Spring AOP之坑:完全搞清楚advice的执行顺序
要完全理解Spring AOP首先要理解AOP的核心概念和术语,这些术语并不是Spring指定的,而且很不幸,这些术语并不能直观理解,但是,如果Spring使用自己的术语,那将更加令人困惑。
- Aspect:切面 ,由一系列切点、增强和引入组成的模块对象,可定义优先级,从而影响增强和引入的执行顺序。事务管理(Transaction management)在java企业应用中就是一个很好的切面样例。
- Join point:接入点 ,程序执行期的一个点,例如方法执行、类初始化、异常处理。 在Spring AOP中,接入点始终表示方法执行。
- Advice:增强 ,切面在特定接入点的执行动作,包括 "around," "before" and "after"等多种类型。包含Spring在内的许多AOP框架,通常会使用拦截器来实现增强,围绕着接入点维护着一个拦截器链。
- Pointcut:切点 ,用来匹配特定接入点的谓词(表达式),增强将会与切点表达式产生关联,并运行在任何切点匹配到的接入点上。通过切点表达式匹配接入点是AOP的核心,Spring默认使用AspectJ的切点表达式。
- Introduction:引入 ,为某个type声明额外的方法和字段。Spring AOP允许你引入任何接口以及它的默认实现到被增强对象上。
- Target object:目标对象 ,被一个或多个切面增强的对象。也叫作被增强对象。既然Spring AOP使用运行时代理(runtime proxies),那么目标对象就总是代理对象。
- AOP proxy:AOP代理 ,为了实现切面功能一个对象会被AOP框架创建出来。在Spring框架中AOP代理的默认方式是:有接口,就使用基于接口的JDK动态代理,否则使用基于类的CGLIB动态代理。但是我们可以通过设置
proxy-target-class="true",完全使用CGLIB动态代理。 - Weaving:织入 ,将一个或多个切面与类或对象链接在一起创建一个被增强对象。织入能发生在编译时 (compile time )(使用AspectJ编译器),加载时(load time),或运行时(runtime) 。Spring AOP默认就是运行时织入,可以通过
枚举AdviceMode来设置。
模拟aspect advice的执行过程
在这里我们 不再展示测试代码 ,而是通过简单的代码来 模拟aspect advice的执行过程 。
尽管Spring AOP是通过 动态代理 来实现的,但是我们可以绕过代理,直接模拟出它的执行过程,示例代码:
package doubt;
public class AspectAdviceInvokeProcess {
public static void main(String[] args){
try {
//正常执行
AspectInvokeProcess(false);
System.out.println("=====分割线=====");
//异常执行
AspectInvokeProcess(true);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 切面执行过程
* @param isException
* @throws Exception
*/
public static void AspectInvokeProcess(boolean isException) throws Exception{
try {
try {
aroundAdvice(isException);
} finally {
afterAdvice();
}
afterReturningAdvice();
return;
} catch (Exception e) {
afterThrowingAdvice(e);
throw e;
return;
}
}
/**
* 环绕增强
* @param isException
* @throws Exception
*/
private static void aroundAdvice(boolean isException) throws Exception {
System.out.println("around before advice");
try {
JoinPoint_Proceed(isException);
} finally {
System.out.println("around after advice");
}
}
/**
* 编织后的接入点执行过程
* @param isException
*/
public static void JoinPoint_Proceed(boolean isException){
beforeAdvice();
targetMethod(isException);
}
/**
* 前置增强
*/
private static void beforeAdvice() {
System.out.println("before advice");
}
/**
* 目标方法
* @param isException
*/
private static void targetMethod(boolean isException) {
System.out.println("target method 执行");
if(isException)
throw new RuntimeException("异常发生");
}
/**
* 后置增强
*/
private static void afterAdvice() {
System.out.println("after advice");
}
/**
* 正常返回增强
*/
private static void afterReturningAdvice() {
System.out.println("afterReturning");
}
/**
* 异常返回增强
* @param e
* @throws Exception
*/
private static void afterThrowingAdvice(Exception e) throws Exception {
System.out.println("afterThrowing:"+e.getMessage());
