Java并发篇(7)深入剖析ReentrantLock
可重入锁(ReentrantLock),表示该锁能够支持一个线程对资源的重复加锁,还支持两种获取锁的方式:
- 公平锁:按照锁的请求时间顺序获取锁
- 非公平锁:任意一个线程在请求锁时都有机会获得锁
Synchronized与ReentrantLock对比
synchronized 关键字修饰的方法和同步代码块也是支持可重入的,它们的区别是:
| Synchronized | ReentrantLock | |
|---|---|---|
| 加锁方式 | 隐式加锁 | 显式加锁,调用 lock() 加锁与 unlock() 解锁 |
| 等待锁时 是否可中断 | 不可中断 | 可中断 |
| 锁的 公平性 | 非公平锁 | 默认值是非公平锁,可以设置为公平锁 |
| 锁绑定多个条件 | 只能绑定一个锁条件 | 可以设置多个锁条件 Condition 对象 |
ReentrantLock实现可重入分析
tryAcquire()获取锁源码
final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) {
// 获取当前线程
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
// 获取当前同步状态
int c = getState();
// 如果为0代表没加锁
if (c == 0) {
// 直接尝试获取锁
if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
// 判断当前线程是否已经获取了该锁,如果是实现可重入
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
// 实现可重入,将同步状态 + 1
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
复制代码
tryRelease()释放锁源码
protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {
// 将同步状态 - 1
int c = getState() - releases;
// 判断当前线程与已经获取锁的线程是否相同
if (Thread.currentThread() != getExclusiveOwnerThread())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
boolean free = false;
// 判断同步状态是否等于0, 如果是才真正释放锁
if (c == 0) {
free = true;
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
}
setState(c);
return free;
}
复制代码
可重入分析总结
- ReentrantLock内部维护
state成员变量,可实现多次对state变量自增实现可重入锁 - 获取
n次锁就要释放n次锁,只有当state等于0时表示锁成功释放。
公平锁与非公平锁实现分析
ReentrantLock内部有两个内部类 FairSync 和 NonfairSync ,分别代表公平锁和非公平锁的类,内部重写了 AQS 的请求获取锁方法 tryAcquire() 方法 自定义锁请求方式 。先来看 lock() 方法
lock()方法分析
// NonfairSync
final void lock() {
if (compareAndSetState(0, 1))
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());
else
acquire(1);
}
// FairSync
final void lock() {
acquire(1);
}
复制代码
从上面的代码可以得到下面的不同点:
- 非公平锁直接
CAS尝试获取锁,获取失败才调用acquire(),而公平锁调用acquire();
调用 acquire() 方法实际上是调用 FairSync 和 NonfairSync 各自内部的 tryAcquire() 方法,
public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
selfInterrupt();
}
复制代码
tryAcquire()源码解析
NonfairSync的tryAcquire()方法
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
return nonfairTryAcquire(acquires);
}
final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) {
// 获取当前线程
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
// 获取当前同步状态
