mybatis精讲(六)--二级缓存
[TOC]
简介
- 上一章节我们简单了解了二级缓存的配置。今天我们详细分析下二级缓存以及为什么不建议使用二级缓存。
- 一级缓存针对的是sqlsession。二级缓存针对的是namespace层面的。
配置
- 之前我们已经提到了配置二级缓存以及配置自定义的二级缓存。下面我们从头开始实现二级缓存。
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
- 通过上面的代码我们可以看出来,`cacheEnabled`这个属性是控制二级缓存的配置的。而这个属性在Configuration中默认是true。这里说明了mybatis默认是开启缓存功能的。二级缓存和一级缓存的区别其实除了范围以外,他们的不同点就是顺序不同。真正开启二级缓存的是在mapper的xml中配置cache标签就行了。
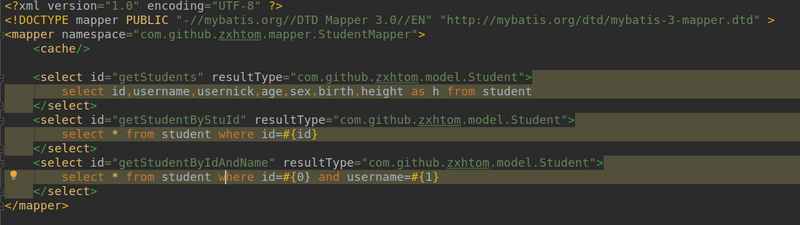
- 我们这里在StudentMapper.xml中配置.然后我们在test类中进行获取两次sqlsession调用同一个sql.
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionFactoryUtils.openSqlsession();
StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
Student student = mapper.getStudentByIdAndName("1", "1");
System.out.println(student);
SqlSession sqlSession1 = SqlSessionFactoryUtils.sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
StudentMapper mapper1 = sqlSession1.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
Student studentByIdAndName = mapper1.getStudentByIdAndName("1", "1");
System.out.println(studentByIdAndName);
- 但是结果确实很意外。事实上并没有只调用一次sql。而是调用了两次。这仅仅是结果上的异常。我们用的是Student这个结果接受的。我们再从代码层面上看看
@Data
@Builder
@Accessors(chain = true)
public class Student {
/**
* 学生索引id
* */
* private String id;
* /**
* * 姓名
* */
* private String userName;
/**
* 用户昵称
* */
* private String userNick;
/**
* 年龄
* */
* private Integer age;
* /**
* * 性别 true : 男 ; false : 女
* */
* private SexEnum sex;
* /**
* * 生日
* */
* private Date birth;
* /**
* * 身高
* */
* private Double height;
* }
