SpringSession:请求与响应重写
我们知道, HttpServletRequset 和 HttpServletResponse 是 Servlet 标准所指定的 Java 语言与 Web 容器进行交互的接口。接口本身只规定 java 语言对 web 容器进行访问的行为方式,而具体的实现是由不同的 web 容器在其内部实现的。
那么在运行期,当我们需要对 HttpServletRequset 和 HttpServletResponse 的默认实例进行扩展时,我们就可以继承 HttpServletRequestWrapper 和 HttpServletResponseWrapper 来实现。
在 SpringSession 中因为我们要实现不依赖容器本身的 getSession 实现,因此需要扩展 HttpServletRequset ,通过重写 getSession 来实现分布式 session 的能力。下面就来看下 SpringSession 中对于 HttpServletRequset 的扩展。
1、请求重写
SpringSession 中对于请求重写,在能力上主要体现在存储方面,也就是 getSession 方法上。在 SessionRepositoryFilter 这个类中,是通过内部类的方式实现了对 HttpServletRequset 和 HttpServletResponse 的扩展。
1.1 HttpServletRequset 扩展实现
private final class SessionRepositoryRequestWrapper
extends HttpServletRequestWrapper {
// HttpServletResponse 实例
private final HttpServletResponse response;
// ServletContext 实例
private final ServletContext servletContext;
// requestedSession session对象
private S requestedSession;
// 是否缓存 session
private boolean requestedSessionCached;
// sessionId
private String requestedSessionId;
// sessionId 是否有效
private Boolean requestedSessionIdValid;
// sessionId 是否失效
private boolean requestedSessionInvalidated;
// 省略方法
}
复制代码
1.2 构造方法
private SessionRepositoryRequestWrapper(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, ServletContext servletContext) {
super(request);
this.response = response;
this.servletContext = servletContext;
}
复制代码
构造方法里面将 HttpServletRequest 、 HttpServletResponse 以及 ServletContext 实例传递进来,以便于后续扩展使用。
1.3 getSession 方法
@Override
public HttpSessionWrapper getSession(boolean create) {
// 从当前请求线程中获取 session
HttpSessionWrapper currentSession = getCurrentSession();
// 如果有直接返回
if (currentSession != null) {
return currentSession;
}
// 从请求中获取 session,这里面会涉及到从缓存中拿session的过程
S requestedSession = getRequestedSession();
if (requestedSession != null) {
// 无效的会话id(不支持的会话存储库)请求属性名称。
// 这里看下当前的sessionId是否有效
if (getAttribute(INVALID_SESSION_ID_ATTR) == null) {
// 设置当前session的最后访问时间,用于延迟session的有效期
requestedSession.setLastAccessedTime(Instant.now());
// 将requestedSessionIdValid置为true
this.requestedSessionIdValid = true;
// 包装session
