SpringCloud的十倍性能优化与SmartBuf编码
smartbuf-springcloud 是一个基于 smartbuf 的 spring-cloud 序列化插件。
SmartBuf 介绍
smartbuf 是一种新颖、高效、智能、易用的跨语言序列化框架,它既拥有不亚于 protobuf 的高性能,也拥有与 json 相仿的通用性、可扩展性、可调试性等。
在 Java 语言生态中,它通过以下插件支持多种 RPC 框架:
-
smartbuf-dubbo: 为dubbo提供了stream模式的序列化扩展插件 -
smartbuf-springcloud: 为spring-cloud提供了packet模式的序列化扩展插件
以下为 smartbuf-springcloud 插件的具体介绍。
smartbuf-springcloud 介绍
此插件内部封装了 smartbuf 序列化框架的 packet 模式,通过自定义的 SmartbufMessageConverter 向 spring 容器中暴露了一个名为 application/x-smartbuf 的 HTTP 消息编码解码器。
这个新增的 application/x-smartbuf 编码器在复杂对象的数据传输过程中,可以提供优于 protobuf 的高性能。
application/x-smartbuf 编码
此插件在配置文件 META-INFO/spring.factories 中声明了一个名为 SmartbufAutoConfiguration 的自动注解配置,即自定义 Auto-Configuration 。
spring-boot 初始化时会主动扫描并注册它,因此不需要你做额外的配置。更多资料请参考 SpringBoot文档 。
SmartbufAutoConfiguration 会向 spring 容器中增加一个新的 SmartbufMessageConverter 对象,它是一个自定义的 HttpMessageConverter ,其 MediaType 为 application/x-smartbuf 。
spring-mvc 启动后会把这个新增的 HttpMessageConverter 加入 messageConverters 中,如果后续 http 请求的头信息中包括 accept: application/x-smartbuf 或 content-type: application/x-smartbuf ,则 spring-mvc 会将该请求的 OutputStream 编码或 InputStream 解码委托给 SmartbufMessageConverter 处理。
整个过程和 application/json 的实现原理类似,不同之处在于 application/x-smartbuf 底层采用了另外一种序列化方案: SmartBuf
总结:你不需要做任何额外的配置,此插件会自动向 spring-mvc 中注册一个名为 application/x-smartbuf 的数据编码解码器,它对于正常的 http 请求没有任何影响,只有头信息中的 accept 或 content-type 匹配到它时才会被激活。
实例演示
本章节通过一个简单的实例,介绍如何将 smartbuf-springcloud 引入自己的工程中,以及如何在代码中使用它。
增加Maven依赖
你可以通过以下 maven 坐标添加 smartbuf-springcloud 的依赖:
<dependency> <groupId>com.github.smartbuf</groupId> <artifactId>smartbuf-springcloud</artifactId> <version>1.0.0</version> </dependency>
使用 application/json
spring-cloud 底层使用 http 与服务端的 spring-mvc 进行通信。例如服务端的 Controller 可能类似这样:
@RestController
public class DemoController {
@PostMapping("/hello")
public String sayHello(String name) { return "hello " + name; }
}
调用方可以声明这样的 FeignClient 与服务端通信:
@FeignClient(name = "demo")
public interface DemoClient {
@PostMapping(value = "/hello", consumes = "application/json", produces = "application/json")
String hello(@RequestParam("name") String name);
}
调用方通过 DemoClient 请求服务端的 DemoController 时, feign 会根据接口中声明的 consumes 和 produces ,向服务端发送类似于这样的请求:
=== MimeHeaders ===
accept = application/json
content-type = application/json
user-agent = Java/1.8.0_191
connection = keep-alive
