java 字典
java 字典
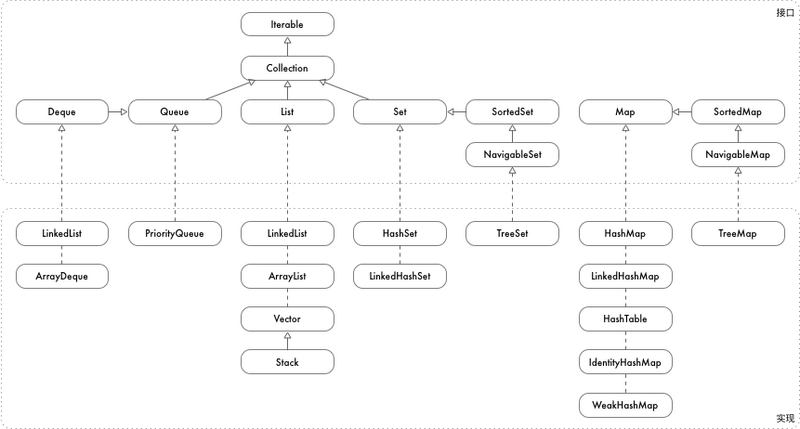
数据结构总览
Map
Map 描述的是一种映射关系,一个 key 对应一个 value,可以添加,删除,修改和获取 key/value,util 提供了多种 Map
-
HashMap: hash 表实现的 map,插入删除查找性能都是 O(1),key 没有顺序 -
TreeMap: 红黑树实现的 map,插入删除查找都是 O(lgn),key 按从大到小顺序排列 -
Hashtable: hash 实现,线程安全,key 和 value 都不能为空,key 没有顺序 -
LinkedHashMap: hash + 链表实现,按插入顺序排序 -
IdentityHashMap: 判断 key 相等的条件是,两个引用指向同一个对象,即key == e.key -
WeakHashMap: 弱引用 map,不会获取数据的强引用,当数据被 GC 清理时,数据将被删除
Map 的主要接口如下:
-
isEmpty: 判断是否没有元素 -
size: 获取元素个数 -
get: 获取指定 key 的 value -
getOrDefault: 获取指定 key 的 value,如果没有 key,返回默认值 -
containsKey: 判断字典是否包含 key -
containsValue: 判断字典是否包含 value -
keySet: key 的集合 -
values: value 的集合 -
entrySet: 包含 key/value 的集合,主要用于遍历 -
put: 添加一个 key/value -
putIfAbsent: key 不存在才添加,如果 key 存在,返回 value,如果 key 不存在,返回 null -
putAll: 合并 map,不存在的 key 添加,已存在的 key 覆盖 -
remove(key): 删除,返回老 value -
remove(key, val): 存在map[key] = val才删除,返回是否有元素删除 -
replace(key, newVal): 替换,返回老 value -
replace(key, val, newVal: 存在map[key] = val才替换,返回是否有元素替换 -
repalceAll: 对所有的 key/value 执行BiFounction替换原来的 value -
compute: 所选的 key/oldValue 执行BiFounction替换原来的 value;如果 key 不存在,则 oldValue 为 null -
computeIfPresent: key 存在才执行BiFounction替换原来的 value -
computeIfAbsent: key 不存在才对 key 执行Founction作为 value 插入 -
merge: 用 oldValue 和 newValue 执行BiFounction替换原来的 value;如果 key 不存在,则 oldValue 为 null
{
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>(Map.of(
"key0", "val0", "key1", "val1", "key2", "val2", "key3", "val3"
));
assertEquals(map.size(), 4);
assertFalse(map.isEmpty());
assertTrue(map.containsKey("key3"));
assertTrue(map.containsValue("val3"));
assertEquals(map.get("key3"), "val3");
assertEquals(map.get("key6"), null);
assertEquals(map.getOrDefault("key3", "defaultValue"), "val3");
assertEquals(map.getOrDefault("key6", "defaultValue"), "defaultValue");
assertThat(map.keySet(), equalTo(Set.of("key0", "key1", "key2", "key3")));
assertThat(map.values(), hasItems("val0", "val1", "val2", "val3"));
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : map.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + " => " + entry.getValue());
}
map.forEach((k, v) -> System.out.println(k + " => " + v));
map.clear();
assertTrue(map.isEmpty());
}
{
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("key0", "val0");
map.putAll(Map.of("key1", "val1", "key2", "val2"));
assertEquals(map.putIfAbsent("key3", "val3"), null);
assertEquals(map.putIfAbsent("key3", "val33"), "val3");
assertThat(map, equalTo(Map.of(
"key0", "val0", "key1", "val1", "key2", "val2", "key3", "val3"
)));
}
{
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>(Map.of(
"key0", "val0", "key1", "val1", "key2", "val2", "key3", "val3"
));
assertEquals(map.remove("errorKey"), null);
assertEquals(map.remove("key0"), "val0");
assertFalse(map.remove("key1", "errorValue"));
