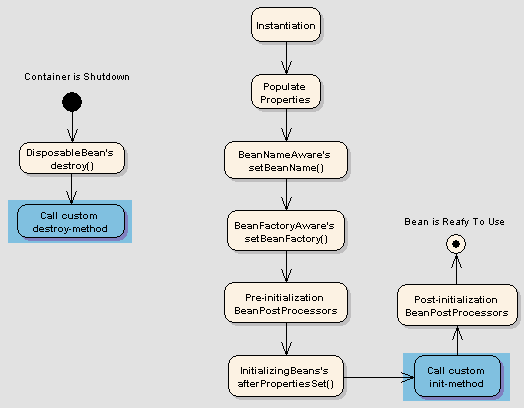
生命周期回调方法
Spring 框架提供了以下4种方法来控制 Bean 的生命周期事件:
-
InitializingBean和DisposableBean回调接口 -
*Aware接口提供一些特殊的实现 -
Bean配置文件中的自定义init()和destroy()方法 -
@PostConstruct和@PreDestroy注解
InitializingBean 和 DisposableBean 接口
org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean 接口允许 bean 在容器设置了 bean 的所有必要属性之后执行初始化工作。
InitializingBean 接口指定一个方法:
void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception;
这并不是初始化 bean 的首选方法,因为它将 bean 类与 spring 容器紧密地耦合在一起。更好的方法是在 applicationContext.xml 文件的 bean 定义中使用 init-method 属性。
类似地,实现 org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean 接口允许 Bean 在包含它的容器被销毁时获得回调。
DisposableBean 接口指定一个方法:
void destroy() throws Exception;
// 实现上述接口的示例bean:
package cn.howtodoinjava.task;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
public class DemoBean implements InitializingBean, DisposableBean
{
//Other bean attributes and methods
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception
{
//Bean initialization code
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception
{
//Bean destruction code
}
}
*Aware 接口
Spring 提供了一系列 *Aware 接口,允许 bean 向容器表明它们需要某种基础设施依赖。每个接口都需要您实现一个方法来将依赖项注入 bean 。
这些接口可以概括为:
*Aware 接口 |
重写方法 | 目的 |
|---|---|---|
ApplicationContextAware |
void setApplicationContext (ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException; |
接口将由任何希望将其运行的 ApplicationContext 通知给它的对象来实现。 |
ApplicationEventPublisherAware |
void setApplicationEventPublisher (ApplicationEventPublisher applicationEventPublisher); |
设置此对象运行的 ApplicationEventPublisher 。 |
BeanClassLoaderAware |
void setBeanClassLoader (ClassLoader classLoader); |
将 bean 类加载器提供给 bean 实例的回调。 |
BeanFactoryAware |
void setBeanFactory (BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException; |
将拥有的工厂提供给 Bean 实例的回调。 |
BeanNameAware |
void setBeanFactory (BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException; |
在创建此 bean 的 bean 工厂中设置 bean 的名称。 |
BootstrapContextAware |
void setBootstrapContext (BootstrapContext bootstrapContext); |
设置该对象在其中运行的 BootstrapContext 。 |
LoadTimeWeaverAware |
void setLoadTimeWeaver (LoadTimeWeaver loadTimeWeaver); |
设置此对象包含 ApplicationContext 的 LoadTimeWeaver 。 |
MessageSourceAware |
void setMessageSource (MessageSource messageSource); |
设置此对象在其中运行的 MessageSource 。 |
NotificationPublisherAware |
void setNotificationPublisher (NotificationPublisher notificationPublisher); |
为当前的托管资源实例设置 NotificationPublisher 实例。 |
PortletConfigAware |
void setPortletConfig (PortletConfig portletConfig); |
设置运行该对象的 PortletConfig 。 |
PortletContextAware |
void setPortletContext (PortletContext portletContext); |
设置此对象在其中运行的 PortletContext 。 |
ResourceLoaderAware |
void setResourceLoader (ResourceLoader resourceLoader); |
设置此对象在其中运行的 ResourceLoader 。 |
ServletConfigAware |
void setServletConfig (ServletConfig servletConfig); |
设置运行该对象的 ServletConfig 。 |
ServletContextAware |
void setServletContext (ServletContext servletContext); |
设置运行该对象的 ServletContext 。 |
下面的 Java 代码块展示了使用 *Aware 接口 来控制 bean 生命周期的用法。
package cn.howtodoinjava.task;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanClassLoaderAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactoryAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanNameAware;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEventPublisher;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEventPublisherAware;
