springBoot中Bean的生命周期
springboot中Bean的生命周期
今天主要分享一下Springboot中Bean的生命周期的过程,如有不足,欢迎指正交流。
Bean生命周期的过程
Bean生命周期一般有下面的四个阶段:
-
Bean的定义
-
Bean的初始化
-
Bean的生存期
-
Bean的销毁
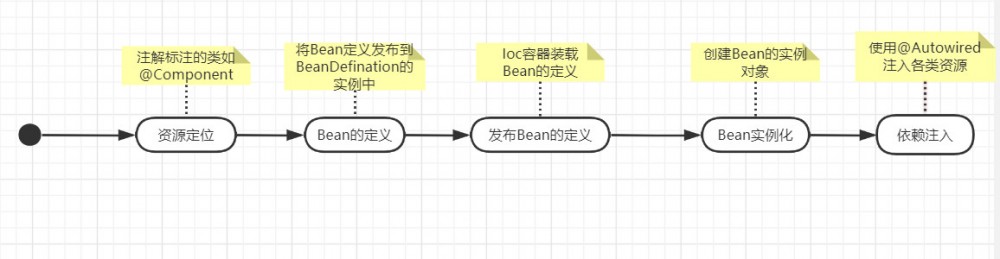
Bean的定义过程:
-
第一步,资源定位,就是Spring根据我们定义的注解(@Component),找到相应的类。
-
找到了资源就开始解析,并将定义的信息保存起来,此时,并没有初始化bean,这点需要注意。
-
然后将bean的定义发布到SpringIoc的容器中,此时,SpringIoc的容器中还是没有Bean的生成。只是定义的信息。
Bean的初始化
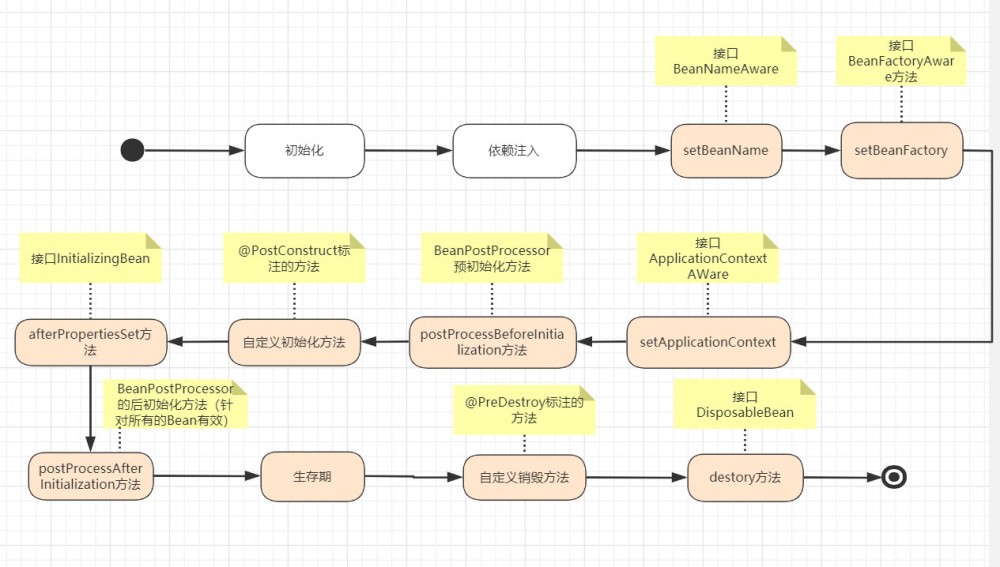
经过Bean的定义,初始化,SPring会继续完成Bean的实例和化和依赖注入,这样从IoC容器中就可以得到一个依赖注入完成的Bean。下图是初始化图的示例:
Bean的生命周期
通过代码测试Bean的生命周期
加入生命周期的接口
BeanNameAware,BeanFactoryAware,ApplicationContextAware,INitiali zingBean,DisposableBean这几个接口, 并实现里面的方法
代码实现
环境: jdk 1.8 springboot2.2 idea
-
定义接口Person类和Furit类
package chen.beanprocessor.model; public interface Person { void service(); // 设置水果类型 void eatFruit(Fruit fruit); } /** * @Author Chen * @Date 2020/4/18 17:04 **/ public interface Fruit { void use(); } -
定义Person和Fruit的实现类Children和Apple,并将Apple类注入到Children中,在Children中加入生命那个周期的接口:
/** * @Author Chen * @Date 2020/4/18 17:07 * 水果实现类Apple **/ @Component public class Apple implements Fruit { @Override public void use() { System.out.println(this.getClass().getSimpleName()+"这个苹果很甜"); } } @Component public class Children implements Person, BeanNameAware, BeanFactoryAware, ApplicationContextAware, InitializingBean, DisposableBean { Fruit fruit = null; // 注入水果类 public Children(@Autowired Fruit fruit){ this.fruit = fruit; } @Override public void service() { fruit.use(); } @Override public void eatFruit(Fruit fruit) { this.fruit = fruit; } @Override public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException { System.out.println("this"+this.getClass().getSimpleName()+"调用BeanFactory的setBeanFactory方法"); } @Override public void setBeanName(String name) { System.out.println("this"+this.getClass().getSimpleName()+"调用setBeanName的方法"); } @Override public void destroy() throws Exception { System.out.println("this"+this.getClass().getSimpleName()+"调用DisposableBean的方法"); } @Override