currentSession = new HttpSessionWrapper(requestedSession, getServletContext());
// 不是新的session,如果是新的session则需要改变sessionId
currentSession.setNew(false);
// 将session设置到当前请求上下文
setCurrentSession(currentSession);
// 返回session
return currentSession;
}
}
else {
// 这里处理的是无效的sessionId的情况,但是当前请求线程 session有效
if (SESSION_LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
SESSION_LOGGER.debug(
"No session found by id: Caching result for getSession(false) for this HttpServletRequest.");
}
// 将invalidSessionId置为true
setAttribute(INVALID_SESSION_ID_ATTR, "true");
}
// 是否需要创建新的session
if (!create) {
return null;
}
if (SESSION_LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
SESSION_LOGGER.debug(
"A new session was created. To help you troubleshoot where the session was created we provided a StackTrace (this is not an error). You can prevent this from appearing by disabling DEBUG logging for "
+ SESSION_LOGGER_NAME,
new RuntimeException(
"For debugging purposes only (not an error)"));
}
// 创建新的session
S session = SessionRepositoryFilter.this.sessionRepository.createSession();
// 设置最后访问时间,也就是指定了当前session的有效期限
session.setLastAccessedTime(Instant.now());
// 包装下当前session
currentSession = new HttpSessionWrapper(session, getServletContext());
//设置到当前请求线程
setCurrentSession(currentSession);
return currentSession;
}
复制代码
上面这段代码有几个点,这里单独来解释下。
-
getCurrentSession- 这是为了在同一个请求过程中不需要重复的去从存储中获取session,在一个新的进来时,将当前的 session 设置到当前请求中,在后续处理过程如果需要getSession就不需要再去存储介质中再拿一次。
-
getRequestedSession- 这个是根据请求信息去取
session,这里面就包括了sessionId解析,从存储获取session对象等过程。
- 这个是根据请求信息去取
- 是否创建新的
session对象- 在当前请求中和存储中都没有获取到
session信息的情况下,这里会根据create参数来判断是否创建新的session。这里一般用户首次登录时或者session失效时会走到。
- 在当前请求中和存储中都没有获取到
1.4 getRequestedSession
根据请求信息来获取 session 对象
private S getRequestedSession() {
// 缓存的请求session是否存在
if (!this.requestedSessionCached) {
// 获取 sessionId
List<String> sessionIds = SessionRepositoryFilter.this.httpSessionIdResolver
.resolveSessionIds(this);
// 通过sessionId来从存储中获取session
for (String sessionId : sessionIds) {
if (this.requestedSessionId == null) {
this.requestedSessionId = sessionId;
}