}
}
复制代码
同一aspect,不同advice的执行顺序
上述代码的执行结果,直接体现了 同一apsect中不同advice的 执行顺序,结果如下:
around before advice before advice target method 执行 around after advice after advice afterReturning ===============分割线============== around before advice before advice target method 执行 around after advice after advice afterThrowing:异常发生 java.lang.RuntimeException: 异常发生 复制代码
得出结论:
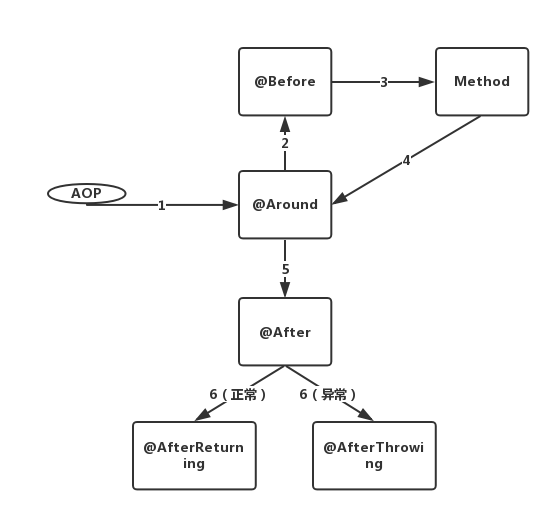
不同aspect,advice的执行顺序
详情可见,《Spring官方文档》 docs.spring.io/spring/docs…
Spring AOP通过指定 aspect 的优先级,来控制 不同aspect,advice的执行顺序 ,有两种方式:
-
Aspect 类添加 注解 :org.springframework.core.annotation.Order,使用注解
value属性指定优先级。 -
Aspect 类实现 接口 :org.springframework.core.Ordered,实现 Ordered 接口的 getOrder() 方法。
其中,数值越低,表明优先级越高, @Order 默认为最低优先级,即最大数值:
/** * Useful constant for the lowest precedence value. * @see java.lang.Integer#MAX_VALUE */ int LOWEST_PRECEDENCE = Integer.MAX_VALUE; 复制代码
最终, 不同aspect,advice的执行顺序 :
- 入操作(Around(接入点执行前)、Before),优先级越高,越先执行;
- 一个切面的入操作执行完,才轮到下一切面,所有切面入操作执行完,才开始执行接入点;
- 出操作(Around(接入点执行后)、After、AfterReturning、AfterThrowing),优先级越低,越先执行。
- 一个切面的出操作执行完,才轮到下一切面,直到返回到调用点;
如下图所示:
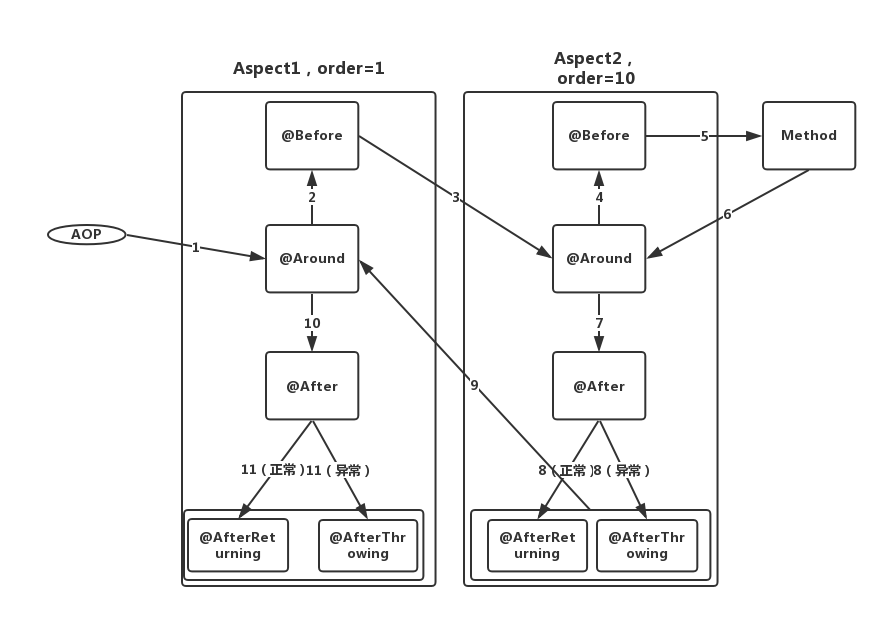
先入后出,后入先出
同一aspect,相同advice的执行顺序
同一aspect,相同advice的执行顺序 并不能直接确定,而且 @Order 在 advice 方法上也无效,但是有如下两种变通方式:
- 将两个 advice 合并为一个 advice,那么执行顺序就可以通过代码控制了
- 将两个 advice 分别抽离到各自的 aspect 内,然后为 aspect 指定执行顺序
Transactional Aspect的优先级
Spring事务管理(Transaction Management),也是基于Spring AOP。
在Spring AOP的使用中,有时我们必须明确自定义aspect的优先级低于或高于事务切面(Transaction Aspect),所以我们需要知道:
- 事务切面优先级:默认为最低优先级
LOWEST_PRECEDENCE = Integer.MAX_VALUE 复制代码
- 事务的增强类型:Around advice,其实不难理解,进入方法开启事务,退出方法提交或回滚,所以需要环绕增强。
public abstract aspect AbstractTransactionAspect extends TransactionAspectSupport implements DisposableBean {
protected AbstractTransactionAspect(TransactionAttributeSource tas) {
setTransactionAttributeSource(tas);
}
@SuppressAjWarnings("adviceDidNotMatch")
Object around(final Object txObject): transactionalMethodExecution(txObject) {
MethodSignature methodSignature = (MethodSignature) thisJoinPoint.getSignature();
// Adapt to TransactionAspectSupport's invokeWithinTransaction...
try {
return invokeWithinTransaction(methodSignature.getMethod(), txObject.getClass(), new InvocationCallback() {
public Object proceedWithInvocation() throws Throwable {
return proceed(txObject);
}
});
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Error err) {
throw err;
}
catch (Throwable thr) {
Rethrower.rethrow(thr);
throw new IllegalStateException("Should never get here", thr);
}
}
}
复制代码
- 如何修改事务切面的优先级: 在开启事务时,通过设置
@EnableTransactionManagement和<tx:annotation-driven/>中的,order属性来修改事务切面的优先级。 详情可见,《Spring官方文档》 docs.spring.io/spring/docs…










![[HBLOG]公众号](https://www.liuhaihua.cn/img/qrcode_gzh.jpg)