assertTrue(map.remove("key1", "val1"));
assertThat(map, equalTo(Map.of(
"key2", "val2", "key3", "val3"
)));
}
{
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>(Map.of(
"key0", "val0", "key1", "val1", "key2", "val2", "key3", "val3"
));
assertEquals(map.replace("errorKey", "replaceValue"), null);
assertEquals(map.replace("key0", "replaceValue"), "val0");
assertFalse(map.replace("key1", "errorValue", "replaceValue"));
assertTrue(map.replace("key1", "val1", "replaceValue"));
assertThat(map, equalTo(Map.of(
"key0", "replaceValue", "key1", "replaceValue", "key2", "val2", "key3", "val3"
)));
}
{
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>(Map.of(
"key0", "val0", "key1", "val1", "key2", "val2", "key3", "val3"
));
map.replaceAll((k, v) -> k + v);
assertThat(map, equalTo(Map.of(
"key0", "key0val0", "key1", "key1val1", "key2", "key2val2", "key3", "key3val3"
)));
}
{
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>(Map.of(
"key0", "val0", "key1", "val1", "key2", "val2"
));
assertEquals(map.compute("key0", (k, v) -> k + v), "key0val0");
assertEquals(map.computeIfPresent("key1", (k, v) -> k + v), "key1val1");
assertEquals(map.computeIfPresent("key6", (k, v) -> k + v), null);
assertEquals(map.computeIfAbsent("key2", k -> k + k.replace("key", "val")), "val2");
assertEquals(map.computeIfAbsent("key3", k -> k + k.replace("key", "val")), "key3val3");
assertThat(map, equalTo(Map.of(
"key0", "key0val0", "key1", "key1val1", "key2", "val2", "key3", "key3val3"
)));
}
{
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>(Map.of(
"key0", "val0", "key1", "val1", "key2", "val2"
));
assertEquals(map.merge("key0", "newVal", (oldValue, newValue) -> (oldValue + "->" + newValue)), "val0->newVal");
assertEquals(map.merge("key3", "newVal", (oldValue, newValue) -> (oldValue + "->" + newValue)), "newVal");
assertThat(map, equalTo(Map.of(
"key0", "val0->newVal", "key1", "val1", "key2", "val2", "key3", "newVal"
)));
}
Hashtable
Hashtable 的 key/value 都不允许为空
{
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
assertDoesNotThrow(() -> map.put(null, 1));
assertDoesNotThrow(() -> map.put(1, null));
}
{
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new Hashtable();
assertThrows(NullPointerException.class, () -> map.put(null, 1));
assertThrows(NullPointerException.class, () -> map.put(1, null));
}
IdentityHashMap
IdentityHashMap 判断相等的条件是 key 和 entry.key 是否为同一个引用对象
Map<String, String> map = new IdentityHashMap<>();
String key1 = new String("key1");
map.put(key1, "val1");
assertFalse(key1 == "key1");
assertTrue(key1.equals("key1"));
assertEquals(map.get(key1), "val1");
assertEquals(map.get("key1"), null);
WeakHashMap
WeakHashMap 的 key 为弱引用,当原对象被 GC 回收时,这个 key 也会被自动删除
{
Map<String, String> map = new WeakHashMap<>();
String key1 = new String("key1");