S session = SessionRepositoryFilter.this.sessionRepository
.findById(sessionId);
if (session != null) {
this.requestedSession = session;
this.requestedSessionId = sessionId;
break;
}
}
this.requestedSessionCached = true;
}
return this.requestedSession;
}
复制代码
这段代码还是很有意思的,这里获取 sessionId 返回的是个列表。当然这里是 SpringSession 的实现策略,因为支持 session ,所以这里以列表的形式返回的。OK,继续来看如何解析 sessionId 的:
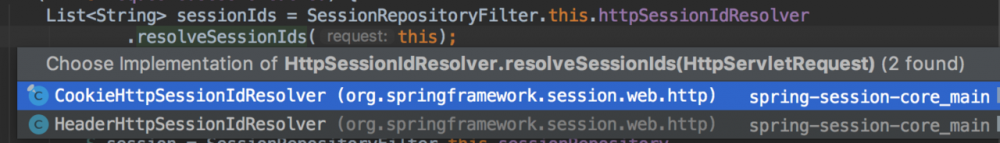
这里可以看到 SpringSession 对于 sessionId 获取的两种策略,一种是基于 cookie ,一种是基于 header ;分别来看下具体实现。
1.4.1 CookieHttpSessionIdResolver 获取 sessionId
CookieHttpSessionIdResolver 中获取 sessionId 的核心代码如下:
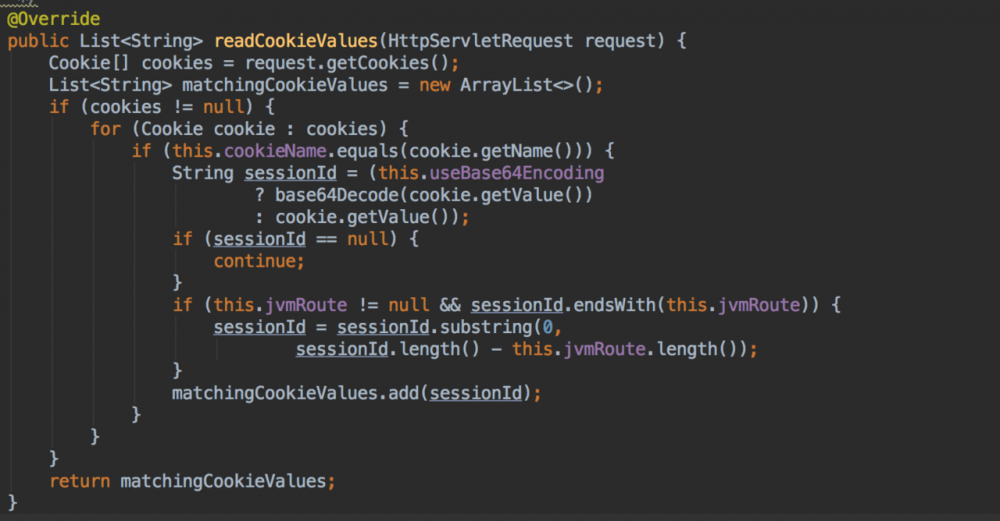
cookie 。从
request 将
cookie 信息拿出来,然后遍历找当前
sessionId 对应的
cookie ,这里的判断也很简单, 如果是以
SESSION 开头,则表示是
SessionId ,毕竟
cookie 是共享的,不只有
sessionId
,还有可能存储其他内容。
另外这里面有个 jvmRoute,这个东西实际上很少能够用到,因为大多数情况下这个值都是null。这个我们在分析 CookieSerializer 时再来解释。
1.4.2 HeaderHttpSessionIdResolver 获取 sessionId
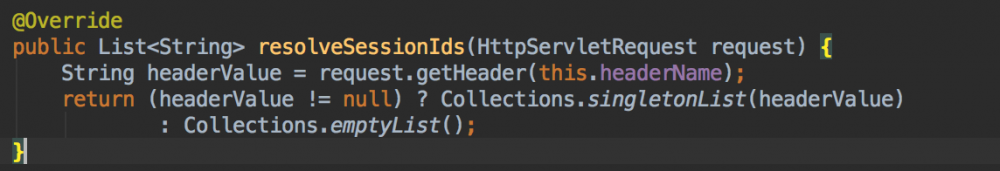
headerName 从
header
中取值。
回到 getRequestedSession ,剩下的代码中核心的都是和 sessionRepository 这个有关系,这部分就会涉及到存储部分。不在本篇的分析范围之内,会在存储实现部分来分析。
1.5 HttpSessionWrapper

上面的代码中当我们拿到 session 实例是通常会包装下,那么用到的就是这个 HttpSessionWrapper 。
HttpSessionWrapper 继承了 HttpSessionAdapter ,这个 HttpSessionAdapter 就是将SpringSession 转换成一个标准 HttpSession 的适配类。 HttpSessionAdapter 实现了标准 servlet 规范的 HttpSession 接口。
1.5.1 HttpSessionWrapper
HttpSessionWrapper 重写了 invalidate 方法。从代码来看,调用该方法产生的影响是:
-
requestedSessionInvalidated置为true,标识当前session失效。 - 将当前请求中的
session设置为null,那么在请求的后续调用中通过getCurrentSession将拿不到session信息。 - 当前缓存的 session 清楚,包括sessionId,session实例等。
- 删除存储介质中的session对象。
1.5.2 HttpSessionAdapter
SpringSession 和标准 HttpSession 的配置器类。这个怎么理解呢,来看下一段代码:
@Override
public Object getAttribute(String name) {
checkState();
return this.session.getAttribute(name);
}
复制代码
对于基于容器本身实现的 HttpSession 来说, getAttribute 的实现也是有容器本身决定。但是这里做了转换之后, getAttribute 将会通过 SpringSession 中实现的方案来获取。其他的 API 适配也是基于此实现。
SessionCommittingRequestDispatcher
实现了 RequestDispatcher 接口。关于 RequestDispatcher 可以参考这篇文章 【Servlet】关于RequestDispatcher的原理 。 SessionCommittingRequestDispatcher 对 forward 的行为并没有改变。 对于 include 则是在 include 之前提交 session 。为什么这么做呢?
