Spring Controller层测试 – 04 SpringBootTest & MockMVC
这种测试方案会加载完整的SpringContext,但我们仍然不需要Web Server,需要继续通过MockMVC来模拟请求。
在测试的时候主要用到了 @ SpringBootTest 注解。看下代码:
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
@AutoConfigureMockMvc
public class WorkerControllerSpringBootMockTest {
@Autowired
private MockMvc mockMvc;
private JacksonTester<Worker> jsonWorker;
@Before
public void setup() {
JacksonTester.initFields(this, new ObjectMapper());
System.out.println();
}
@Test
public void getWhenExists() throws Exception {
//when
MockHttpServletResponse response =
mockMvc.perform(get("/worker/2").accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON))
.andReturn().getResponse();
//then
assertThat(response.getStatus()).isEqualTo(HttpStatus.OK.value());
assertThat(response.getContentAsString()).isEqualTo(jsonWorker.write(new Worker("raccoon", 23)).getJson());
}
@Test
//@DirtiesContext
public void getWhenNotExists() throws Exception {
//when
MockHttpServletResponse response =
mockMvc.perform(get("/worker/26").accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON))
.andReturn().getResponse();
//then
assertThat(response.getStatus()).isEqualTo(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND.value());
assertThat(response.getContentAsString()).isEmpty();
}
@Test
public void getByNameWhenExists() throws Exception {
//when
MockHttpServletResponse response =
mockMvc.perform(get("/worker?name=HanMeimei").accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON))
.andReturn().getResponse();
//then
assertThat(response.getStatus()).isEqualTo(HttpStatus.OK.value());
assertThat(response.getContentAsString()).isEqualTo(jsonWorker.write(new Worker("HanMeimei", 16)).getJson());
}
@Test
public void getByNameWhenNotExists() throws Exception {
//when
MockHttpServletResponse response =
mockMvc.perform(get("/worker?name=LiLei").accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON))
.andReturn().getResponse();
//then
assertThat(response.getStatus()).isEqualTo(HttpStatus.OK.value());
assertThat(response.getContentAsString()).isEmpty();
}
@Test
public void add() throws Exception {
MockHttpServletResponse response = mockMvc.perform(
post("/worker").contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
.content(jsonWorker.write(new Worker("Jerry", 12)).getJson())
).andReturn().getResponse();
assertThat(response.getStatus()).isEqualTo(HttpStatus.CREATED.value());
}
@Test
public void workerFilter() throws Exception {
//when
MockHttpServletResponse response =
mockMvc.perform(get("/worker/2").accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON))
.andReturn().getResponse();
//then
assertThat(response.getStatus()).isEqualTo(HttpStatus.OK.value());
assertThat(response.getHeaders("X-CHOBIT-APP")).containsOnly("chobit-header");
}
}
@SpringBootTest和@AutoConfigureMockMvc
使用 @ SpringBootTest 注解会加载整个Context。这样我们可以自动获得所有在Context中注入的Bean,以及从application.properties中加载的配置信息。
在 @ SpringBootTest 中声明webEnvironment为 WebEnvironment . MOCK (默认值就是 WebEnvironment . MOCK )后,结合 @ AutoConfigureMockMvc 注解,在测试的时候会得到一个模拟的Web/Servlet环境。
因为没有Web Server,所以就无法使用 RestTemplate ,也就只能继续使用 MockMVC 了。这次 MockMVC 的实例是由 @ AutoConfigureMockMvc 注解来完成的。这归功于SpringBoot的自动化配置。
所有参与测试的对象的关系如下图:
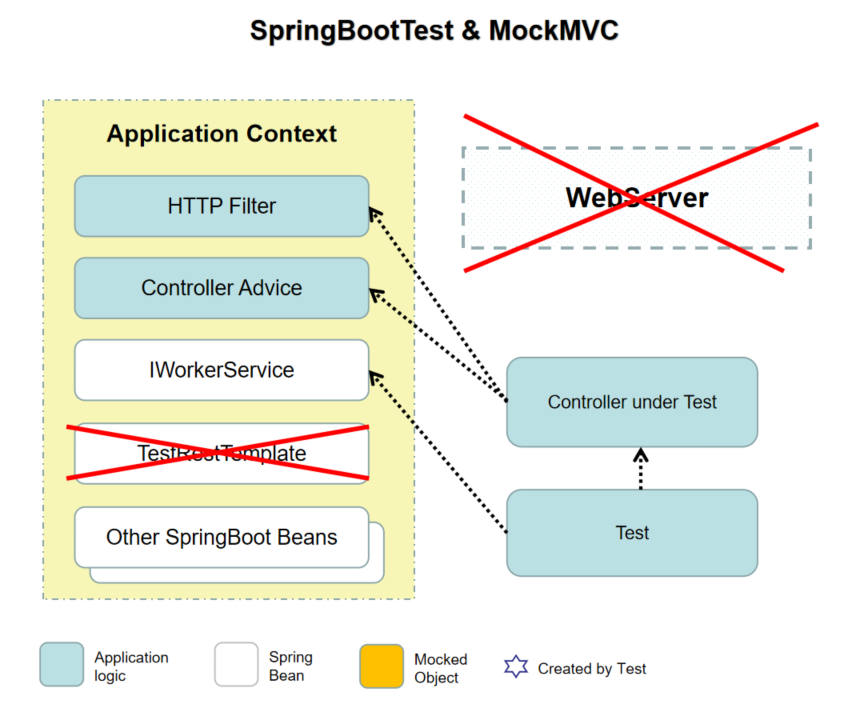
总结
这种测试方案更倾向于集成测试。它的关注点主要在于SpringBoot不同类之间的交互。
在这个测试方案中,请求仍然是通过MockMVC模拟的。不过因为有一个完整的Context,请求处理过程中的所有逻辑都是真实的,请求返回结果也是真实的。因此测试效果和使用Web Server几乎是差不多的了。
如果还是要只测试Controller中的逻辑,也可以继续使用 @ MockBean 注解来mock一个 IWorkerService 实例来覆盖Context中已有的实例。即使使用了真正的WebServer,也可以继续使用MockBean。同样在测试中也需要继续mock数据。
概括来说,这种测试的位置稍显尴尬:如果要执行单元测试来测试WEB层的逻辑,建议优先第二种方案;如果要执行集成测试,启动一个真正的Web Server,使用 RestTemplate 进行测试会更彻底也更加方便。
其他:示例代码可在CSDN下载,地址:https://download.csdn.net/download/tianxiexingyun/11065824










![[HBLOG]公众号](https://www.liuhaihua.cn/img/qrcode_gzh.jpg)