map.put(key1, "val1");
assertEquals(map.get("key1"), "val1");
key1 = null;
System.gc();
assertEquals(map.get("key1"), null);
}
{
Map<String, String> map = new WeakHashMap<>();
String val1 = new String("val1");
map.put("key1", val1);
assertEquals(map.get("key1"), "val1");
val1 = null;
System.gc();
assertEquals(map.get("key1"), "val1");
}
SortedMap
SortedMap 继承自 Map ,key 是有序的,提供了顺序相关的几个接口
firstKey lastKey headMap tailMap subMap
SortedMap<String, String> map = new TreeMap<>(Map.of(
"key0", "val0", "key1", "val1", "key2", "val2",
"key3", "val3", "key4", "val4"
));
assertEquals(map.firstKey(), "key0");
assertEquals(map.lastKey(), "key4");
assertThat(map.headMap("key2").keySet(), equalTo(Set.of("key0", "key1")));
assertThat(map.tailMap("key3").keySet(), equalTo(Set.of("key3", "key4")));
assertThat(map.subMap("key2", "key3").keySet(), equalTo(Set.of("key2")));
NavigableMap 继承自 SortedMap ,提供了如下几个接口
lowerKey higherKey floorKey ceilingKey lowerEntry higherEntry floorEntry ceilingEntry pollFirstEntry pollLastEntry headSet tailSet subSet
{
NavigableMap<String, String> map = new TreeMap<>(Map.of(
"key0", "val0", "key1", "val1", "key2", "val2",
"key3", "val3", "key4", "val4"
));
assertEquals(map.lowerKey("key3"), "key2");
assertEquals(map.higherKey("key3"), "key4");
assertEquals(map.floorKey("key3"), "key3");
assertEquals(map.ceilingKey("key3"), "key3");
assertEquals(map.lowerEntry("key3").getKey(), "key2");
assertEquals(map.higherEntry("key3").getKey(), "key4");
assertEquals(map.floorEntry("key3").getKey(), "key3");
assertEquals(map.ceilingEntry("key3").getKey(), "key3");
map.remove("key3");
assertEquals(map.floorKey("key3"), "key2");
assertEquals(map.ceilingKey("key3"), "key4");
assertEquals(map.floorEntry("key3").getKey(), "key2");
assertEquals(map.ceilingEntry("key3").getKey(), "key4");
}
{
NavigableMap<String, String> map = new TreeMap<>(Map.of(
"key0", "val0", "key1", "val1", "key2", "val2",
"key3", "val3", "key4", "val4"
));
assertEquals(map.pollFirstEntry().getKey(), "key0");
assertArrayEquals(map.keySet().toArray(), new String[]{"key1", "key2", "key3", "key4"});
assertEquals(map.pollLastEntry().getKey(), "key4");
assertArrayEquals(map.keySet().toArray(), new String[]{"key1", "key2", "key3"});
}
{
NavigableMap<String, String> map = new TreeMap<>(Map.of(
"key0", "val0", "key1", "val1", "key2", "val2",
"key3", "val3", "key4", "val4"
));
assertArrayEquals(map.headMap("key2", true).keySet().toArray(), new String[]{"key0", "key1", "key2"});
assertArrayEquals(map.tailMap("key3", false).keySet().toArray(), new String[]{"key4"});
assertArrayEquals(map.subMap("key2", false, "key3", true).keySet().toArray(), new String[]{"key3"});
}
链接
- 测试代码: https://github.com/hatlonely/...
正文到此结束
热门推荐
相关文章
Loading...










![[HBLOG]公众号](https://www.liuhaihua.cn/img/qrcode_gzh.jpg)

