java并发编程学习之FutureTask
FutureTask
在 java并发编程学习之三种线程启动方式 中有提过。主要的方法如下:
- cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning):取消任务的执行失败,返回false,比如任务已经执行结束,或者已经被取消,或者不能被取消。如果执行成功了,返回ture。mayInterruptIfRunning的作用是是否中断,如果是true则中断,本质还是调用interrupt方法。
- isCancelled:判断任务是否被取消,任务结束包括正常执行结束或异常结束,返回true。
- isDone:是否执行结束,包括正常执行结束或异常结束。结束返回true。
- get:获取返回值,没有得到返回值前一直阻塞。
public class FutureTaskDemo {
static class Thread1 implements Callable {
@Override
public Object call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("before fun");
fun();
System.out.println("after fun");
return null;
}
public void fun() {
while (true) {
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread1 thread1 = new Thread1();
FutureTask futureTask = new FutureTask(thread1);
Thread thread = new Thread(futureTask);
thread.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("cancel:" + futureTask.cancel(true));
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("isCancelled:" + futureTask.isCancelled());
System.out.println("isDone:" + futureTask.isDone());
System.out.println(futureTask.get());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("InterruptedException");
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
System.out.println("ExecutionException");
} catch (CancellationException e) {
System.out.println("CancellationException");
}
}
}
运行结果如下:
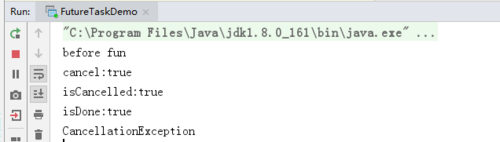
由于任务被取消,所以抛出CancellationException异常。注意的是,此时thread1线程还在跑,isCancelled和isDone返回的是true。cancel并不能让任务真正的结束。
正文到此结束
热门推荐
相关文章
Loading...










![[HBLOG]公众号](https://www.liuhaihua.cn/img/qrcode_gzh.jpg)