import org.springframework.context.MessageSource;
import org.springframework.context.MessageSourceAware;
import org.springframework.context.ResourceLoaderAware;
import org.springframework.context.weaving.LoadTimeWeaverAware;
import org.springframework.core.io.ResourceLoader;
import org.springframework.instrument.classloading.LoadTimeWeaver;
import org.springframework.jmx.export.notification.NotificationPublisher;
import org.springframework.jmx.export.notification.NotificationPublisherAware;
public class DemoBean implements ApplicationContextAware,
ApplicationEventPublisherAware, BeanClassLoaderAware, BeanFactoryAware,
BeanNameAware, LoadTimeWeaverAware, MessageSourceAware,
NotificationPublisherAware, ResourceLoaderAware
{
@Override
public void setResourceLoader(ResourceLoader arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
@Override
public void setNotificationPublisher(NotificationPublisher arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
@Override
public void setMessageSource(MessageSource arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
@Override
public void setLoadTimeWeaver(LoadTimeWeaver arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
@Override
public void setBeanName(String arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory arg0) throws BeansException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
@Override
public void setBeanClassLoader(ClassLoader arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
@Override
public void setApplicationEventPublisher(ApplicationEventPublisher arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext arg0)
throws BeansException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
}
自定义 init() 和 destroy() 方法
bean 配置文件中的默认 init 和 destroy 方法有两种定义方法:
- 适用于单个
Bean的Bean本地定义 - 全局定义适用于在
bean上下文中定义的所有bean
Bean 本地定义
本地定义如下:
<beans>
<bean id="demoBean" class="com.howtodoinjava.task.DemoBean"
init-method="customInit"
destroy-method="customDestroy"></bean>
</beans>
全局定义
全局定义如下,这些方法将为 <beans> 标记下给出的所有 bean 定义调用。当你有一种配置可以为所有 bean 定义通用方法名称(如 init() 和 destroy( ))时,这很实用。可帮助你不用为所有 bean 单独提及 init 和 destroy 方法。
<beans default-init-method="customInit" default-destroy-method="customDestroy">
<bean id="demoBean" class="com.howtodoinjava.task.DemoBean"></bean>
</beans>
Java 程序代码示例:
package cn.howtodoinjava.task;
public class DemoBean
{
public void customInit()
{
System.out.println("Method customInit() invoked...");
}
public void customDestroy()
{
System.out.println("Method customDestroy() invoked...");
}
}
@PostConstruct 和 @PreDestroy 注解
从 Spring 2.5 开始,你还可以使用注解通过 @PostConstruct 和 @PreDestroy 注解指定生命周期方法。
-
@PostConstruct注解的方法将在使用默认构造函数构造bean之后调用,并在它的实例返回给请求对象之前调用。 -
@PreDestroy注解方法在bean即将在bean容器中销毁之前被调用。
Java 代码示例如下:
package cn.howtodoinjava.task;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import javax.annotation.PreDestroy;
public class DemoBean
{
@PostConstruct
public void customInit()
{
System.out.println("Method customInit() invoked...");
}
@PreDestroy
public void customDestroy()
{
System.out.println("Method customDestroy() invoked...");
}
}
综上,这一切都与 Spring 容器内部的 Spring bean 生命周期有关。记住给定的生命周期事件类型,这是 Spring 面试中经常问到的问题。

关注微信公众号 java干货 不定期分享干货资料
原文链接: Spring 5 – Bean scopes










![[HBLOG]公众号](https://www.liuhaihua.cn/img/qrcode_gzh.jpg)