服务端的 spring-mvc 会根据头信息中的 accept 和 content-type ,确定使用 application/json 来执行 input 的解码和 output 的编码。
使用 application/x-smartbuf
如前文所言, smartbuf-springcloud 会自动向 spring-mvc 中注册一个名为 application/x-smartbuf 的编码解码器,因此在引入 maven 依赖之后,不需要做任何额外的配置。
你只需要将 DemoClient 修改为这样,注意 consumes 和 produces 的变化:
@FeignClient(name = "demo")
public interface DemoClient {
@PostMapping(value = "/hello", consumes = "application/x-smartbuf", produces = "application/x-smartbuf")
String hello(@RequestParam("name") String name);
}
之后 feign 就会使用 application/x-smartbuf 与服务端 spring-mvc 进行通信,此时头信息就类似这样:
=== MimeHeaders ===
accept = application/x-smartbuf
content-type = application/x-smartbuf
user-agent = Java/1.8.0_191
connection = keep-alive
更妙的是,你可以同时创建两个接口,让 application/json 与 application/x-smartbuf 共存:
@FeignClient(name = "demo")
public interface DemoClient {
@PostMapping(value = "/hello", consumes = "application/json", produces = "application/json")
String helloJSON(@RequestParam("name") String name);
@PostMapping(value = "/hello", consumes = "application/x-smartbuf", produces = "application/x-smartbuf")
String helloSmartbuf(@RequestParam("name") String name);
}
客户端可以通过 helloJSON 使用 application/json 编码方式,通过 helloSmartbuf 使用 application/x-smartbuf 编码方式,而服务端会根据请求方指定的编码类型自动进行切换。
具体演示代码在此工程的 demo 子模块中,你可以直接 checkout 到本地执行。
性能对比
smartbuf 的优点在于其分区序列化所带来的高压缩率,尤其是面对复杂对象、数组时,它的空间利用率远超其他序列化方案。
对于RPC而言,序列化耗时往往是纳秒级,而逻辑处理、数据传输往往是毫秒级的,因此以下测试将采用单线程测试相同接口、相同次数的调用下, json 与 smartbuf 的数据传输量和总耗时的差别。
下面我们通过三个不同类型的接口测试一下 json 与 smartbuf 的区别。
hello 测试
hello 即前文提到的 helloJson 和 helloSmartbuf 接口,输入输出参数都是 String ,接口内部代码逻辑非常简单。单线程循环调用 400,000 次总耗时分别为:
-
JSON: 169秒 -
SmartBuf: 170秒
网络输入( bytes_input )输出( bytes_output )总量分别为:
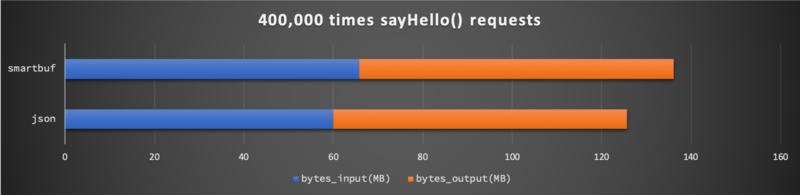
由于 smartbuf 编码中需要额外几个字节来描述完整的数据信息,因此在处理 String 这种简单数据时,它的空间利用率并不如 json 。
getUser 测试
getUser 接口的实现方式如下:
@RestController
public class DemoController {
private UserModel user = xxx; // initialized at somewhere else
@PostMapping("/getUser")
public UserModel getUser(Integer userId) { return user; }
}
其中 user 是一个专门用于测试的、随机分配的对象,其具体模型可以查阅 demo 源码中的 UserModel 类。
调用方的 FeignClient 定义如下:
@FeignClient(name = "demo")
public interface DemoClient {
@PostMapping(value = "/getUser", consumes = "application/json", produces = "application/json")
UserModel getUserJSON(@RequestParam("userId") Integer userId);
@PostMapping(value = "/getUser", consumes = "application/x-smartbuf", produces = "application/x-smartbuf")