因为 include 方法使原先的 Servlet 和转发到的 Servlet 都可以输出响应信息,即原先的 Servlet 还可以继续输出响应信息;即请求转发后,原先的 Servlet 还可以继续输出响应信息,转发到的 Servlet 对请求做出的响应将并入原先 Servlet 的响应对象中。
所以这个在 include 调用之前调用 commit ,这样可以确保被包含的 Servlet 程序不能改变响应消息的状态码和响应头。
2 响应重写
响应重写的目的是确保在请求提交时能够把session保存起来。来看下 SessionRepositoryResponseWrapper 类的实现:
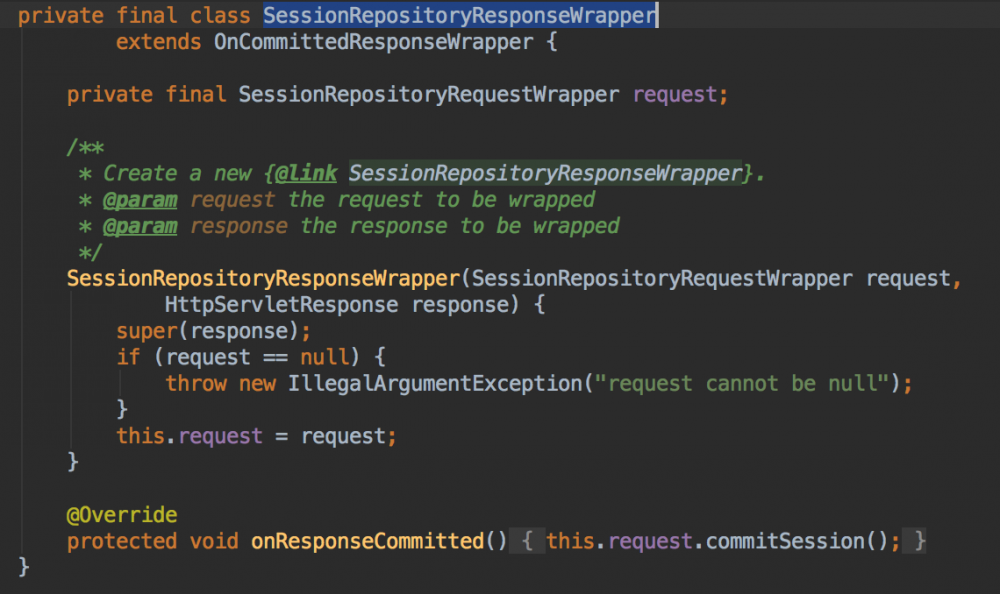
onResponseCommitted ,也就是上面说的,在请求提交时能够通过这个回调函数将
session
保存到存储容器中。
2.1 session 提交
最后来看下 commitSession
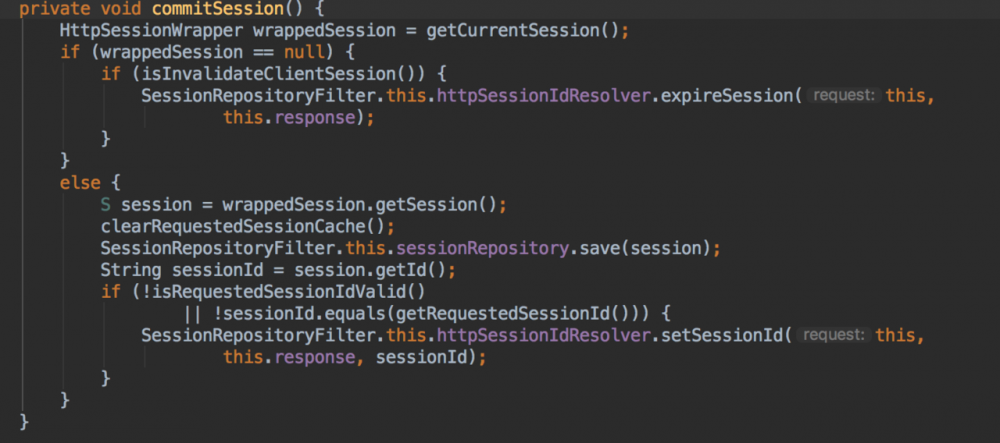
这个过程不会再去存储容器中拿 session 信息,而是直接从当前请求中拿。如果拿不到,则在回写 cookie 时会将当前 session 对应的 cookie 值设置为空,这样下次请求过来时携带的 sessionCookie 就是空,这样就会重新触发登陆。
如果拿到,则清空当前请求中的 session 信息,然后将 session 保存到存储容器中,并且将 sessionId 回写到 cookie 中。
小结
本篇主要对 SpringSession 中重写 Request 和 Response 进行了分析。通过重写 Request 请求来将 session 的存储与存储容器关联起来,通过重写 Response 来处理 session 提交,将 session 保存到存储容器中。
后面我们会继续来分析 SpringSession 的源码。最近也在学习链路跟踪相关的技术,也准备写一写,有兴趣的同学可以一起讨论。










![[HBLOG]公众号](https://www.liuhaihua.cn/img/qrcode_gzh.jpg)