public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception { System.out.println("this"+this.getClass().getSimpleName()+"调用Initializing的afterPropertiesSet()的方法"); } @Override public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException { System.out.println("this"+this.getClass().getSimpleName()+"调用Application的setApplicationContext的方法"); } @PostConstruct public void init(){ System.out.println(this.getClass().getSimpleName()+"注解@PostConstruct的自定义的初始化方法"); } @PreDestroy public void destory1(){ System.out.println(this.getClass().getSimpleName()+"调用@dPrDestory的自定义销毁的方法"); } }
3.定义测试类
@SpringBootApplication
public class BeanprocessorApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(BeanprocessorApplication.class, args);
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(BeanConfig.class);
Person person = applicationContext.getBean(Children.class);
System.out.println("===========初始化完成==========");
person.service();
applicationContext.close();
}
}
测试结果
thisChildren调用setBeanName的方法 thisChildren调用BeanFactory的setBeanFactory方法 thisChildren调用Application的setApplicationContext的方法 Children注解@PostConstruct的自定义的初始化方法 thisChildren调用Initializing的afterPropertiesSet()的方法 2020-04-18 17:28:38.902 INFO 9784 --- [ main] c.b.BeanprocessorApplication : Started BeanprocessorApplication in 0.682 seconds (JVM running for 1.29) thisChildren调用setBeanName的方法 thisChildren调用BeanFactory的setBeanFactory方法 thisChildren调用Application的setApplicationContext的方法 Children注解@PostConstruct的自定义的初始化方法 thisChildren调用Initializing的afterPropertiesSet()的方法 ===========初始化完成========== Apple这个苹果很甜 Children调用@dPrDestory的自定义销毁的方法 thisChildren调用DisposableBean的方法 Children调用@dPrDestory的自定义销毁的方法 thisChildren调用DisposableBean的方法
测试结果可以清晰的看到bean的生命周期的过程。从测试结果来看,Bean被初始化了两次,这是因为在初始化Children这个类时,还初始化了注入的Apple这个类。
码字不易,点个赞呗
码字不易,点个赞呗
码字不易,点个赞呗
追本溯源,方能阔步前行
参考资料:
《深入浅出SpringBoot》 杨开振
正文到此结束
热门推荐
相关文章
Loading...










![[HBLOG]公众号](https://www.liuhaihua.cn/img/qrcode_gzh.jpg)