- 细心的伙伴也许能够发现。我们这个实体并没有实现序列化。但是之前我们已经说过了二级缓存的实体需要序列化。按道理来说应该报错的。这就说明我们二级缓存开启,或者确切的说应该说是二级缓存没有起到作用。
-
- 那么我们先将实体进行序列化。然后启动发现并没有任何效果。我们来看看
CacheingExecutor.commit()这个方法里面有事物的提交tcm.commit()。
- 那么我们先将实体进行序列化。然后启动发现并没有任何效果。我们来看看
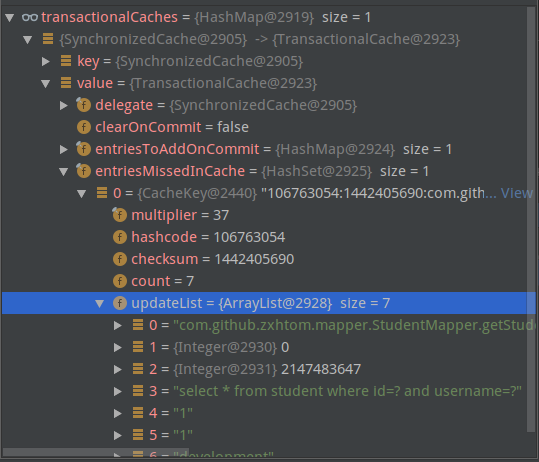
- 这个地方就是进行缓存存储的。我们再来看看mybatis是如何解析mapper.xml中配置的cache标签的。
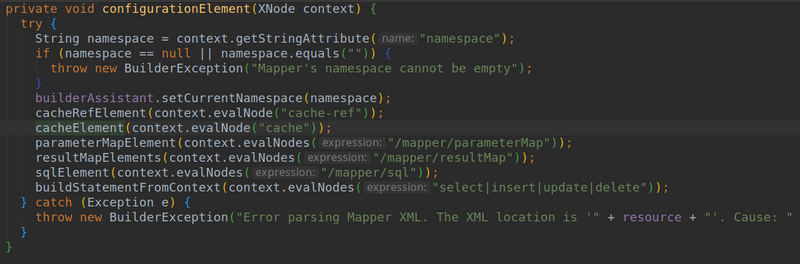
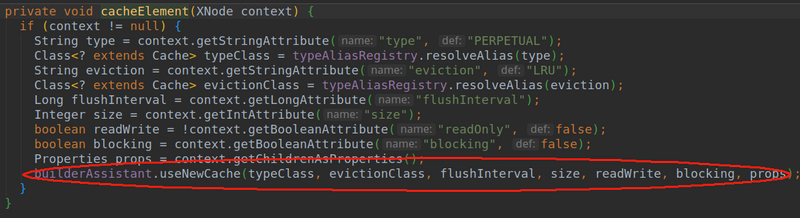
- 由上面代码我们得知mybatis会创建一个缓存对象。里面具体是通过一个build方法来创建的。我们在来看看build方法里是啥东西。
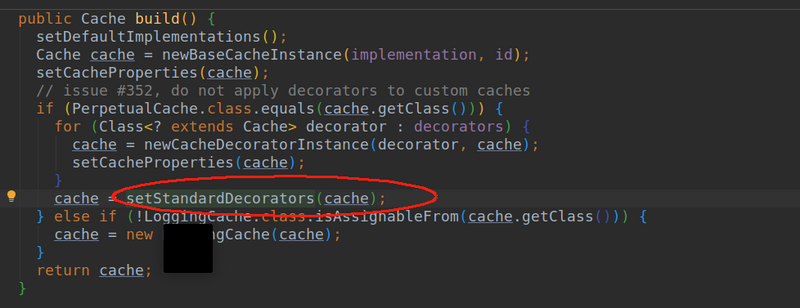
- setStandardDecorators这个方法我们不知道做啥的。但是熟悉设计模式的都知道Decorator这个词是装饰者模式。这里这个方法也是用来装饰用的。看看mybatis为我们装饰了那些东西。
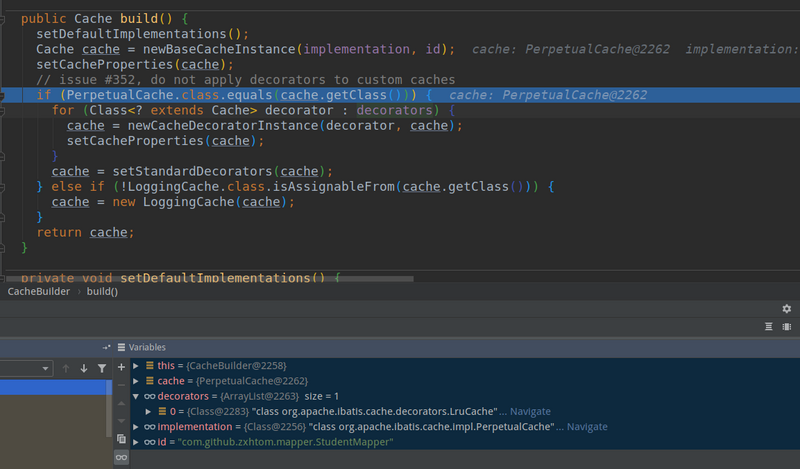
- 首先在newBaseCacheInstance方法中创建原始对象PreprtualCache.然后是加载默认提供的回收机制用的Cache。这个实在build前设置的。
-
- 然后就是通过setStandardDecorators进行装饰了。
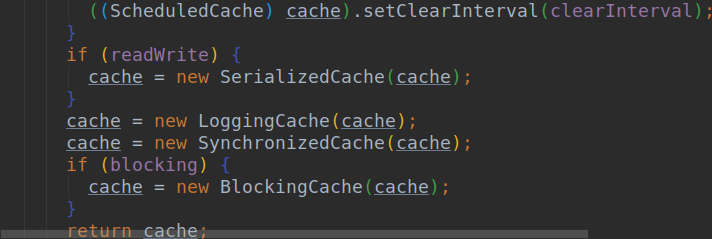
- 所以他的装饰链为:SynchronizedCache->LogginCache->SerializedCache->LruCache->PerPetualCache
- 而在上面的tcm.commit就是在SerializedCache进行缓存对象的。所以我们之前的代码是sqlsession没有提交。所以代码只要稍微改动下。
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionFactoryUtils.openSqlsession();
StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
Student student = mapper.getStudentByIdAndName("1", "1");
System.out.println(student);
sqlSession.commit();
SqlSession sqlSession1 = SqlSessionFactoryUtils.sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
StudentMapper mapper1 = sqlSession1.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
Student studentByIdAndName = mapper1.getStudentByIdAndName("1", "1");
System.out.println(studentByIdAndName);