int c = getState();
// 如果为0代表没加锁
if (c == 0) {
// 直接尝试获取锁
if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
// 判断当前线程是否已经获取了该锁
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
// 实现可重入,将同步状态 + 1
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
复制代码
非公平锁内部调用了 nonfairTryAcquire() 方法实现非公平锁的请求,源码如上;非公平锁整个获取锁的流程如下图:
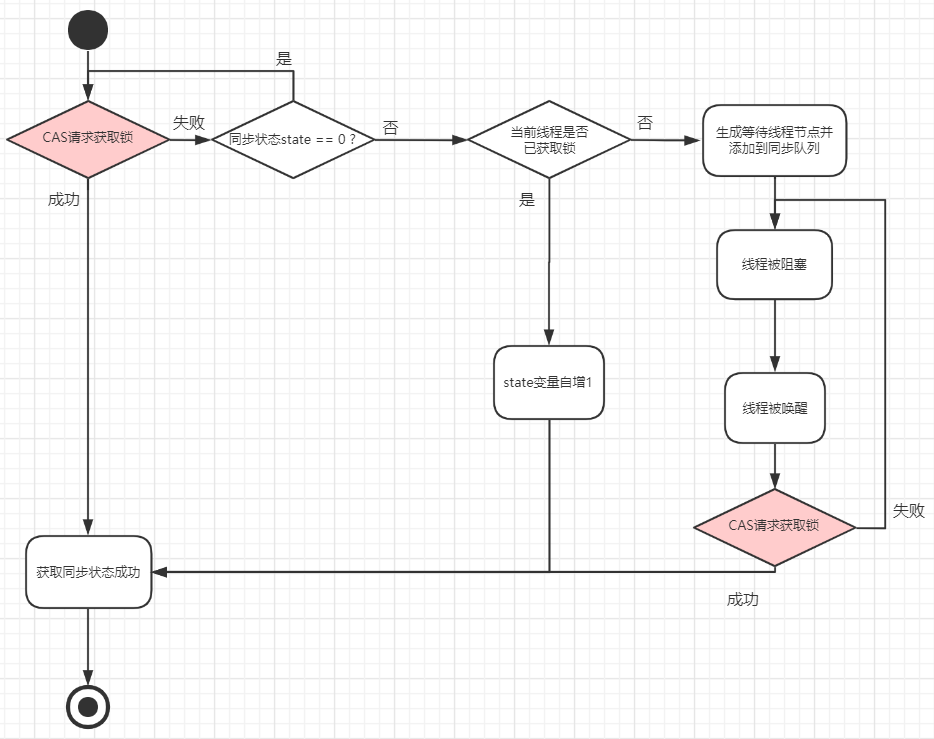
注意:线程被唤醒是所有线程都会被唤醒,而不是只有前驱节点为头节点的线程被唤醒,这是与公平锁的一个重要区别
FairSync的tryAcquire()方法
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
// 获取当前线程
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
// 获取当前同步状态
int c = getState();
// 判断是否处于可获取状态
if (c == 0) {
// 如果队列为空并且成功设置同步状态则代表成功获取锁,否则需要排队
if (!hasQueuedPredecessors() &&
compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
// 判断是否当前线程获取了这个锁
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
// 如果是则将state自增1实现可重入
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
复制代码
两个获取锁方法的不同点:
- 如果锁已经被释放(
state = 0) ,公平锁先调用方法hasQueuedPredecessors()判断队列中是否有节点,如果有则排队,而非公平锁则直接CAS尝试获取锁,源码如下:
// NonfairSync的tryAcquire()方法
if (c == 0) {
// 直接尝试获取锁
if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
// FairSync的tryAcquire()方法
if (c == 0) {
// 如果队列为空并且成功设置同步状态则代表成功获取锁,否则需要排队
if (!hasQueuedPredecessors() &&
compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
复制代码
获取锁失败之后的操作
- 如果获取不到锁,都要调用
acquireQueued()将线程节点添加到队列尾部,等待执行线程唤醒,addWaiter()是创建一个等待线程节点,源码如下:
public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
selfInterrupt();
}
// addWaiter()源码
private Node addWaiter(Node mode) {
// 创建新的节点
Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode);
Node pred = tail;
// 如果尾节点不为空则说明队列不为空,排到队列尾部
if (pred != null) {
node.prev = pred;
if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) {
pred.next = node;
return node;
}
}
// 初始化队列
enq(node);
return node;
}
// enq()源码
private Node enq(final Node node) {
// 死循环初始化队列
for (;;) {
Node t = tail;
if (t == null) { // 二次判断队列是否为空, 以防调用过程中队列已经初始化
if (compareAndSetHead(new Node()))
tail = head;
} else {
// 队列不为空,正常添加到队列尾部
node.prev = t;
if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) {
t.next = node;
return t;
}
}
}
}
复制代码
正文到此结束
热门推荐
相关文章
Loading...










![[HBLOG]公众号](https://www.liuhaihua.cn/img/qrcode_gzh.jpg)