UserModel getUserSmartbuf(@RequestParam("userId") Integer userId);
}
单线程循环调用 300,000 次的总耗时分别为:
-
JSON: 162秒 -
SmartBuf: 149秒
网络输入( bytes_input )输出( bytes_output )总量分别为:
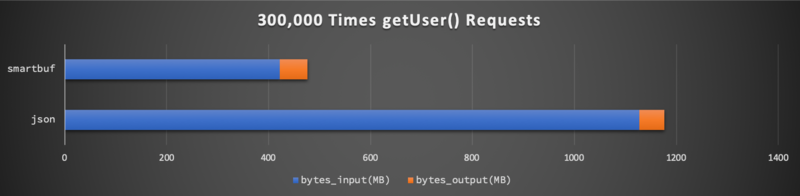
可以看到请求参数 userId 数据类型单一,因此 json 和 smartbuf 所使用的网络流量几乎一样。而返回结果 UserModel 是一个比较复杂的对象,因此 json 网络资源消耗量是 smartbuf 的将近 三倍 。
因为测试环境为 localhost ,网络传输耗时对接口的总耗时没有太大影响。
queryPost 测试
queryPost 接口的实现方式如下:
@RestController
public class DemoController {
private List<PostModel> posts = xxx; // initialized at somewhere else
@PostMapping("/queryPost")
public List<PostModel> queryPost(String keyword) { return posts; }
}
此接口返回值 posts 是一个预先分配的、用于测试的 PostModel 数组,此数组长度为固定的 100 ,其具体模型及初始化可以查阅 demo 源码。
客户端、调用方的 FeignClient 定义如下:
@FeignClient(name = "demo")
public interface DemoClient {
@PostMapping(value = "/queryPost", consumes = "application/json", produces = "application/json")
List<PostModel> queryPostJSON(@RequestParam("keyword") String keyword);
@PostMapping(value = "/queryPost", consumes = "application/x-smartbuf", produces = "application/x-smartbuf")
List<PostModel> queryPostSmartbuf(@RequestParam("keyword") String keyword);
}
单线程循环调用 100,000 次的总耗时分别为:
-
JSON: 195秒 -
SmartBuf: 155秒
网络输入( bytes_input )输出( bytes_output )总量分别为:
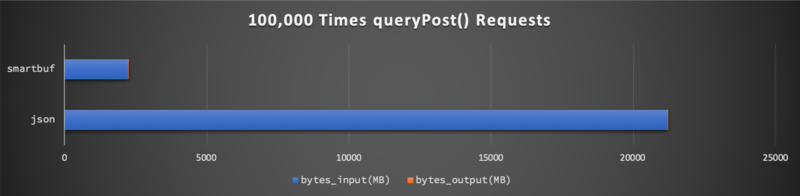
可以看到请求参数 keyword 数据类型单一,因此 json 和 smartbuf 所使用的网络流量几乎一样。而返回结果 List<PostModel> 是一个复杂对象的大数组,因此 json 网络资源消耗量是 smartbuf 的将近 十倍 。
因为测试环境为 localhost ,网络传输耗时对接口的总耗时没有太大影响。
总结
在输入输出数据格式都非常简单的 RPC 接口调用中,此插件所提供的 application/x-smartbuf 编码没有任何性能优势。
当接口数据中存在复杂对象、数组、集合等较大数据时,使用 application/x-smartbuf 可以大幅降低 net 输入输出的字节流大小,比如在上文 queryPost 测试中,使用 application/x-smartbuf 时网络输入输出字节总量仅为 application/json 的 十分之一 。
难能可贵的是,实际应用中 application/x-smartbuf 与 application/json 即可以共存,也可以无缝切换。
比如对于某些简单接口,可以直接采用简单的 application/json 编码,而对于数据量比较大的复杂接口,可以采用高效率的 application/x-smartbuf 编码进行性能优化。
比如开发测试时直接使用 application/json 编码,上线时再切换为 application/x-smartbuf 编码。
本文同步发布于GitHub、个人主页等
- 本文标签: springboot UI App 开发 ACE springcloud GitHub value 源码 Connection id 配置 stream 智能 参数 js Word Keep-Alive 大数据 key 测试 同步 服务端 map 测试环境 CTO REST https http 性能优化 数据 json java dubbo cat IO Agent 空间 插件 git src 模型 调试 实例 spring 总结 线程 message Feign 代码 list maven client
- 版权声明: 本文为互联网转载文章,出处已在文章中说明(部分除外)。如果侵权,请联系本站长删除,谢谢。
- 本文海报: 生成海报一 生成海报二










![[HBLOG]公众号](https://www.liuhaihua.cn/img/qrcode_gzh.jpg)