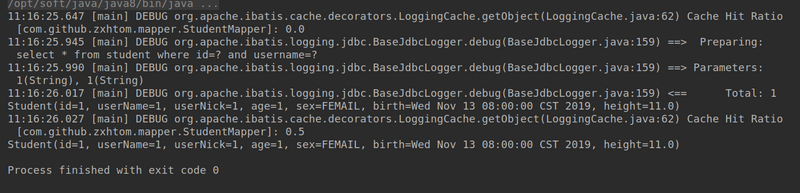
synchronized
源码
CachingExecutor
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql)
throws SQLException {
//获取Cache对象
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
if (cache != null) {
//根据statment配置刷新缓存,默认是insert、update、delete会刷新缓存
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
//二级缓存开启入口。
if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) {
//这个方法主要用来处理存储过程。后续章节说明
ensureNoOutParams(ms, boundSql);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
//通过缓存事物查询数据
List<E> list = (List<E>) tcm.getObject(cache, key);
if (list == null) {
//调用委托类查询数据
list = delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
//加入缓存,供下次获取
tcm.putObject(cache, key, list);
}
return list;
}
}
//没有开启二级缓存则继续往下走
return delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
# 缺点
- 二级缓存因为更加广泛,所以容易造成脏数据。尤其是在关联查询的时候有序无法控制刷新力度。很容易出现脏读。
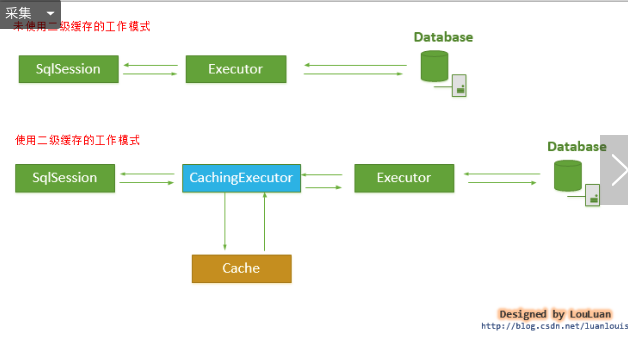
自定义二级缓存
- 在之前我们了解到的
PerpetualCache是缓存链上最基本的缓存类。我们自定义的缓存就是替代这个类的。在mybatis中会现根据我们注册进来的类进行实例化。如果没有则用默认的PerpetualCache这个类作为基础缓存类。
<span id="addMe">加入战队</span>
微信公众号

正文到此结束
- 本文标签: 关联查询 XEN mapper UI session 实例 http executor 代码 缓存 mybatis SqlSessionFactory 配置 id 解析 src https cache NSA Statement list Action map IO App build 源码 plugin IDE synchronized key 微信公众号 sql 一级缓存 CTO 详细分析 update sqlsession 数据 索引 XML ACE 学生 二级缓存 设计模式
- 版权声明: 本文为互联网转载文章,出处已在文章中说明(部分除外)。如果侵权,请联系本站长删除,谢谢。
- 本文海报: 生成海报一 生成海报二
热门推荐
相关文章
Loading...










![[HBLOG]公众号](https://www.liuhaihua.cn/img/qrcode_gzh.jpg)

