Spring IOC 的简单使用
Spring IOC (Inversion Of Control反转控制容器
一、对于IOC容器的简单理解
在java开发中将程序中的对象交给容器管理,而不是在对象的内部管理。
那么两个简单的问题去分析理解IOC容器
1.为什么叫反转:
IOC容器实现了将对象的管理由对象内部直接管理(比如在一个类的main方法中new了一个String对象)转换成在容器中被动的被注入,创建。把这种对对象管理方式的改变称为反转。
2.控制了什么:
IOC容器控制了外部资源的统一获取(不仅仅包括对象,还有其他的文件)
(敲下黑板:spring容器是IOC容器,但是IOC容器不是spring容器,因为基于IOC容器设计的框架不仅只有spring)
二、应用上下文
现在我们手上有了一个魔杖(IOC容器)但是我们还需要对应的魔咒(应用上下文)来驱动魔杖
spring容器有两种实现:
1.最基础的BeanFactory(实体工厂)由于功能过于简单所以不经常使用
2.由BeanFactory派生的多种应用上下文,其抽象接口是ApplicationContext,spring根据应用场景的不同给我们设计了几种应用上下文:
(1) AnnotationConfigApplicationContext:从一个或多个基于java的配置类中加载上下文定义,适用于java注解的方式;
(2)ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:从类路径下的一个或多个xml配置文件中加载上下文定义,适用于xml配置的方式;
(3)FileSystemXmlApplicationContext:从文件系统下的一个或多个xml配置文件中加载上下文定义,也就是说系统盘符中加载xml配置文件;
(4)AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext:专门为web应用准备的,适用于注解方式;
我们在这里使用的是ClassPathXmlApplication,xml配置方式三、简单的实现IOC控制对象
1.创建一个应用上下文applicationContext_ioc.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd
">
<beans>
2.创建一个类Student
package spring.ioc.unities;
public class Student {
private String stuNo;
private String stuName;
private int gender;
private String nativePlace;
private String classNo;
private String tel;
public String getStuNo() {
return stuNo;
}
public void setStuNo(String stuNo) {
this.stuNo = stuNo;
}
public String getStuName() {
return stuName;
}
public void setStuName(String stuName) {
this.stuName = stuName;
}
public int getGender() {
return gender;
}
public void setGender(int gender) {
this.gender = gender;
}
public String getNativePlace() {
return nativePlace;
}
public void setNativePlace(String nativePlace) {
this.nativePlace = nativePlace;
}
public String getClassNo() {
return classNo;
}
public void setClassNo(String classNo) {
this.classNo = classNo;
}
public String getTel() {
return tel;
}
public void setTel(String tel) {
this.tel = tel;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [stuNo=" + stuNo + ", stuName=" + stuName + ", gender=" + gender + ", nativePlace="
+ nativePlace + ", classNo=" + classNo + ", tel=" + tel + "]";
}
}
3.在xml中通过bean标签俩控制Bean
(1)标签中必要的两个属性
id(用于识别ioc容器中的bean)
class(id对应的类的位置,通常是包名+类名,建议直接复制,手写有可能出错)
<bean id="stu1" class="spring.ioc.unities.Student"></bean>
(2)标签中其他的属性
scope属性:
| 作用域 | 说明 |
| Singleton | Spring IOC容器中一个bean定义只有一个对象实例,默认情况下会在容器启动时初始化 |
| Prototype | 每次从容器获取bean都是新的对象 |
| Request | 每次Http请求都会创建一个新的bean,只使用在WebApplicationContext中 |
| Session | 类似request,每次有新的会话都会创建一个新的Bean,只使用在WebApplicationContext中 |
3.main函数中测试确认:
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applictionContext_ioc.xml");
Student stuA = (Student) ioc.getBean("stu1");
Student stuB = (Student) ioc.getBean("stu1");
//在ioc中获取的bean:
System.out.println("获取的属性为singleton的bean-------------------------");
System.out.println(stuA.toString()+stuB.toString());
//验证A,B是否是同一个实体
System.out.println("stua和stub是否是一个bean:"+(stuA==stuB));
Student stuC = (Student) ioc.getBean("stu2");
Student stuD = (Student) ioc.getBean("stu2");
System.out.println("获取的属性为prototype的bean-------------------------");
System.out.println(stuC.toString()+stuD.toString());
System.out.println("stuc和stud是否是一个bean:"+(stuC==stuD));
}
获得结果如下:
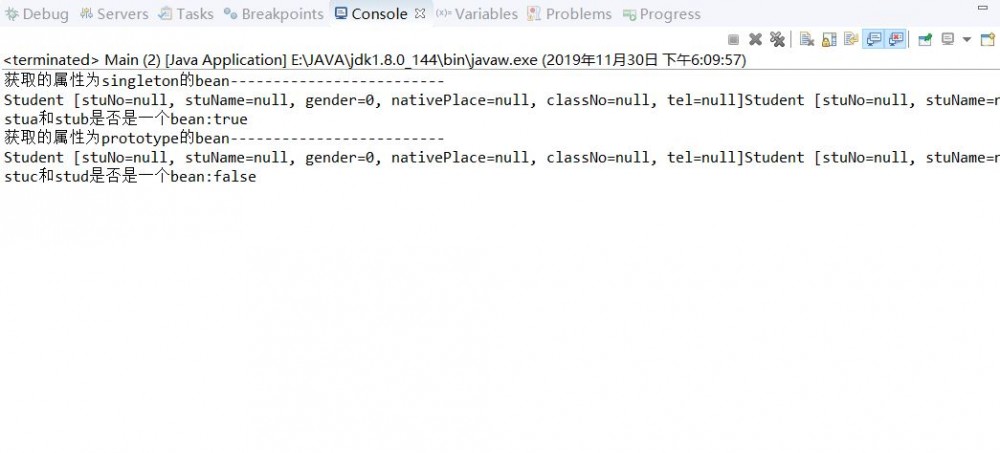
可以看出singleton属性的bean其实是单例模式下的bean.










![[HBLOG]公众号](https://www.liuhaihua.cn/img/qrcode_gzh.jpg)

